Universe, new discoveries
The universe is one of the last frontiers, unexplored, by man, its vast size, and its dense darkness, provoke in those who fix their gaze on him, a feeling of curiosity, which leads them to investigate its mysteries, some scientists, they argue the theory that in itself, the universe, encloses our origin and our destiny, some think that we are not alone, and that we are not the center of everything, as most believe, the different missions that have left the planet earth, with In order to investigate that wonderful and dark place, they are the sample of how interested human beings are, for debunking the mysteries that are in that gigantic place.
Since the famous astronaut Neil Armstrong stepped on the moon for the first time on July 20, 1969, aboard the Apollo 11 spacecraft, scientists have been even more fascinated, to see that there is beyond, that curiosity has provoked that each day intensifies the search, either to know if there is extraterrestrial life or for some world similar to ours in which we can live, and it is precisely the second case in specific of what I want to talk to you.
Dear Steemians, in this opportunity, I want to tell you about the probes, telescope, and equipment that has reached to see all these worlds that scientists and every space dreamer wants to reach, I will also talk about the different worlds and systems that these devices have managed to unveil and they have amazed us that we have wished them that there is something more after heaven.
The Space Probe
A space probe is an artificial instrument that is sent into space to study the different bodies of the Solar System. Planets, satellites, asteroids or comets are the main targets of space probes. They are not manned, and they collect information they send to scientists on Earth.
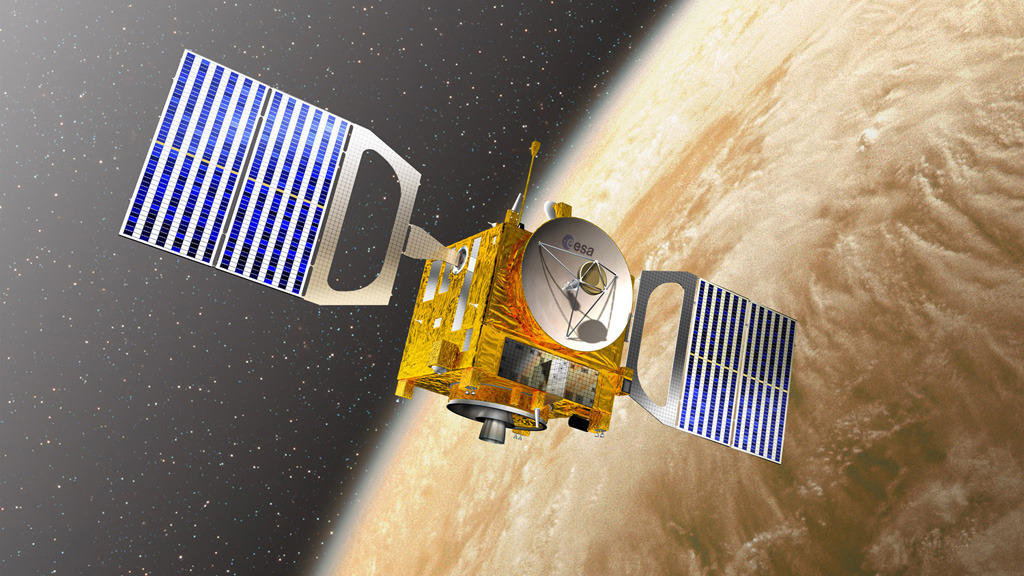

Space probes are also often referred to as artificial satellites. They differ from the latter in that they do not normally orbit around the objects they study. Most of the time they have trajectories of approach, although sometimes they are placed in orbit of a certain star. The probes are equipped with expensive photographic and filming systems, radars and sophisticated means of communication in contact with the Earth.
