First Object Teleported from Earth to Orbit
Researchers in China have teleported a photon from the ground to a satellite orbiting more than 500 kilometers above.
Last year, a Long March 2D rocket took off from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Centre in the Gobi Desert carrying a satellite called Micius, named after an ancient Chinese philosopher who died in 391 B.C. The rocket placed Micius in a Sun-synchronous orbit so that it passes over the same point on Earth at the same time each day.
Micius is a highly sensitive photon receiver that can detect the quantum states of single photons fired from the ground. That’s important because it should allow scientists to test the technological building blocks for various quantum feats such as entanglement, cryptography, and teleportation.
Today, the Micius team announced the results of its first experiments. The team created the first satellite-to-ground quantum network, in the process smashing the record for the longest distance over which entanglement has been measured. And they’ve used this quantum network to teleport the first object from the ground to orbit.
Teleportation has become a standard operation in quantum optics labs around the world. The technique relies on the strange phenomenon of entanglement. This occurs when two quantum objects, such as photons, form at the same instant and point in space and so share the same existence. In technical terms, they are described by the same wave function.
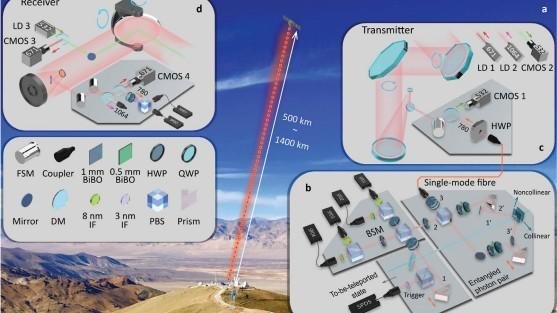
This is the first time that any object has been teleported from Earth to orbit, and it smashes the record for the longest distance for entanglement.
That’s impressive work that sets the stage for much more ambitious goals in the future. “This work establishes the first ground-to-satellite up-link for faithful and ultra-long-distance quantum teleportation, an essential step toward global-scale quantum internet,” says the team.
It also shows China’s obvious dominance and lead in a field that, until recently, was led by Europe and the U.S.—Micius would surely have been impressed. But an important question now is how the West will respond.