Health Science #4; Lipolysis and Ketogenic Diet
Hi everyone,
While flipping through the newspaper today (yeah, I still read them), I read a few articles which is written by doctors that explained obesity and anything that's related to it. Last time, I wrote an article which described some of the arguments on why we should not fear fat as a macronutrient. If you haven't read the post yet, you can click the link below:
There are many advises being given by your friends, relatives and anyone related to you, when you've decided to consult them regarding weight loss. Suddenly, everyone becomes an expert! Even though there are so many guidelines, dos' and don'ts and different kind of tips given by different people, weight loss can be initiated by focusing on three essential components which are:
- Diet
- Physical Activity
- Sleep
We are going to focus on the first component. Next series, I would be explaining the role of exercise and sleep in weight loss. Well, I'm not going to ramble randomly about diet. In this article, I would narrow down the discussion towards ketogenic diet. There were two types of people in this world when we talked about diet:
- Someone who believes caloric control is the key to weight loss
- Someone who thinks controlling the portion of macronutrients is the key to weight loss
Which one am I? I'm more of the latter. I believe that, if you want to lose weight, we have to know, what kind of weight that we're attempting to lose. Is it the water weight? Muscle? Fat? Bones? I just want to clarify that, restricting calories without controlling macronutrients do work. I knew a lot of people who have been limiting caloric intake per day, and they lose lots of weight, but calorie restriction doesn't explain what kind of weight you were losing.
Most of the people out there would say, they were losing fat, but why your body chose to discard fat and not the other like muscles or bones? Muscles are relatively expensive as it requires a lot of energies to operate and generally, our body will try to be conservative regarding energy expenditure. So by that logic, muscles should be degraded first, not fat.
How Glucose Turns Into Fat Cell

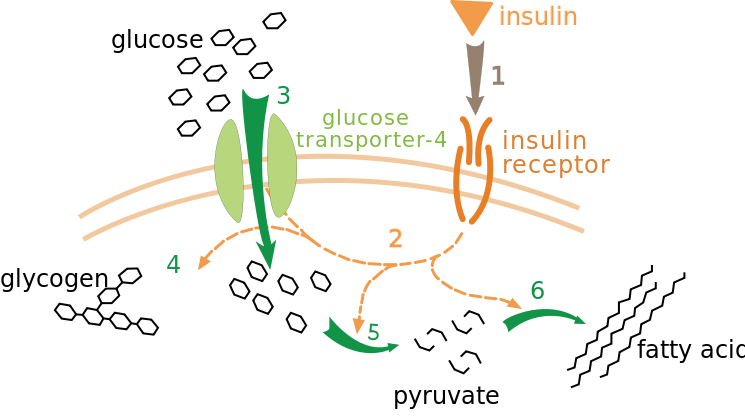
Let's refresh some concept. When you eat some foods which have a high content of carbohydrate, your blood sugar level will rise. As I've mentioned on multiple occasion in my previous article, glucose cannot stay in the blood vessel for so long, or it can cause detrimental effects. Glucose is a molecule which is highly flexible, they can form glycogen, they can be used to make fat cells, and they can combine with circulating proteins to form a compound called an Advanced Glycation End Product (AGE). This particular compound is the culprit which cause people with high blood sugar (pathological) to develop neuropathy.
Insulin is a remarkable hormone. It's released by the Beta cells of the pancreas when the blood sugar level is high. This action is a preventive measure to ensure that any possible consequences that can be caused by a high blood sugar could be avoided. Insulin acts like a key to a lock which is located on cells called the Glucose Transporter 4 (GLUT 4). It activates the transport protein to take in some glucose into the cell so that it can be used for energy.
What happens if all of the cells are fully occupied with glucose? Well, they will be converted into glycogen and stored in the liver and muscles. After those places has been fully occupied with glycogen, where do you think the rest of the glucose would be saved? Hint, everyone hates them and would like to lose them. It's the fat cells. That's how you become fat in the first place. The process is called de novo lipogenesis or simply translated to "New Fat Making".
The Role Of insulin In Hunger and Obesity
To make it simple, I would say, there were two kinds of insulin:
- Insulins which will be secreted when we consume some foods
- Insulins which will be secreted before we consume foods (cephalic phase of insulin release)
Insulin will increase the expression of hunger hormones called ghrelin and block the signal sent by satiety hormones called leptin. Imagine, you are walking through a cafeteria, there is a lot of foods, and some of them are your favourites. Suddenly you feel hungry, even though you just ate your breakfast this morning. Well, insulin, specifically the cephalic phase insulins were responsible for increasing ghrelin making you motivated to eat.
As the insulin practically blocks the signal sent by leptin, the satiety centre in the brain would have some difficulty reading this signal making you hungry. For your information, leptin is released by the fat cells. Theoretically, if someone has a high proportion of fats, then the amount of leptin would be greater, isn't it? So by that logic, an obese people should have less appetite. So, why fat people tend to eat more when they have twice or thrice of the leptin signal?
This is because they have high insulins which would block most of the leptin signal. This is how insulin makes you fat. Oh yeah, there is one more thing. The role of insulin in disabling a hormone which is responsible for using fat for energy. The hormone is called Hormone Sensitive Lipase (HSL). This particular hormone is sensitive to insulin so it will not trigger lipolysis if the amount of insulin is high in the blood circulation.