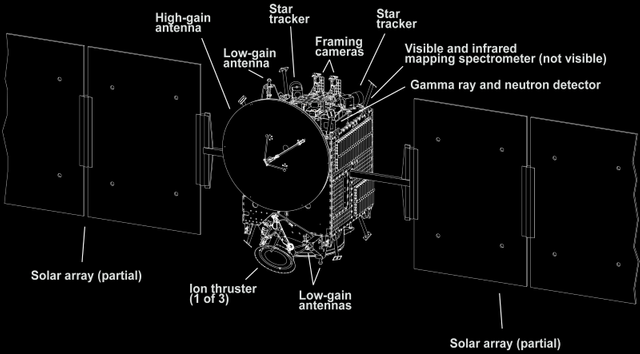
The space probes are always equipped with cinematographic cameras of observations that show us the object go aside from terrestrial atmospheric perturbations and in an inaccessible angle of sight with our eyes from the Earth and even from the Earth orbit. It is important to note the difference with artificial satellites, which they are destined only to be placed on Earth orbit.
However, certain probes are also destined to be put into orbit around other planets, planetary satellites or even around small asteroids. The United States largely dominates this domain of solar system exploration, by space probes. They send to 1964 the first space probe to Mars, then in 1972 to Jupiter, in 1973 to Saturn and Jupiter, and another to Mercury, in 1977 to Uranus and Neptune as well as Jupiter and Saturn. In the 20th century, only Pluto has not yet been subjected to a space probe exploration.
Parts of the Space probe
All the space probes are mounted on a support structure, to which at least these 3 systems must be incorporated:
Energetic System
Batteries, solar panels to provide electricity to the systems, although they can also incorporate radiative sources of energy.
Observation Instrument
Photographic cameras, or spectrum analyzers.
Communication equipment
It consists of different types of antennas and transmitters, to transmit information collected back to the earth.
Chemical composition
The space probes are made of a super resistant material, called Aluminum 7075.
The body of most of the space probes is made of this impressive material, the probe "New Horizons" is made in the
a form of a triangle, almost 0.76 meters (2.5 feet) thick.
Space satellites
Artificial Satellites. They are spacecraft manufactured on Earth and shipped in a launch vehicle, a type of rocket that sends a payload into outer space. Artificial satellites can orbit around moons, comets, asteroids, planets, stars or even galaxies. After its useful life, artificial satellites can remain orbiting as space junk.
.jpg)
A little bit of history about the Satellites
The artificial satellites were born during the Cold War, between the United States and the Soviet Union, which both intended to reach the moon and in turn launch a satellite into space orbit. In May 1946, the RAND Project presented the report Preliminary Design of Experimental World-Circling Spaceship, in which it was said that "A satellite vehicle with appropriate instrumentation may be one of the most powerful scientific tools of the twentieth century. The realization of a satellite ship would produce an impact comparable to the explosion of the atomic bomb ... ».

The space age began in 1946 when scientists began using the captured German V-2 rockets to make measurements of the atmosphere. Before that time, scientists used balloons that reached 30 km altitude and radio waves to study the ionosphere. From 1946 to 1952 the V-2 and Aerobee rockets were used for the investigation of the upper part of the atmosphere, which allowed measurements of pressure, density, and temperature to an altitude of 200 km.
The United States had considered launching orbital satellites since 1945 under the Navy Aeronautics Office. The RAND Project of the Air Force presented its report but it was not believed that the satellite was a potential military weapon, but rather a scientific, political and propaganda tool. In 1954, the Secretary of Defense said: "I know of no US satellite program."
Following pressure from the American Rocket Society (ARS), the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the International Geophysical Year, military interest increased and by early 1955 the Air Force and the Navy were working on the Orbiter Project, which would evolve to use a Jupiter-C rocket in the launch of a satellite named Explorer 1 on January 31, 1958.
On July 29, 1955, the White House announced that the United States would attempt to launch satellites beginning in the spring of 1958. This became the Vanguard Project. On July 31, the Soviets announced that they intended to launch a satellite in the fall of 1957.
Difference between probe and satellite
A satellite is any object that orbits around another, which is called the principal. Artificial satellites are spacecraft manufactured on Earth and shipped in a launch vehicle, a type of rocket that sends a payload into outer space. Artificial satellites can orbit around moons, comets, asteroids, planets, stars or even galaxies.
