Part #13 [mystery of geology] rocks and minerals..... ???
hallo steemian, rock and mineral is my current study, in this section I will present some studies on geology. Do you know If we talk about rocks and minerals, we will find many facts about it...
 |
 |
Rock.......?
Geology is based on the study of rocks. Beginning with knowing how the rocks were formed, changed, then how until the rocks now occupy parts of the mountains, the plains of the continent to the deep basin below sea level. Wherever you turn, you will always meet objects called rocks or rocks. Call it a crack in the yard, then on the road that the foundation or the edge is made of stone. At the base or river bank, even look at parts of your house may be mostly made of stone. The rocks or rocks you see everywhere, there are the same colors and types, but also many different ones. Not surprisingly, rocks are a major part of our Earth.
Rocks are aggregates of minerals that are already frozen / hard. Rocks are one of the elements of the earth's crust that provide inorganic minerals through weathering which further produces soil. Rocks have a mineral composition, physical properties, and diverse ages. Rarely rock consists of one mineral, but is generally a combination of two or more minerals.
Based on the process of occurrence of rock is divided into 3, namely :
Igneous rock
Sedimentary rock
Metamorphic rock
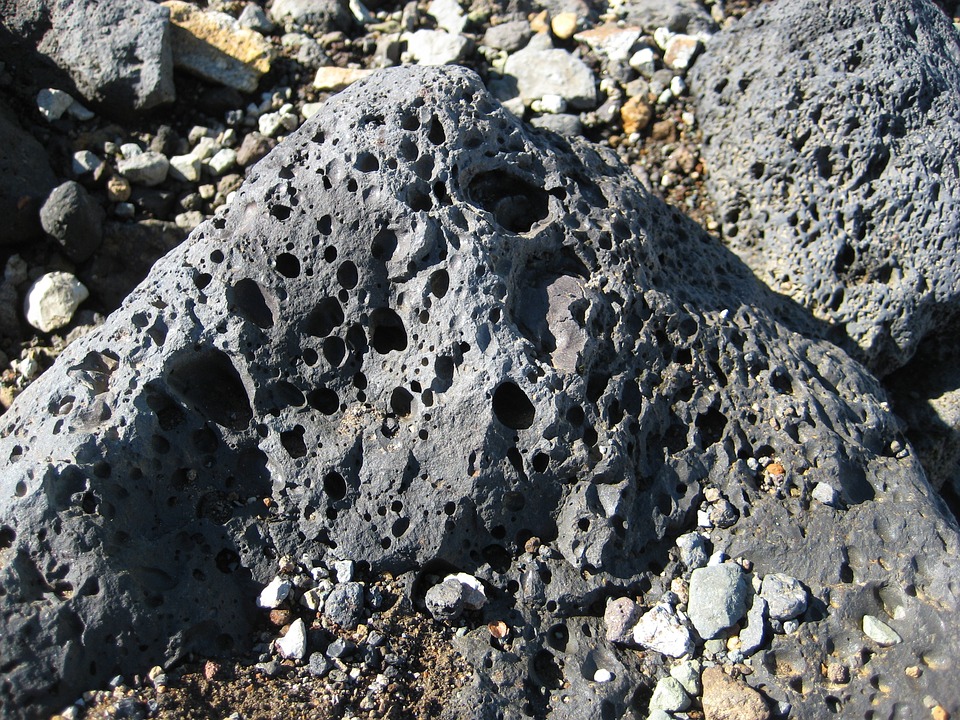

This rock is a type of rock formed from magma that cools and hardens, with or without crystallization, either below the surface or on the surface. Magma is a thick liquid liquid and incandescent mobile with temperatures ranging from 1500-2500ºC found in the lower crust.

The word sediment comes from the Latin word sedimentum, which means "drowning" or simply can be interpreted by "sediment", which is used for solid materials precipitated by fluid.
Sedimentary rocks are rocks formed as a result of other rocks (rocks, metamorphic rocks, or sedimentary rocks themselves) through weathering, erosion, transport, and sedimentation, which ultimately undergoes lithification or sedimentation . Other mechanisms that can form sedimentary rocks are evaporation, landslide, volcanic eruption.
Sedimentary rocks make up only about 5% of the total volume of the earth's crust. But since sedimentary rocks are formed on the surface of the earth, even though they are relatively small but in the case of sedimentary rocks nearly cover the igneous and metamorphic rocks, Sedimentary rocks cover about 75% of the Earth's surface.
Weathering
weathering (weather) is the destruction of rocks on the earth's shell due to the influence of weather (temperature, rainfall, humidity, or wind). Therefore weathering is the destruction of rocks from the clump form into smaller grains even being destroyed or dissolved in water.
Weathering can be divided into 3, namely :
Physical weathering, is the process by which rocks are destroyed into smaller forms by various causes, but without any significant change in chemical composition and mineral deposits.
Chemical weathering, is a process by which changes in the chemical and mineral composition of rocks occur.
Weathering biology, The cause is the process of organisms that are plant and human animals, animals that can do weathering, among others earthworms, and insects.
