Http Vs Https And Why Ssl Is The Future?

Previously we have outlined how to make your WordPress website secure, but now we go deeper into details and explain the magic behind “HTTP”, “HTTPS” and “SSL”. Today everyone exchanges information: from personal data to credit card details and identification numbers. The security of this exchange became an extremely important matter. Cyber attacks are a common occurrence; the targets are governments, banks, businesses and even individual websites. By using techniques like phishing, man-in-the-middle attack, malware or most recently ransomware, they all steal large amounts of sensitive data. Even the big guys such as HBO get attacked. All these attacks emphasize the importance of being “secure by default”. So why is HTTPS and SSL certificates so important all of a sudden? A picture will say more than a thousand words:
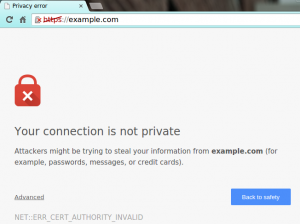
First, it started with Chrome, and now most web browsers are devaluing the insecure HTTP protocol, eventually forcing all sites to use HTTPS if they hope to use modern features. Today HTTPS and SSL certificates are becoming a necessary element of a trustworthy online business because websites and apps without HTTPS will simply get the message “Your connection is not private”. This new approach from modern browsers is a large push to increase the security on the Internet.
Web browser companies have been forcing all sites to switch from HTTP to HTTPS. #HTTPSeverywhere CLICK TO TWEET
HTTP vs HTTPS

Before we start talking about the future, let’s back up a bit and talk about what are the differences between HTTP and HTTPS.
In simple terms, the HyperText Protocol (HTTP) is a basic communication protocol that both clients and servers must implement to be able to communicate. The protocol transfers information between the browser and the server in clear text. If you have a way to access the network where information passes through, you can see the information transmitted. Thus it is very likely that somewhere along this communication protocol aggressive advertisers, some security agency or a bored internet troll is inspecting or storing this information.
Eventually, this issue was meant to become a security control, so HTTP Secure (HTTPS) was introduced. Firstly, with HTTPS the client and the server have to establish a communication. Then pass the clear text HTTP messages through it while protecting them from eavesdroppers. So this means that your communication with another party in a public medium, such as the Internet, reaches the intended party unaltered.
As a result, HTTPS is the secure variant of the HTTP protocol, which has long underway within modern web. The latest push from browsers like Chrome is a big step towards an HTTPS dominated world! HTTPS keeps you safe from people spying and tampering when doing something as online banking to communicating with your friends. So the question remains, how does one go about changing from HTTP to HTTPS? Entering, SSL certificates.
What is SSL?
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) is the standard implementation for establishing a safe and encrypted link between two points on the internet. The term has been updated to Transport Layer Security (TLS), but it is still known simply as SSL for simplicity.
The SSL protocol jumps in before the HTTP connection starts and uses a method of encryption called public key cryptography to secure the connection. It secures the connection in two ways: by encrypting the information, so that only the server can read the resulting plaintext, and by providing authentication, which ensures the server you are communicating with is not an imposter.
You know a website is using SSL when you see HTTPS at the beginning of the URL and the “green padlock” or the “green address bar” in your browser. All the major browsers, including mobile browsers, implement this indicator in one way or another.
Every website is capable of obtaining an SSL certificate and is the only widely deployed option for in-transit encryption between clients and servers, though it didn’t use to be. Barriers to buying a certificate have been removed because the web became “secure by default”. This means any website can now set up HTTPS.
Moreover, studies have shown that information that may even seem irrelevant or unimportant can be used to identify a user, especially when it’s combined. You don’t know who is using your site or why they are using it. By providing HTTPS, you can keep a site protected and also create a more secure web.

Why are SSL Certificates the Future?
We can conclude that in order to prevent data breaches, almost every industry started becoming “secure by default” thus, supporting SSL certificates. Since Google announced that they want to encrypt the entire web and will use the HTTPS as a ranking signal, SSL certificates became imperative for the internet industry.
Moreover, there is a new HTTP protocol version, HTTP/2. The last time the protocol was updated, was in 1997. All popular web browsers are in agreement that migration to the new protocol will be impossible without having an SSL certificate. Besides, you will benefit from the powerful web features such as higher performance, full-screen mode, geolocation, device orientation and much more, but only if you own an SSL certificate. The reason for that is because these functionalities require access to sensitive data that developers think is not safe to be provided within the old HTTP. This requirement is strengthening once more the SSL’s position in ensuring a safer web.
SSL certificates are the future! #SSL CLICK TO TWEET
So it doesn’t matter how we will call SSL certificates in the future. What matters is to continue the fight against cyber threats and ensure the highest level of web security. The bottom line is this: If you’re serving anything via an insecure connection, you need to start planning how you’re going to switch to HTTPS. And for that, you need an SSL certificate. Better be safe than sorry!
Google's ranking system is fascinating and it keeps improving the way things are done on internet. I am looking forward for updates on this topic, as I am a SEO enthusiast. Good read!