A space probe is a device that is sent to space in order to study bodies of our Solar System, such as planets, satellites, asteroids or comets.
Space probes are often also called artificial satellites, although, strictly speaking, a probe differs from a satellite in that it does not establish an orbit around an object (either the Earth or the Sun), but rather it is thrown towards an object concrete, or ends with an escape route to the outside of the solar system.
Samples obtained by the different probes and satellites
Cassini space probe
The main mission of the Cassini probe is the study of the planet Saturn, its ring system and its satellites. The launch was accompanied by the European descent probe Huygens that later landed on Titan, the largest satellite on the planet and the most interesting from the scientific and biological point of view of the entire Solar System. This project is the result of cooperation between the US space agency NASA and the European space agency ESA and is the largest project ever undertaken by both agencies. The ships were the best equipped and prepared for all launched until the launch date and were designed and built to minimize the possibility of component failure. The number of mechanical parts is negligible and most have been replaced by fixed elements that do not require mechanism since they are the ones that have the most failures.
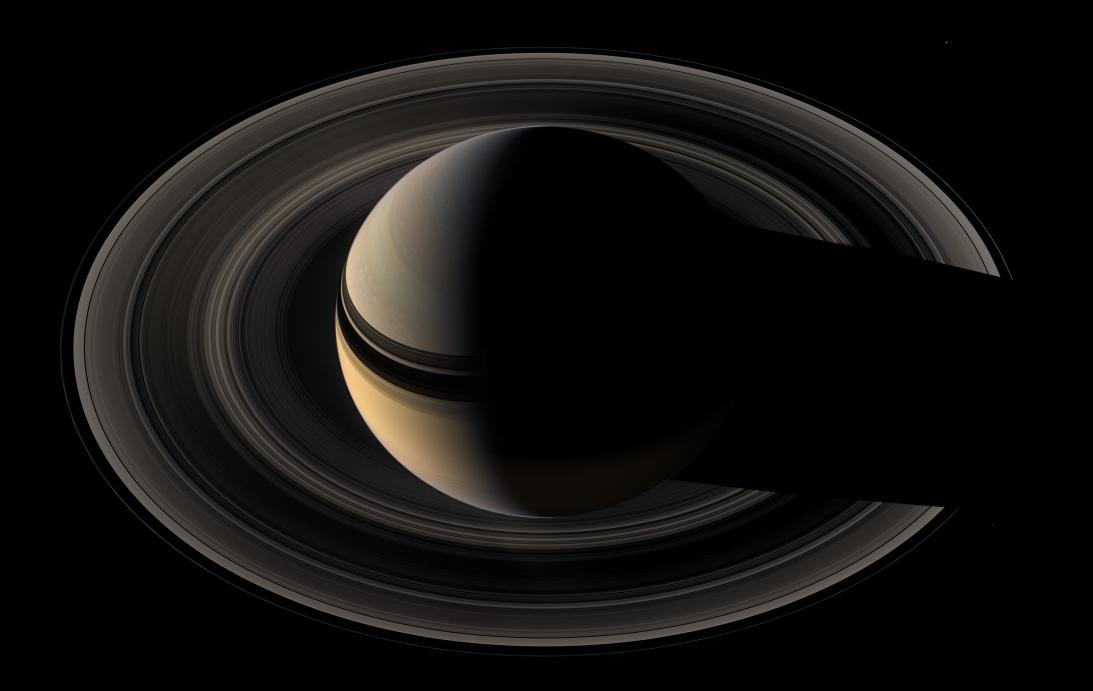

Saturn, between its rings. Cassini space probe
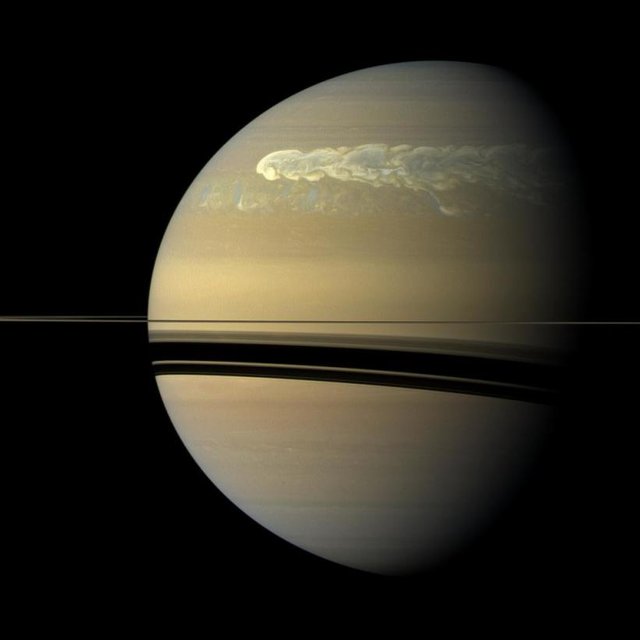

A huge storm in the northern hemisphere of Saturn appears in this true-color image. It was taken 12 weeks after the storm began, and the clouds at that moment had formed a tail that enveloped the planet. Cassini space probe
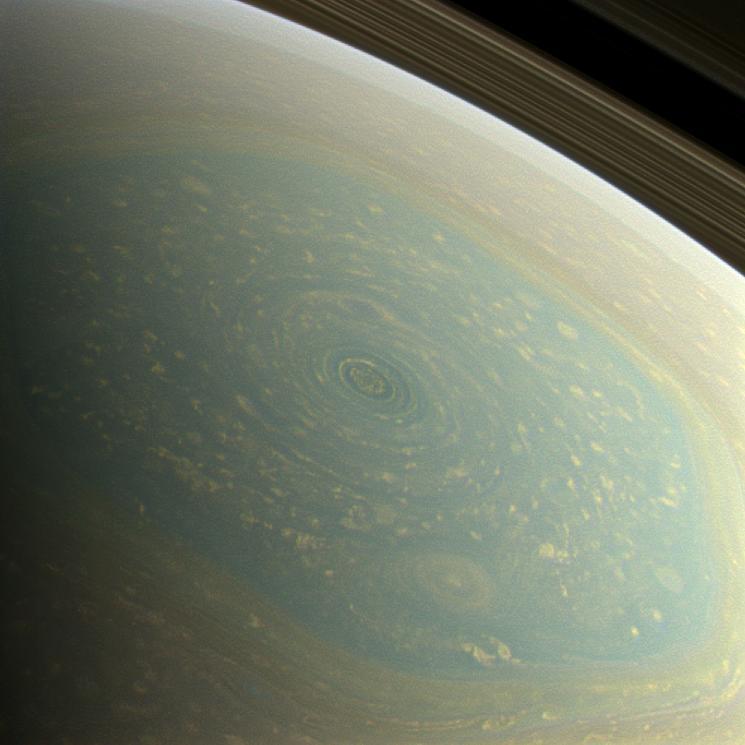

A storm similar to a hurricane surrounds the north pole of Saturn within the famous "hexagon," which scientists believe is a wandering jet stream that revolves around the north pole. Cassini space probe
