THE SCIENTISTS HAVE CREATED NEW ULTRA-DENSE TECHNOLOGY TO STORE DATA
As I have recently learned from the statistics of IBM company, the humanity creates more and more new information daily (app. 2.5 million of TB), which actually need to be stored on various media. And as you have already realized these media require space and service. If to consider traditional information storage systems, such as hard drives, we all know for sure that they store information in the corpuscles of magnetic medium or in the form of holes, burned by the laser in the special layer of optic medium. All attempts to make the storage media much more compact have actually led just to minimizing of the existing technology. As the information volume grows every day the scientists are always looking for the developing method of the most compact technology to store data. And since recently the scientists from Holland have elaborated the new atomic ultra-dense technology, which I’d like to observe in my today’s article.

How does the new technology work?
Like I have mentioned above, the group of scientists from Holland has elaborated innovative atomic storage medium, containing a capacity in 8 000 bits within the size of 96x126 nanometers, and now it actually may be observed with the help of the microscope only. A copper bottom layer serves as the ground for this new atomic medium, and upon that it consists of the chlorine atom matrix, fixed there in a strict order. If to measure the quantity of these atoms and the distance between them as well, we would be able to know the density of the first atomic medium. As far as I know, the scientists have already achieved the density in 500 terabits for one square inch. And it significantly exceeds the storage density of the newest media, existing in our world today. For illustrative purposes, if we were able now to record the whole quantity of books available into the atomic media, it would actually look like a usual label.
However, if to discuss both recording and reading processes, here it’s worth mentioning that they would be far different from the ones we used to apply today. For example, to record or just to read out some kind of information from the medium of a new type, we would actually require the whole scanning tunneling microscope, applying quantum tunneling effect in its work at least. The microscope’s tag receives an electrical potential, and being edged up to the atomic value, starts moving over the examined surface. And if it collides with the atom, then the electrons start spreading from the tag onto the atom upon the effect of quantum tunneling. But exactly at this very moment, some sort of powers is starting its formation, what enables the tag of the microscope to serve as something like “lift crane” for the atoms, which couldn’t fix heavily to the surface of the bottom layer. And with the help of such “lift crane”, it’s possible to lift the atoms and to direct them into the targeted point with a high accuracy.
Every bit of the information need to be recorded, is coded via mutual arrangement of two copper atoms and one chlorine atom. The various combinations of the atoms correspond the logic values 1 and 0.
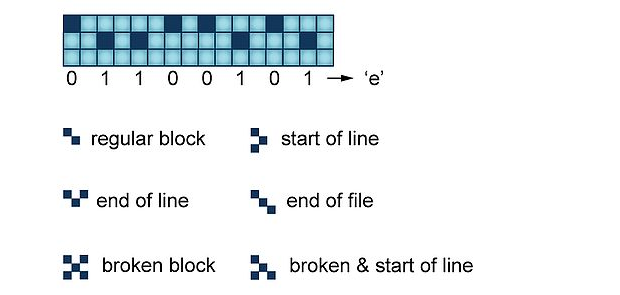
The problem of realisation
Nevertheless, the transfer of the atoms and their set up at a specified position is just one of the issues need to be resolved. If to discuss the second issue, which is connected with the problem of data organization, the scientists are now on their way to make the process of reading out the information more convenient and efficient in use. Moreover, the problem of how to make the storage itself more reliable than now remains to be under discussion. All memory array contains the separate blocks, having 64 bits of storage capacity each. Every block is complete with the identifiers, applying chlorine atoms in its work and it is similar to the popular QR code in some way. And as far as I understand, this identifier can indicate the location of the certain block and may be additionally used to fix the issues in the information stored.
The prospects in the future
Nowadays, according to the various sources of information provided, this technology is just at the early stage of its laboratory development. It can start working only under the conditions of the clean vacuum and upon the temperature of liquid nitrogen gas (196degrees Celsius). However, the scientists are already planning the next steps to come closer to the practical realization of this technology.
If you asked my viewpoint toward the prospects of this technology in the future, I would answer that mostly it’s real to realize it, but not so soon, as you probably might think. I consider, that the first practical application of this technology will be available at least in 20 years for experimental purposes, and in 30-40 years for the common use only.
Follow me, to be the first to learn about my publications devoted to popular science and educational topics
With Love,
Kate
The number of genuine innovations is greatly increased in recent days. We live in interesting time...Thank you for post.
technologies are developed rapidly. This data storage approach is pretty innovative, will see where it leads to