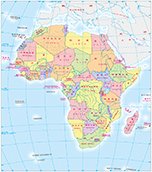
Africa
Africa's recorded history begins with the ascent of Egyptian human advancement in the fourth thousand years BC, and in succeeding hundreds of years takes after the improvement of the numerous different social orders past the Nile Valley. From an early date this has included basic cooperations with non-African civic establishments. These extended from the Phoenicians, who set up the dealer domain of Carthage, to the Romans, who colonized all of North Africa in the principal century BC.

Christianity started its spread through extensive zones of northern Africa as of now, coming to as far south as Kush and Ethiopia. In the late seventh century, North and East Africa were vigorously affected by the spread of Islam, which in the long run prompted the presence of new societies, for example, those of the Swahili individuals in East Africa, and effective kingdoms incorporating the Songhai Realm in the sub-saharan west. More distant south, Ghana, Oyo, and the Benin Domain created with little impact from either Islam or Christianity.
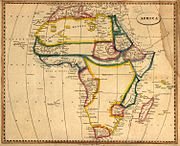
The ascent of Islam prompted an expansion in the Bedouin slave exchange that would come full circle in the nineteenth century. This forecasted the constrained transport of African individuals and societies to the New World in the Atlantic slave exchange, and the start of the European scramble for Africa. Africa's frontier period endured from the late 1800s until the appearance of African freedom developments in 1951, when Libya turned into the primary previous settlement to end up autonomous. In spite of the fact that Liberia being the main post-pilgrim free nation, built up 1847. Current African history has been overflowing with transformations and wars and the development of present day African economies and democratization over the landmass.
African history has been a test for scientists in the field of African investigations because of the shortage of composed sources in huge parts of Sub-Saharan Africa. Insightful procedures, for example, the account of oral history, chronicled phonetics, prehistoric studies and hereditary qualities have been critical.