Albert Einstein, the great genius of the 20th century
Source
Albert Einnstein, 1879 -1955), was the creator of the "Theory of relativity". He spent his childhood in Munich; at fifteen he separated from his parents, entered a Swiss school, then studied at the Polytechnic School of Zürich, where he remained until 1900. He could not get a position as a secondary school teacher, and in 1902 he decided to enter the patent office of Bern, where he remained until 1909.
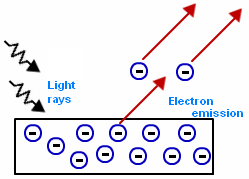
Already in 1901 Einstein, had published his first work, then in 1905 published three fundamental memories, one of them on the Brownian motion of particles in suspension in a liquid at rest, a phenomenon that confirmed the hypothesis of the molecular structure of matter. Another article that later gave him the Nobel Prize, was the one that dealt with the photoelectric effect; in it he presented his hypothesis about the granular nature of light, which supposedly consisted of photons, whose energy only depended on frequency.
Source
The third work in Einstein's life was his famous article on the Electrodynamics of bodies in motion, starting point of the special theory of relativity, generalization of Newtonian mechanics, which contains this as a case particular.
The postulates of this theory are: a) The speed of light in vacuum has the same value in all reference systems, so that it is impossible to catch a beam of light by purely mechanical means; b) Natural laws must be expressed in the same way in all inertial systems of reference, that is, natural phenomena are relative to the systems of reference, but the laws they obey are not relative but absolute. On the basis of both principles, Einstein deduced the Lorentz transformation formulas, which link the coordinates and time that characterize two systems that move rectilinearly and uniformly, one in relation to the other.
On the formulas known by Lorentz, Einstein managed to interpret them without the help of the concept of ether, and found the formula for the variation of mass with velocity:

Source
where the resting mass is represented by (m0), the moving mass (m), (v) is the considered speed of the body and (c) equals (300,000 km / sec), which would be the speed of light in a vacuum. Another remarkable consequence of the postulates of the special theory of relativity is the famous law of numerical equivalence, between mass and energy represented by the expression: E = mc²
Source
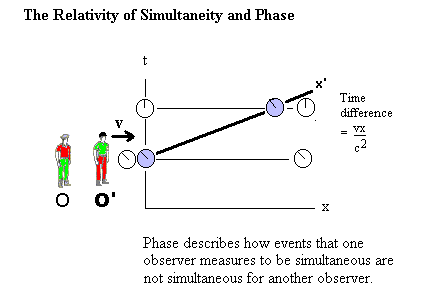
All of Einstein's statements were the results of a deep epistemological critique of the concepts of space, time and natural law, and in particular of the concept of simultaneity of two distant events. Einstein showed that simultaneity, and in general the order of succession of phenomena in time, is relative; That is, that simultaneous events relative to a reference system cease to be so with respect to other systems. Newtonian mechanics was thus substantially modified; the new mechanics approaches electromagnetism, and the laws of dynamics remain constant, if they are subjected to the Lorentz transformation.
The modifications introduced by Einstein in mechanics are quantitatively important only for velocities comparable to that of the Light, so that they become sensitive in the domain of atomic and nuclear physics. In 1907, Einstein applies the hypothesis of Planchk. about the discontinuity in the exchanges of energy and the specific heat of the solids, demonstrating that they decrease at low temperatures.
Einstein, begins his university career, teaching first in zürich, then in Prague and again in Zürich. From 1913 he devoted himself entirely to research; he only taught about his own theories, those that included increasingly disparate fields of physics. Between 1913 and 1933, Einstein lived in Germany, where he was appointed academic.
In 1913, he published his first report on the theory of relativity, which occupied him until the end of his days. A postulate of this theory is that natural laws must be invariable, not only with respect to transformations indicated by Lorentz, on inertial systems, but with respect to all kinds of coordinate transformations (movements and accelerations).
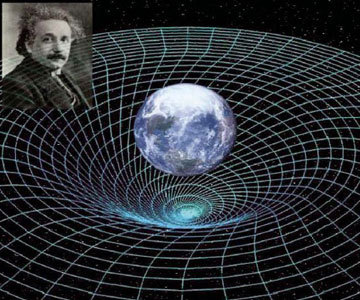
Another postulate is that a accelerated system is equivalent, in an infinitesimal region of space-time, to a gravitational field. According to this theory, space is not homogeneous and lacks structure, but has a curvature, which increases in the vicinity of the masses. The movement of a body in a field of gravitational forces is conceived as a generalized inertial movement.

Source
From the previous theory, Einstein deduced three effects susceptible of empirical verification: The redshift of the spectral lines emitted by the stars, the precession of the perihelion of Mercuryand the deviation of the light rays when passing through a field intense gravitation. These three effects were confirmed with great precision.
In 1921, Einstein began a triumphal tour through various countries of the world, and received all kinds of honors; in the same year he was awarded the Nobel Prize. Without neglecting his work on the theory of relativity. He continued to investigate among his studies we can mention: the atomic structure of matter and light. He deduced Planck's formula, on the distribution of blackbody energy, assuming that the diapers were Bohr atoms.
In 1950, Einstein believed he had realized the dream that had haunted him for more than thirty years, such as the construction of a unified theory of gravitational and electromagnetic fields "Geometric theory of classical fields" which he could not specify, however , the third theory of relativity, could be the formal development of what in itself, he wanted to achieve. Einstein's works produced radical and irreversible changes in almost all departments of physics. Planck called him the Copernicus of the twentieth century, for he remodeled the vision of the physical world, which in turn had important philosophical consequences.
Death of Albert Einstein
"Albert Einstein, dies the 76 years on April 18, 1955 in Princeton, New Jersey, the cause was the hemorrhage that caused the rupture of an abdominal aortic aneurysm.
Earlier, in 1948, Einstein had suffered severe abdominal pain, and Dr. Rudolph Nissen at the Jewish hospital in Brooklyn performed an exploratory laparostomy on December 31, before the surgical finding of an abdominal aortic aneurysm the size of a mandarin the surgeon proceeded to cover it with cellophane in order to reinforce the wall of the aorta (technique introduced by Rea that same year), by then there was no definitive technique to solve it. In 1951 Dubois performed the first successful replacement of aortic aneurysm with a lyophilized allograft. Among the background of Einstein were being a chain smoker and the death of his father due to myocardial infarction.
Einstein remained relatively asymptomatic for 6 and a half years, until in 1955 he began to experience vague abdominal pain. Three days later they became stronger, adding nausea and vomiting. His doctors proposed a new intervention given the suspicion of cholecystitis or a crack in the aneurysm. By the year of Einstein's death there were already techniques to repair his illness, however the experience was little. When not giving guarantees on the result of the surgery, Einstein rejected it saying the following sentence:
"I want to go when I want. It is bad taste to artificially prolong life. I've done my part, it's time to leave. I will do it with elegance."
Source
References:
https://www.biografiasyvidas.com/monografia/einstein/
https://manyworldstheory.com/2014/02/
http://teoriaderuedas.com/evolucion_de_la_materia/tercera_fase-interacciones/efecto_fotoelectrico_y_compton/
http://www.kids.csic.es/cientificos/einstein.html