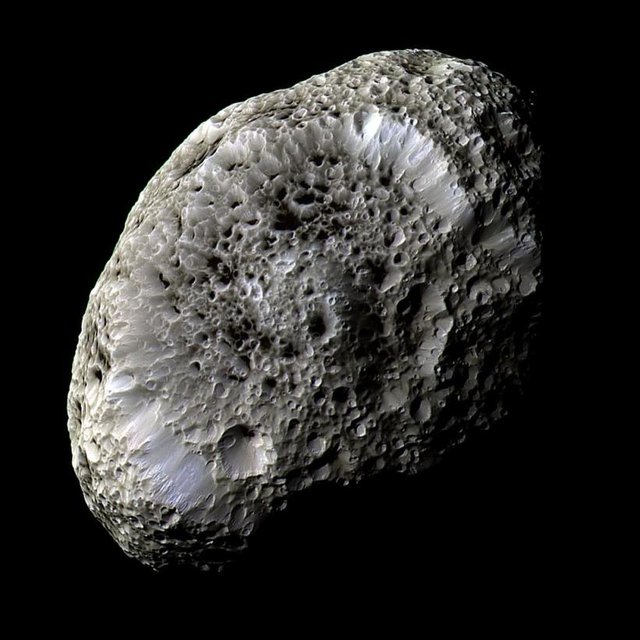
This stunning false-color view of Hyperion, a moon of Saturn, reveals details of the strange surface of the satellite. Cassini space probe
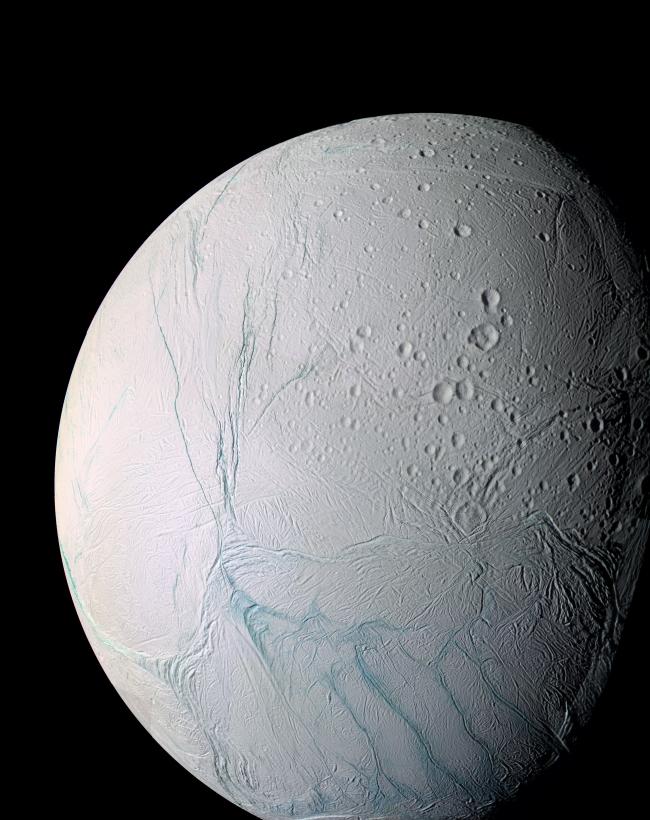

The tortured surface of Saturn's moon Enceladus and its fascinating geological activity tell the story of the past and present struggles of a small world.
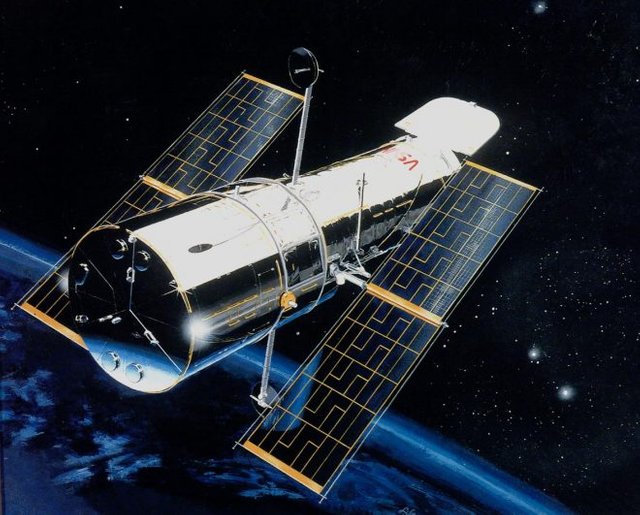
Space Telescope
A space observatory is a set of facilities designed to study, by capturing any type of electromagnetic wave, the stars, and galaxies of the universe. Space observatories are equipped with powerful and special telescopes capable of detecting different waves that come from space millions of light years away from Earth.

Kepler telescope
Kepler Space Telescope. Optical instrument located in the space designed to capture and study images of planets similar to the Earth to determine if life is possible in them.
