Intuitive EOS Development Methods 1: intro to Decentralized and Semi-Decentralized Methods
Repository
https://github.com/feekayo/eostuts1
What will I learn
- Different development methods for EOS dApps
- How to implement basic profile management with both methods
Requirements
- Linux or MacOS system with 7GB of RAM
- Basic knowledge of C++
- Basic knowledge of EOS development
Level
Intemediate
Introduction
I plan on creating a guide (in a series of tutorials) for first time developers on the EOS blockhain to quickly develop applications on the blockchain using two very separate methodologies
- A Fully Decentralized method
- A Semi Decentralized method
In this tutorial series we would be developing two separate feature rich micro-blogging services using the above methods while exploring their similarities and differences.
During the course of this tutorial series, I hope to delve deep into intuitive methods for creating robust EOS dApps while using tools such as Scatter, EOSJS, ReactJS, NodeJS, Demux and IPFS
I would also be providing intuitive guides towards tokenization, vesting and creation of reward pools through simple inflation techniques (similar to Steem).
Let’s get started!
Overview of Existing Tutorials
We won’t be diving too deep into low level details in this tutorial series.
This tutorial contains more than a bit of a jumpstart
You should also check-out https://developers.eos.io, https://eosio.stackexchange.com among other existing resources so as to properly understand and get into the development ecosystem.
Development Methods in EOS
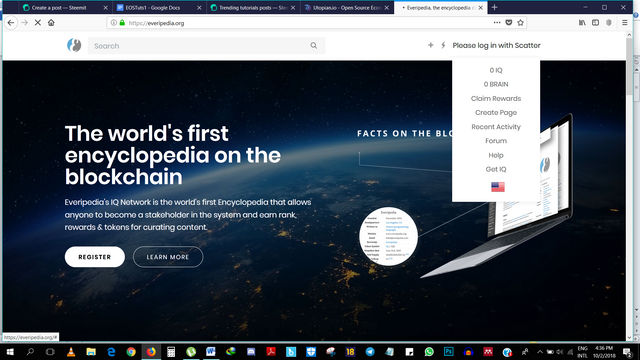
To best understand the differences between the two development methods, I’ld ask that you explore two dApps already deployed on the EOS blockchain.
When you try to Login to use either application, you see the glaring differences.
.png)
Everipedia: requires you to Login with a Scatter Wallet. This wallet holds your keys and helps sign all transactions you make using the application.
This approach has the following advantages
- You’re totally anonymous on the service
- Your keys and tokens are secure from third parties
- Your relationship with the service is trustless as nobody holds your keys or tokens
There are however a few uncomfortable truths about this system that could hinder its wide appeal.
- You absolutely require an EOS account to use the service
- Use is not intuitive; as the average joe might have trouble setting up and signing transactions with a scatter wallet
- Creation EOS accounts is computationally expensive; especially on a large scale
However; I must say, I love this approach towards dApp development as it is completely decentralized; total decentralization can never be a bad thing.
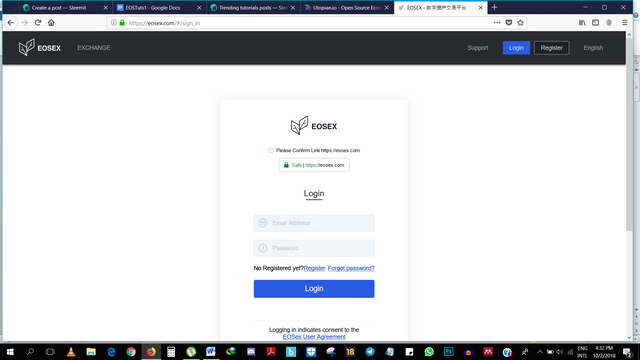
As for the Semi-Decentralized approach
.png)
Eosex.com:- From basic interaction with the app, you would see that this is a total departure from the method used in Everipedia.
It allows account registration and use in a way we’ve been used to this whole time. In user experience, in my opinion, it beats the Everipedia approach hands down!
Why? You might ask
- Intuitive use for everyone
- Anybody can sign up; even without an EOS account or wallet
- Doesn’t require Scatter to sign transactions
- Eliminates EOS account creation RAM cost
Of course there are disadvantages like
- You have to give up personal information
- Requires a degree of trust in the smart contract
- What of your tokens, how do we handle them?
- Your users do not have access to core EOS functions like active keys, owner keys and account recovery
NOTE:- The most widely used is the decentralized approach
Designing DApps with each method.
To clearly show the differences between each method. We would be creating two smart contracts for creating user profiles on each dApp type
The Fully Decentralized approach.
#include <dcent.hpp>
void dcent::create(
account_name application,
account_name username
){
require_auth(username);//a single account's details requires validation
profile_table profiles(_self,_self);//initialize profile table
auto iter = profiles.find(username);//check if username is in use
eosio_assert(iter == profiles.end(),"account already exists"); //if user name exists stop everything
profiles.emplace(application,[&](auto & row){//create a new user profile
row.username = username;
});
print("profile created"); //pass message to client
}
Above is a well commented code for creating a new profile for a user on your dApp. It assumes that the user requesting access to your smart contract already has an EOS account.
