Military operation
A military operation is the coordinated military actions of a state, or a non-state actor, in response to a developing situation. These actions are designed as a military plan to resolve the situation in the state's favor. Operations may be of a combat or non-combat nature and are referred to by a code name for the purpose of national security. Military operations are often known for their more generally accepted common usage names than their actual operational objectives.

Types of military operations
Military operations can be classified by the scale and scope of force employment, and their impact on the wider conflict. The scope of military operations can be:
Theater: this describes an operation over a large, often continental, area of operation and represents a strategic national commitment to the conflict, such as Operation Barbarossa, with general goals that encompass areas of consideration outside the military, such as the economic and political impact.
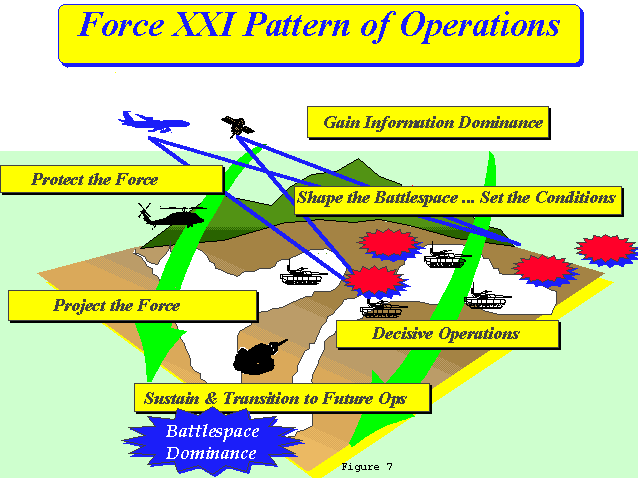
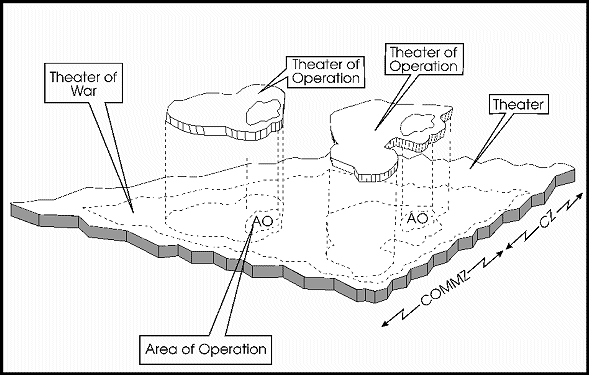
Campaign: this describes either a subset of the theatre of operation, or a more limited geographic and operational strategic commitment, such as the Battle of Britain, and need not represent total national commitment to a conflict, or have broader goals outside the military impact.
Battle: this describes a subset of a campaign that will have specific military goals and geographic objectives, as well as clearly defined use of forces, such as the Battle of Gallipoli, which operationally was a combined arms operation originally known as the "Dardanelles landings" as part of the Dardanelles Campaign, where about 480,000 Allied troops took part.
![]()
Engagement: this describes a tactical combat event or contest for a specific area or objective by actions of distinct units. For example, the Battle of Kursk, also known from its German designation as Operation Citadel, included many separate engagements, several of which were combined into the Battle of Prokhorovka. The Battle of Kursk, in addition to describing the initial German offensive operation, also included two Soviet counter-offensive operations: Operation Kutuzov and Operation Polkovodets Rumyantsev.

Strike: this describes a single attack, upon a specified target. This often forms part of a broader engagement. Strikes have an explicit goal, such as rendering facilities such as airports inoperable, assassinating enemy leaders, or limiting the delivery of supplies to enemy troops.

Operational level of war
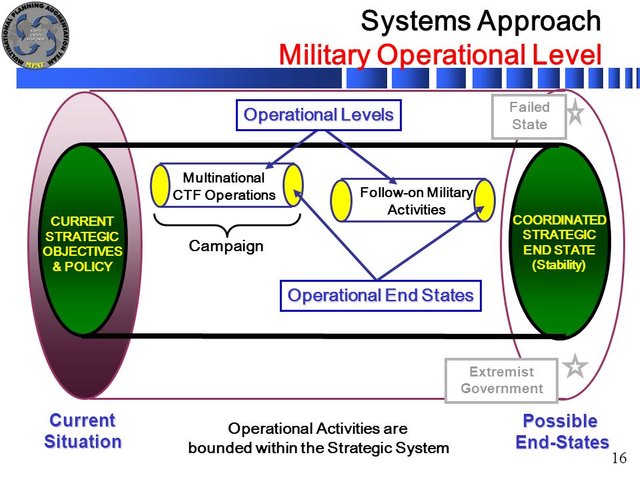
The operational level of war occupies roughly the middle ground between the campaign's strategic focus and the tactics of an engagement. It describes "a distinct intermediate level of war between military strategy, governing war in general, and tactics, involving individual battles". For example, during World War II, the concept applied to use of Soviet Tank Armies.
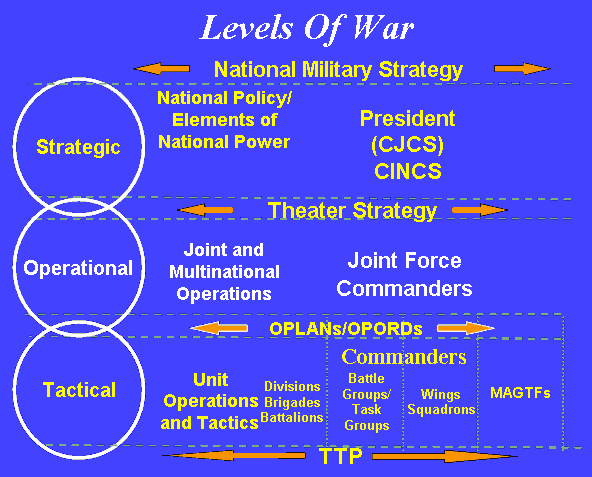
In the field of military theory, the operational level of war (also called the operational art, as derived from Russian: оперативное искусство, or the operational warfare) represents the level of command that connects the details of tactics with the goals of strategy.
In Joint U.S. military doctrine, operational art is "the cognitive approach by commanders and staffs—supported by their skill, knowledge, experience, creativity, and judgment—to develop strategies, campaigns, and operations to organize and employ military forces by integrating ends, ways, and means." It correlates political needs and military power. Operational art is defined by its military-political scope, not by force size, scale of operations or degree of effort. Likewise, operational art provides theory and skills, and the operational level permits doctrinal structure and process.