The Kepler Space Telescope, also known as a Kepler probe, is an artificial satellite of NASA that orbits the sun since March 2009. It owes its name to the three laws that describe the characteristics of planetary orbits to the astronomer and mathematician Johannes Kepler. (1571-1630).
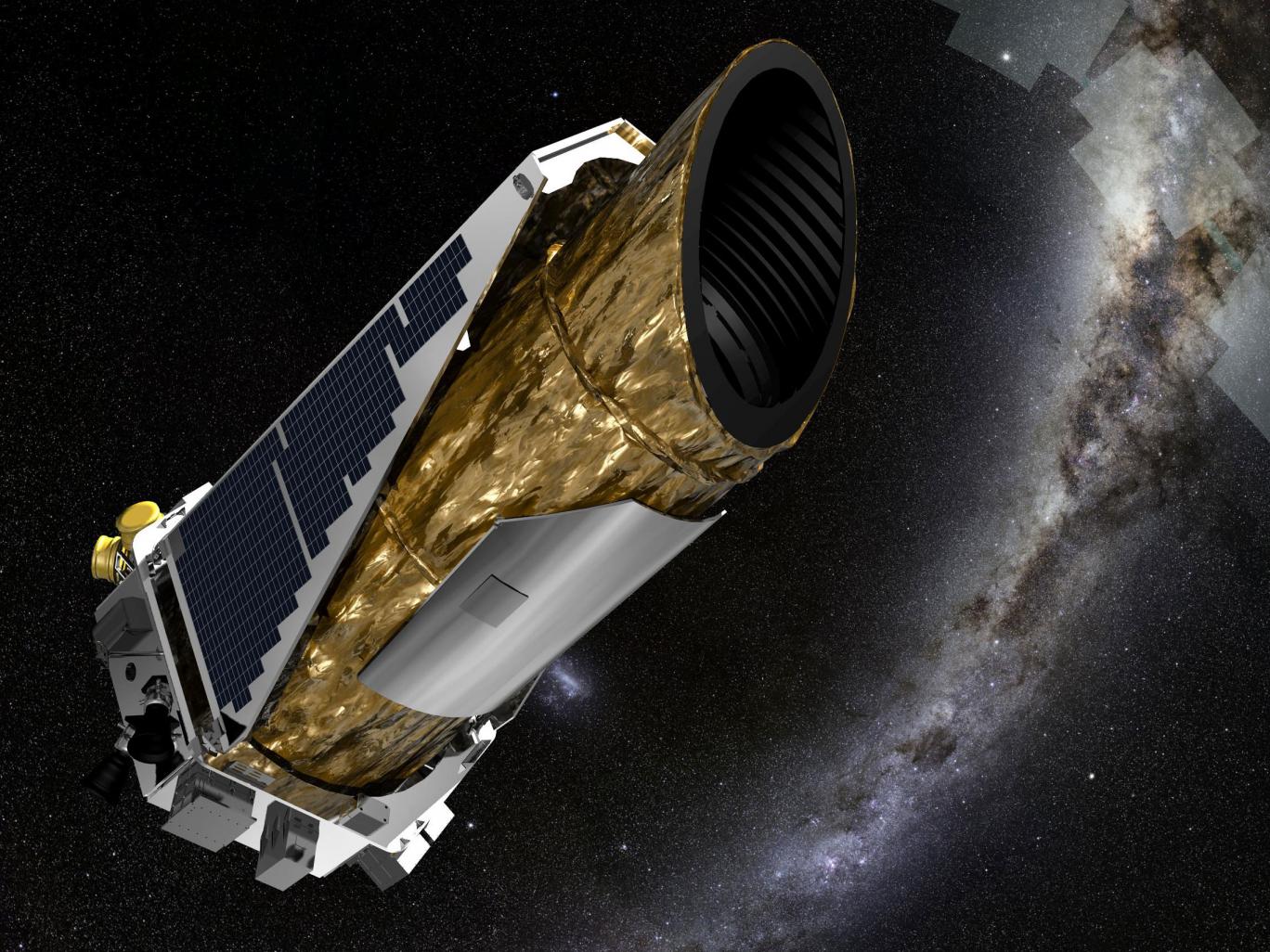

Located in an orbit that will perform in 371 days around the Sun in an elliptical way. It has been considered that optimal distance to maintain communications with the Earth and the companies LAST and Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., are in charge of controlling the ship from the research center of the University of Colorado in the United States. Its shape will make it possible for the telescope to avoid the dazzling brightness of celestial objects by looking for extrasolar planets, especially those of similar size to Earth, orbiting their star at a distance comparable to that of our planet.