Erosion
Erosion is an erosion and change in the shape of rocks, soil or mud caused by the strength of water, wind, ice, the influence of gravity and living organisms. Erosion is not the same as weathering, which is a process of destroying rock minerals with chemical or physical processes, or a combination of both.
Transportation
Transportation is the transport of a material (particle) from one place to another by a media movement (current flow) to the media and the material is stopped (precipitated). Transport media (fluid), among others, gravity, water, ice, and air.
The fluid movement can be divided into two different ways
The laminar stream, all the molecules in the fluid move in parallel to the other in the direction of transport. In a heterogeneous fluid there is almost no mixing during the laminar flow.
Turbulent flow, the molecules in the fluid move in all directions but with a net of movement in the direction of transport. Heterogeneous fluid is completely mixed in turbulent flow.
Sedimentation
Sedimentation is the process of sediment deposition by water, wind, or ice media in a deposition basin under certain P and T conditions. Pettijohn (1975) defines sedimentation as a process for the formation of sediments or sedimentary rocks caused by the precipitation of the constituent material or its origin in a so-called settling environment in the form of rivers, estuaries, lakes, deltas, estuaries, shallow seas and deep seas.
Litification
The process of changing the sediment into a rock is called litification. One of the litification processes is compaction or compaction. At the time the sediment material is deposited continuously in a hollow. The precipitate weights above will weigh on the sediment beneath it. As a result, the sediment grains will become denser and the cavities between the grains will be smaller.
Another process that converts loose sediment into sedimentary rock is cementation. The material to be cement is transported as a solution by water which permeates through the intercropping cavity, then the solution will undergo precipitation in the intercooled cavity and bind the sediment grains. Common materials to cement are calcite, silica and iron oxide.
Classification of Sedimentary Rocks
Based on the process of occurrence, then sedimentary rocks are divided into four categories, namely :
Terrigeneous Clastics Formed from other rock rombakan results through the process of weathering, erosion, transportation, sedimentation and pembatuan (litifikasi). Weathering that plays a role here is the physical weathering. Examples: breccias, conglomerates, sandstones, claystone.
Biochemical-Biogenic-Organic Deposits Sedimentary rocks are formed from the accumulation of organic materials (both flora and fauna) and weathering processes that occur are generally chemical. Examples: limestones, coal, deer.
Chemical Precipitates-Evaporates Batuan This type of sedimentary rock is formed from the accumulation of crystals and chemical solutions deposited after the medium undergoes evaporation. Example: gypsum, batugaram.
Volcaniclastics (Pyroclastic) These sedimentary rocks are produced from the accumulation of volcanic materials. Example: agglomerat, tuf, breksi.
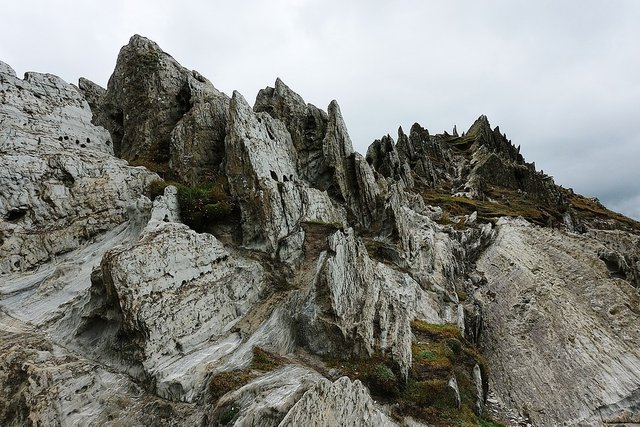

Metamorphic rocks are rocks formed by the process of metamorphism in the rock that has been there before. Rocks of origin (pre-existing) can be igneous, sedimentary or metamorphic. Metamorfosisme process is a process that causes changes in mineral composition, texture and structure in the rocks due to heat and high pressure, and an active chemical solution.
These metamorphism processes alter the minerals of a rock in a solid phase because of the influence or response to physical and chemical conditions in the Earth's crust that are different from the previous conditions. These processes do not include weathering and diagenesis. These metamorphism processes include, Recrystallization, Reorientation, the formation of new minerals (from pre-existing elements)
metamorphic rock is divided into two namely:
- low-grade metamorphism
- high-grade metamorphism
Metamorphic rock structure and texture
In general, the structure found in metamorphic rocks is divided into two major groups namely the structure of foliasi and non-foliasi structure. Foliasi structure is shown by the alignment of minerals of metamorphic rocks, while non-foliasi structure does not show any alignment of metamorphic mineral composite minerals.
Foliasi Structure
Skistose Structure: structures showing flat mineral alignment (biotite, muscovite, feldspar) more than granular minerals.
Gneisic Structure: a structure that exhibits granular mineral alignment, the amount of granular minerals is relatively higher than that of flat mineral.
Structure Slatycleavage: the same as the structure of skistose, the impression of mineralogical alignment is very smooth (in clay minerals).
Phylitic structure: the same as the slatycleavage structure, only the minerals and parallels have started to be somewhat crude.
Nonfoliation structure
Hornfelsik Structure: the structure showing the mineral grains is relatively uniform.
