Biochemistry Involved in the Elimination of Ammonia From the Body System.
Hello beautiful people
Welcome to my blog.
Happy new month!!!! 🙌
Last week, or should I say last month ☺,
I made my first steemstem post, which was though rough but after some mentorship, I guess I am back on track, though I am still on mentorship.
So the post was on the biochemical effects of ammonia on workers.
The post talks on the different levels of exposure of ammonia to individuals, not just workers, from the cleaning agents used at home, the excrete of our pets at home to those working on a daily basis in the factory.
You can read more here
Today, I want to share with you how this ammonia is eliminated from the human body, the pathways involved.
Before we start proper, let's take a quick dive on what ammonia is about and how they affect the body system.
- Ammonia in the environment is a part of the nitrogen cycle and it acts as a precursor for the synthesis of amino acids (end product of protein) and nucleotide in some biological processes of the body.
- Ammonia is known to be much more soluble in water than any known gas so far.
- ammonia is produced from different sources; in the soil from bacteria processes as well as naturally from decomposition of organic waste. In the laboratory, it is produced from reactions involving three molecules of hydrogen and one molecule of nitrogen.
You can read more on the uses of ammonia here
Mechanism of formation of ammonia in the body
From what was discussed in the previous post, ammonia affects people from different levels of ppm (part per million).
There are moistures in the body system such as the eyes, skin, respiratory tracts, and when it interacts them, it tends to form the very caustic ammonium hydroxide. (NH4), this then leads to necrosis (premature death) of body tissues, this is as a result of the disruption of cell membrane lipids.
Now as this cells begin to break down, water is then extracted which results in further damage via inflammatory response.
We are exposed to ammonia on a daily basis in different levels from the external environment to the ammonia produced by the cells in our body and these causes harm to the body system.
I remember one time during my final year project. We were carrying out an experimental analysis making use of alloxan-induced diabetic rats. It was a team of three, one of my team member forgot to clean the rat cage on a Friday, by Monday when I entered into the laboratory, the poor rats were already starving and worst was the cages were a total mess, I was not with my nose mask, I thought of holding my breath to clean the cages (8 cages), it's really unethical to do such stunt when I am no super man.
Ladies and gentlemen two days later I found myself in the Medical Center
The major source of ammonia formation is from the catabolism or breakdown of amino acids; this is to remove the amino group as ammonia.
The biological sources of ammonia includes :Glutamic acid, Amino sugars, Pyrimidine, Glutamine as well as asparagine.
Amminia effect to the body system
The liver and the kidney play a very vital role in the detoxification or elimination processes of ammonia from the body system.
The liver does this by converting ammonia into what is known as urea, this is then passed out in urine.
For humans we pass out ammonia compound in form of urea, for other organism it is quite different.
Birds passes out ammonia compound in form of uric acid.
The inability for the liver to detoxify ammonia from the body can lead to coma or the triggering of seizures in the individual exposed.
The University of Oslo, faculty of basic medical science did a terrific work on how ammonia affects the neurological system using albino wister rats as test subjects, you can read more here.
Their research work showed that the swelling of glial cells in the brain is not a functional requirement for the toxicity of ammonia in the brain, putting forward the effects of ammonia in the brain and how
Three-dimensional imaging and volume analyses of individual cells showed, paradoxically, that the glial cells in the cerebral cortex shrink during ammonia toxicity.
How then is ammonia synthesized?
As said earlier, ammonia is gotten from the catabolism or breakdown of amino acids; the removal of amino group as ammonia from the body system.
There are pathways involved in this process of ammonia removal and they includes the following :
- Transamination
- Trans-deamination
- Oxidative deamination
- Urea cycle
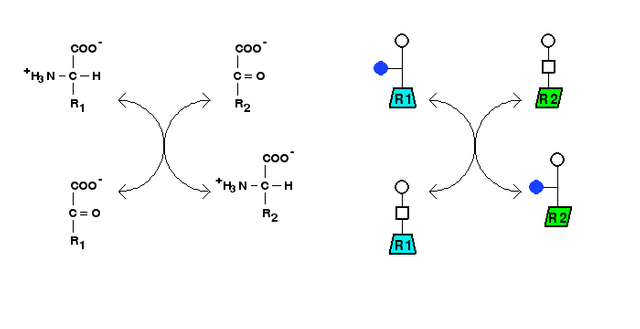
Transamination
Transamination reaction involves the exchange of alpha amino groups, between one alpha amino acid and another alpha keto acid resulting in the formation of a new alpha amino acid.
