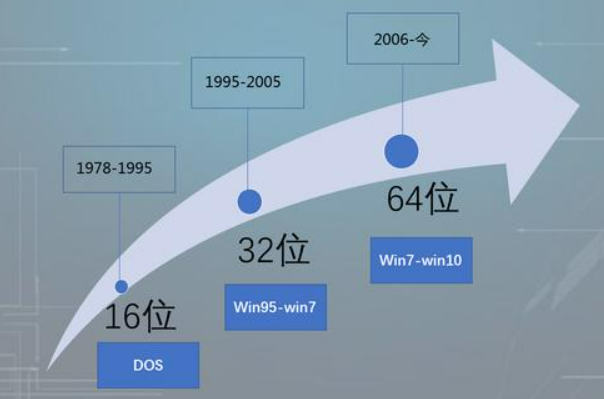
From 16-bit to 32-bit to 64-bit, why is there still no 128-bit system after 16 years?
The 128-bit operating system did not appear because there was no market demand. The 64-bit operating system can fully meet the status quo and is inexhaustible.
The computer's 16-bit, 32-bit, and 64-bit operating systems are embodied in the hardware aspect of the CPU bus and the software aspect of the operating system.
The computer's memory access is done through software and hardware together.
When the cpu is addressed, the logical address of the operating system is first used, and then the hardware address is searched through the bus.
The maximum addressing space of a 32-bit system is 2 to the 32nd power approximately equal to 4Gbit, but it will actually be less than 4Gbit.
The maximum addressing space of a 64-bit system is 2 to the 64th power and greater than 100 million Gbits. At present, our PCs stay at around 16G.
However, the current structure used in distributed computing does not require a 128-bit cpu and operating system.
In actual use, a 32-bit operating system can run on a 32-bit cpu architecture or a 64-bit cpu architecture. It's just that on the 64-bit cpu architecture, the performance of the cpu is not fully utilized, which is a waste.
Therefore, based on the current technological development, there is no demand for a 128-bit CPU and operating system. Moreover, R&D requires costs. For the time being, there is no market, and merchants will not make a loss-making business.