The Semi Decentralized approach
In this method the user doesn’t sign transactions; rather, the application signs transactions for every user. This means that users on the platforms don’t require EOS accounts or wallets, as the application itself handles everything for them.
It also means they are in a blind trust with the application to hold whatever tokens they might accrue using the application.
To better understand this, consider the code below.
#include <sdcent.hpp>
void sdcent::create(
account_name application,
account_name username,
account_name email,
string password
){
require_auth(application);//a single account's details requires validation
profile_table profiles(_self,_self);//initialize the profiles table
auto user_index = profiles.get_index<N(byUser)>();//use the username as an index
auto iter = user_index.find(username);//try to find if the username is in use
eosio_assert(iter == user_index.end(),"account name in use"); //if username is in use terminate
auto email_index = profiles.get_index<N(byEmail)>();//use the email as an index
auto itr = email_index.find(email); //check if email is in use
eosio_assert(itr == email_index.end(),"email name in use"); //if email is in use terminate
profiles.emplace(application,[&](auto & row){//create a new user profile
row.user_id = profiles.available_primary_key();
row.username = username;
row.email = email;
row.password = password;//is expected to be hashed from the frontend (preferably SHA 256)
});
print("account created"); //pass message to client
}
The application validates every transaction on the smart contract. The user doesn’t need to hold any keys to use the application. He or she just uses the application while the application worries about validating the requests made by the user.
Logging into the Semi Decentralized App
Since EOS won't be providing us with default validations in our Semi Decentralized DApp, we would need a means of maintaining sessions across the frontend, backend and smart contracts. For that we would need a login function so as to maintain request legitimacy.
void sdcent::login(
account_name application,
account_name username,
string password,
account_name session_id,
account_name platform
){
profile_table profiles(_self,_self); //init profile table
auto user_index = profiles.get_index<N(byUser)>();//check if username is in use
auto iter = user_index.find(username);//try finding the user on the profiles table
eosio_assert(iter != user_index.end(),"username does not exist");//assert error if username isn't saved on the table
eosio_assert(iter->password!=password, "invalid password"); //assert error if password doesn't match up
uint64_t user_id = iter->user_id;//init user id from search func
session_table sessions(_self,_self);//init sessions table
//the platform field in the sessions table allows for multi platfrom logins to be made by the same user
auto platform_index = sessions.get_index<N(byPlatform)>();
auto itr = platform_index.find(platform);
for(; itr != platform_index.end() && itr->platform; ++iter)//check for pre existing sessions on the same platform
eosio_assert(itr->user_id == user_id, ""+itr->session_id);//return existing session ti the client
sessions.emplace(application,[&](auto & row){//create new blockchain session
row.user_id = user_id;
row.session_id = session_id;
row.platform = platform;
});
print("session created");//pass message to client
}
Conclusion
We can see the two distinct methods of creating and maintaining user profiles on your EOS application.
For further enquiry, please checkout the git repo attached to see how we set up our multi index tables in the .hpp files
I hope to hear your thoughts about the work done and hopefully have a discussion in the comment section.
Next up we would do a recap of using EOSJS and intuitive means of connecting a Frontend react client to our smart contracts and a 3rd party API and MongoDB Database with Demux. We would also be kicking off our dApps
Thanks for your attention.

Thank you for your contribution @feekayo.
After an analysis of your tutorial we suggest the following points:
We suggest that in your title, put the key words of the technologies that you will use in the tutorial, such as ReactJS and NodeJS.
In the Proof of work put the link directly to your code in github, we had to go looking for your code.
Overall we really enjoyed your tutorial and look forward to seeing the next tutorials.
Good job.
Your contribution has been evaluated according to Utopian policies and guidelines, as well as a predefined set of questions pertaining to the category.
To view those questions and the relevant answers related to your post, click here.
Need help? Write a ticket on https://support.utopian.io/.
Chat with us on Discord.
[utopian-moderator]
Thank you for your review, @portugalcoin!
So far this week you've reviewed 5 contributions. Keep up the good work!
Hi @feekayo!
Your post was upvoted by @steem-ua, new Steem dApp, using UserAuthority for algorithmic post curation!
Your post is eligible for our upvote, thanks to our collaboration with @utopian-io!
Feel free to join our @steem-ua Discord server
Hey, @feekayo!
Thanks for contributing on Utopian.
We’re already looking forward to your next contribution!
Get higher incentives and support Utopian.io!
Simply set @utopian.pay as a 5% (or higher) payout beneficiary on your contribution post (via SteemPlus or Steeditor).
Want to chat? Join us on Discord https://discord.gg/h52nFrV.
Vote for Utopian Witness!