Now this is where we start talking biochemistry.
I.e-
amino acid A +keto acid B--> amino acid B + keto acid A.
In the chemical reaction above, we see that amino acid A, reacts with a keto acid such as alpha keto glutarate, to form a new alpha amino acid. In this reaction, the amino group liberated as ammonia is detoxify and excreted from the body as urea.
The reaction is catalysed by an enzymes called the aminotranferase, formally called transaminases.
Let's explain the reaction proper.
Alpha amino acids to know more on what alpha amino acids are)
Keto acids.
Let's explain proper, using alanine as an example of the alpha amino acids and glatamic acid as an example of keto acid.
Glutamate
Alpha alanine reacts with alpha ketoglutarate (a ketogenic amino acid). In this reaction, there is exchange of amino group and that of the carbon skeleton of the ketogenic acid, thus forming pyruvate and glutamate.
In this reaction, ammonia is not eliminated, hence the next reaction.
During this reaction, which serve as precursor to ammonia elimination, all amino acids are transaminated to glutamate.
Deamination
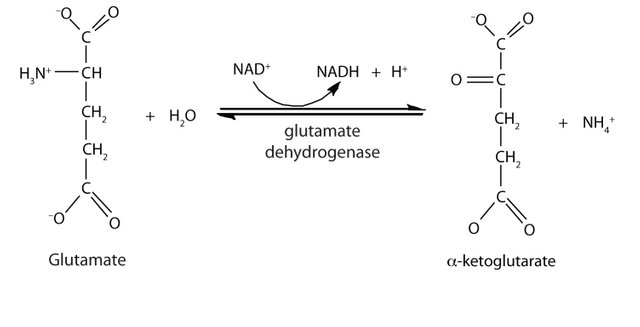
The liver is the only organ responsible for the destination process of alpha amino acids (glutamate) to alpha keto glutarate and ammonia.
Deamination involves the removal of one molecule of an amino group in order to reduce the nitrogen content of the body via the synthesis and elimination of ammonia.
The process of deamination is carried out by the enzyme glutamate dehydrogenase
Glutamate in this process is cleaved to form alpha ketoglutarate and ammonia.
It's important to know that the process of transamination continues into the destination pathway and hence called transdeamination.
During the transamination process, the amino group of all other amino acids are linked to glutamate, thus, the enzyme glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) Is considered as the final reaction to the removal of amino group.
Glutamine hydrolysis yields ammonia and this occurred not in the liver but the kidney.
Detoxification process of ammonia
side track
Ammonia is produced continuously by the cells of the body, external exposure to ammonia occur at different levels which causes health treat to man, higher ppm could result in death of the individual.
How then is this chemical substance eliminated from the body?
- Ammonia produced or the ones that enter the body system is trapped immediately on entry by glutamic acid which forms glutamine (recall that all amino acids are funneled into glutamine, which then undergoes deamination).
Ammonia + Glutamic acid ---> Glutamine +Water
This reaction is catalysed by an enzyme called glutamine synthetase.
The reaction is energy dependent ;energy in form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
The glutamine after formation is transported to the liver where the reaction is reversed by glutaminase enzyme.
Glutamic acid concentrated in the body is much more higher than any other amino acids, and it is transported in the form of ammonia from the brain and intestine to the liver.
Ammonia reaches the liver and is detoxify to urea by the cells of the liver after which the kidney excrete it out, Hence, ammonia produced is immediately detoxified into urea, leading to the urea cycle.
The detoxification process of ammonia is purposed in maintaining the acid-base balance in the body.