Cataclytic Structures: structures showing the destruction of the original rock.
Milonitic Structure: a structure that exhibits a linear orientation by the orientation of minerals in the form of lenticular and fine mineral grains.
Pillonitic Structure: a structure that shows the linearity of the parallel shaped hemispheres and the mineral grains is coarser than the milonitic structure, rather closer to the type of filit structure.
Augen Structure: same flaser structure, only the lenses consist of feldspar grains in finer base period.
Granulose structure: similar to hornfelsik, only the grains have various sizes.
Linear Structures: structures showing the presence of minerals in the form of jarus or fibrous.
- Flaser Structure: the same cataclastic structure, but the structure of the origin rock shaped embedded lens on the basis of milonite.
mineral.... ?
Minerals can be defined as naturally occurring inorganic solids composed of chemical elements in a particular ratio, in which the atoms inside are arranged according to a systematic pattern.
There are two ways to get to know a mineral, the first is by chemically analyzing, and the second most common is by knowing its physical properties.
crystall form
A mineral may be a single crystal or a series of crystals. The crystal structure develops at the time of crystallization of the solution. This form has a regular pattern on its sides with the angle of the rule can be classified into the main crystal system which is characteristic of each mineral. Example: quartz> hexagonal.
specific gravity
Each mineral has a specific gravity. The magnitude is determined by the constituent elements and the density of the bonds of the elements in their crystalline order. Generally, "rock forming minerals", have a specific gravity of about 2.7, although the mean metal type weighs in the range of 5. Pure gold, for example, has a specific gravity of 19.3.
fracture
Minerals have a tendency to break through a plane that has a particular direction. The direction is determined by the inner arrangement of the atoms. It can be said that the field is a "weak" field owned by a mineral.
color
Mineral color is not a main characteristic to be able to distinguish between one mineral to another. But at least there are typical colors that can be used to recognize the existence of certain elements in it. For example, dark colors are minerals, indicating the presence of iron elements. On the other hand minerals with light colors, indicated contain lots of aluminum.
hardness
One of the uses in diagnosing mineral properties is by knowing the hardness of minerals. Hardness is the resistance of a mineral to the ease of abrasion or scratching.
streak
Scratches are the color of mineral powder when scratched on porcelain plate. For ore minerals, scratches can be used as a guide. In minerals that have a non-metallic gloss, usually the scratches are not dyed or light-colored. Scratches can be the same or different from the color of the minerals.
luster
The brightness or the degree of brightness is the intensity of light that is reflected off the surface of a mineral. The gloss depends on the physical quality of the surface (smoothness and transparency). In general, luster is divided into two, namely: metallic gloss and non-metallic gloss.
conclusion
Knowledge of minerals and rocks is an absolute requirement to be able to study the dense parts of the Earth, which consist of rocks. The solid outer part of the Earth is called lithosphere, which means a rocky membrane, taking lithos, from Latin meaning stone, and sphere, which means the membrane.
No less than 2000 types of minerals that we know now. Some of them are solids with simple bonding elements. Each mineral has a fixed elemental composition with a certain ratio.
Supporting literature / Reference
- Responsi, geology dasar, 2010, Departement pendidikan KM HMG “ARC-SINKLIN”
- https://pixabay.com/
- https://id.scribd.com/doc/307379189/Mineral-pdf
- https://www.slideshare.net/nandareda/kelompok-6makalah-batuan-dn-mineral
- http://staffnew.uny.ac.id/upload/132308480/pendidikan/5.MK+Gizi+OR+Mineral.pdf
All about my article part1, part2, part3, part4,part5, part6, part7, part8, part9, part10, part11, part12.
You received a 80.0% upvote since you are a member of geopolis and wrote in the category of "geology".
To read more about us and what we do, click here.
https://steemit.com/geopolis/@geopolis/geopolis-the-community-for-global-sciences-update-4
I am all about rocks minerals and fossils. We own a rock and fossil shop in Roswell NM. I upvoted and resteemed this post. Cool article.
thank you so much ...@roswellrockman
hopefully his shop triumphant.😊
Contenido de calidad me encanto, tienes mi voto.
Muchas gracias @yosicrespon
De estos contenidos necesitamos mas seguidos, de mucho interés. Te invito a pasar por mi blog para que me des tu opinión en mis contenidos sera de mucho gusto.Saludos.
of course, see you on your blog. 😊
Te espero, no lo olvides.
Congratulations! This post has been upvoted from the communal account, @minnowsupport, by rabo from the Minnow Support Project. It's a witness project run by aggroed, ausbitbank, teamsteem, theprophet0, someguy123, neoxian, followbtcnews, and netuoso. The goal is to help Steemit grow by supporting Minnows. Please find us at the Peace, Abundance, and Liberty Network (PALnet) Discord Channel. It's a completely public and open space to all members of the Steemit community who voluntarily choose to be there.
If you would like to delegate to the Minnow Support Project you can do so by clicking on the following links: 50SP, 100SP, 250SP, 500SP, 1000SP, 5000SP.
Be sure to leave at least 50SP undelegated on your account.
Bereeh lagoe kaaa @rabo
Dikit dikit 😀