So imagine, you restricting some calories to lose weight, but you eat a rather high carbohydrate food before exercise and then in the middle of it, all of the glucose and glycogen stores have become depleted. So where are you going to get your energy from? Fat cell? No, you're wrong. Your body is high in insulin and HSL refused to use fat cells for energy, so you're going to degrade some of your muscle to form glucose in the process called gluconeogenesis (production of new glucose from non-carbohydrate sources). That's why, it is easy to lose weight for the first few weeks, but it becomes harder for the subsequent week. Your resting energy expenditure has reduced due to muscle loss. It's a nightmare, isn't it? It's all comes down to a hormone called insulin which makes everything difficult.
Ketogenic Diet To The Rescue

In 1920, a new style of diet was proposed which consists of a high portion of dietary fat with low carbohydrate content. This particular concept was made to control the amount of insulin so that HSL can be enabled to induce lipolysis which will trigger fat loss. People who practice ketogenic diet in the long-term would use ketone bodies instead of glucose as the main energy sources. The transition from using glucose to ketone bodies as the primary source of fuel will trigger a set of flu-like symptoms which would be going on for a week or two. This is the phase when our body tries to adapt to the dietary changes that we're trying to implement.
Accumulation of ketone bodies in the bloodstream has been called as ketosis. Ketosis will not only take place when you have decided to do ketogenic diet as the main dietary routine. Fasting can also boost the amount of ketone bodies in the blood circulation which will provide the body with a set of health benefits. This includes:
- A stable energy source as fat can provide high energy compared with the other macronutrient
- Increase in Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) which is crucial for the brain development.
- Reduce sugar craving
- Reduce triglycerides
- Increase in High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL)
All of the benefits of ketogenic diet would be discussed in the next article. Thank you for your attention.
References
- Dashti HM, Mathew TC, Hussein T, Asfar SK, Behbahani A, Khoursheed MA, et al. Long-term effects of a ketogenic diet in obese patients. Exp Clin Cardiol. 2004;9:200–5.
- Dashti HM, Mathew TC, Hussein T, Asfar SK, Behbahani A, Khoursheed MA, et al. Long-term effects of a ketogenic diet in obese patients. Exp Clin Cardiol. 2004;9:200–5.
- Michael Joseph, MSc. Nutrition Advance. 6 Health Benefits of Ketogenesis and Ketone Bodies. Retrieved March 21, 2018, from https://www.nutritionadvance.com/ketogenesis-benefits-ketone-bodies/
- Endocrineweb. What is Insulin?. Retrieved March 21, 2018, from https://www.endocrineweb.com/conditions/type-1-diabetes/what-insulin





I have read tons of articles about putting the body into ketosis but Im still not sure on the foods that comprises the ketogenic diet food list.
The easiest way to achieve ketosis is through fasting. Food that can induce ketosis would have high fat percentage with a reduce amount if carbohydrate. That can include some nuts, avocado, some lean meat and some fish. I think you can google some of the foods.
@chloroform really ? no rice ?? How can asians get through with this kind of diet. Haha
@chloroform yes, you're right. That's pretty much it.
@sakura1012 that's why this is not a popular diet among asian. You can eat some carbohydrate, but the recommended amount is to stay below 50g of carbohydrates per day to induce ketosis. Some people took 20g as the maximum amount.
Great article @mawarmerah. You have really improve in terms of your writing style. Keep it up.
Thank you @chloroform.
Being A SteemStem Member