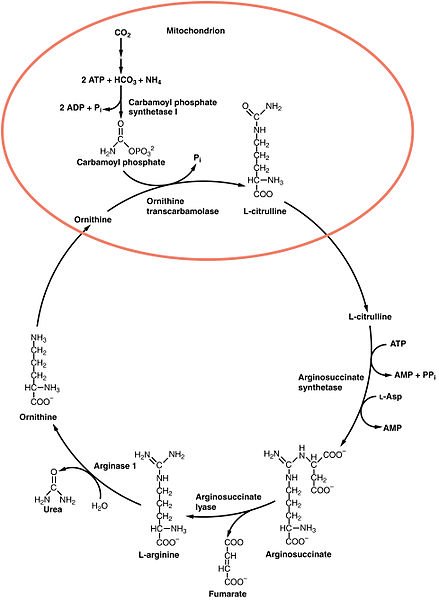
Urea cycle
Urea cycle is the final stage in the elimination of ammonia. The ammonia is removed from the liver via this pathway, and then converted into urea (a water soluble compound).
In this pathway, urea is derived from two main sources, one from ammonia and the other from alpha amino group of aspartic acid.
The formation of urea occurs in 5 steps which are catalysed by enzymatic reactions.
As seen from the pathway above, the urea cycle occur in the cytoplasm and mitochondrion.
The first step involves the formation of carbamoyl phosphate. This step occur in the mitochondrion of the cell. One molecule of ammonia (which was transported from the liver from the detoxification process) reacts with carbon(iv)oxide (CO2) of the body to form carbamoyl phosphate. This reaction is energy dependent ; 2molecules of ATP is required.
The enzyme responsive for this reaction is known as carbomoyl phosphate synthetase -I(CPS-I).
This reaction is regulated allosterically and irreversible, hence considered as the rate limiting step.
- the next step occur still in the mitochondrion and it involves the formation of citrulline. Carbamoyl group formed in the first reaction is transferred to an amino group (NH2) of the amino acid ornithine. This reaction is carried out by Ornithine transcaramoylase (OTC). Citrulline is present in milk, it is also believe to used as a sports performance and cardiovascular health supplement. Citrulline leaves the mitochondrion into the cytoplasm, where further reaction take place to the formation and elimination of urea.
- The next step involves one molecule of aspartic acid, which originates from the Krebs cycle, and citrulline, forming a carbon to nitrogen bond. Argininosuccinate is formed, this reaction is catalysed by the cytoplasmic enzyme :Argininosuccinate synthetase. Hydrolysis of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) to AMP (adenosine monophosphate) is required in this reaction, thus two high energy compounds are used up at this point.
- Argininosuccinate formed from this reaction is split into Arginine and Fumaric acid by the enzyme Argininosuccinate lyase. The fumarate formed act as an inhibitor to this enzyme, it is also channeled to the Krebs cycle where it forms malate, then oxaloacetic acid and finally transaminated to aspartic acid thereby continuing the cycle.
- Arginine formed is hydrolysed to urea and ornithine by the enzyme Arginase.
The ornithine returns to the mitochondrion to react with another molecule of carbamoyl phosphate, thus repeating the Cycle.
The brain is very sexy sensitive to ammonia, and as such even the minute amount of ammonia needs to be eliminated from the body system else it affects the neurological and cardiovascular system.
Deficiency of any enzyme in the urea cycle could result in hyperammonemia, which occur when there is a blockage in one of the steps in the urea cycle.
This results in the accumulation of ammonia, leading to irritation, vomiting, brain damage and ultimately death of the individual if not treated in time.
Conclusion
We are exposed to ammonia on a daily basis from the house hold cleaning materials to the excretes of our pets and other humans around us. The body system produces ammonia on a daily basis and this chemical is detrimental to the health, hence the need to actively detoxify it from the body system.
The liver plays the major role in the detoxification of ammonia.
Hyperammonemia is a deficiency of the urea cycle which occur as a result of liver failure. In this condition ammonia produced are accumulated in the body system resulting in hepatic coma, and ultimately death of the individual.
For workers 👷 exposed to different levels of ammonia it is imperative that protective personal equipments be used to reduce the risk of ammonia. Read my previous post hereon personal protective equipment.
The liver is a vital organ, keep it clean and healthy.
Thanks for reading
References
MURRAY, Robert K, BENDER, David A (2012) . Harper's Illustrated Biochemistry. 29th edition. McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., ISBN 978-0-07-176576-3.



This is an informative read.
Never knew ammonia can be this hazardous.
But then how can one reduce the level of ammonia in the body?