The Kepler Space Telescope will focus on the area called Cygnus-Lyra, in the Milky Way, an area where it will observe more than 100,000 stars simultaneously and every 30 minutes. To know if there are planets and stars orbiting them from a composition and age very similar to the Sun.
It is about detecting changes in that light that are periodic (for days, months or years) and, therefore, indicate that a planet is orbiting around the star in question, which is called a method (planetary transit). "The size of the planet and its distance from the star is inferred from how much brightness the star removes and for how long."
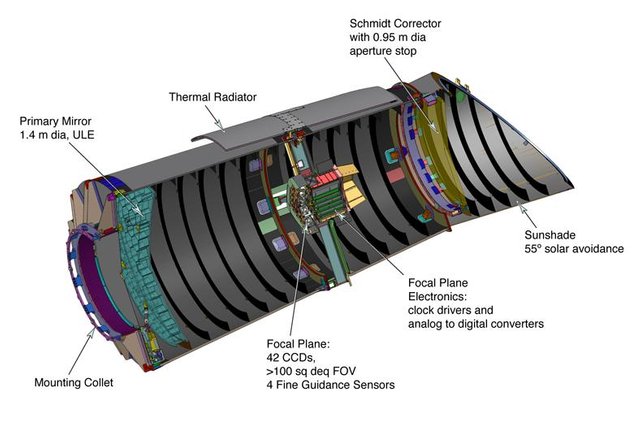
Parts and characteristics of Kepler
The telescope is mounted on a hexagonal aluminum structure occupying an approximate area of 12 square meters, with an approximate weight of 1 ton. It feeds 10 square meters of photovoltaic panels that generate 1kW of electrical energy and uses eight propellers that allow it to maneuver to change orientation when necessary.
For his work, he uses a sensitive Schmidt-type photometer of 0.95 m aperture and a primary mirror of 1.4 meters. It also has the most powerful CCD camera launched into space, which offers a resolution of 95 million pixels which allows viewing up to 3000 light years away.
Its useful life is determined by the estimated duration of the mission that is 3 and a half years, with a possible extension to 6 years.
Discoveries of Kepler
1.-The NASA satellite had its first discovery with the planet HAT-P-7b, which orbits around the star HAT-P-7, in the constellation Cygnus, 1000 light-years away.
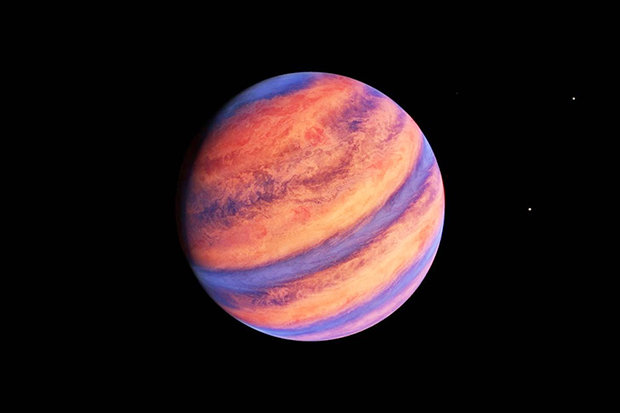

January 2010, Kepler discovered 5 new extrasolar planets: four of the hot Jupiter type, and one of the approximate size of Neptune.

December 2011, NASA announced that the number of candidates detected to date amounted to 2326. Of these, 207 would have a size similar to Earth, although only one (Kepler-22b) was confirmed.
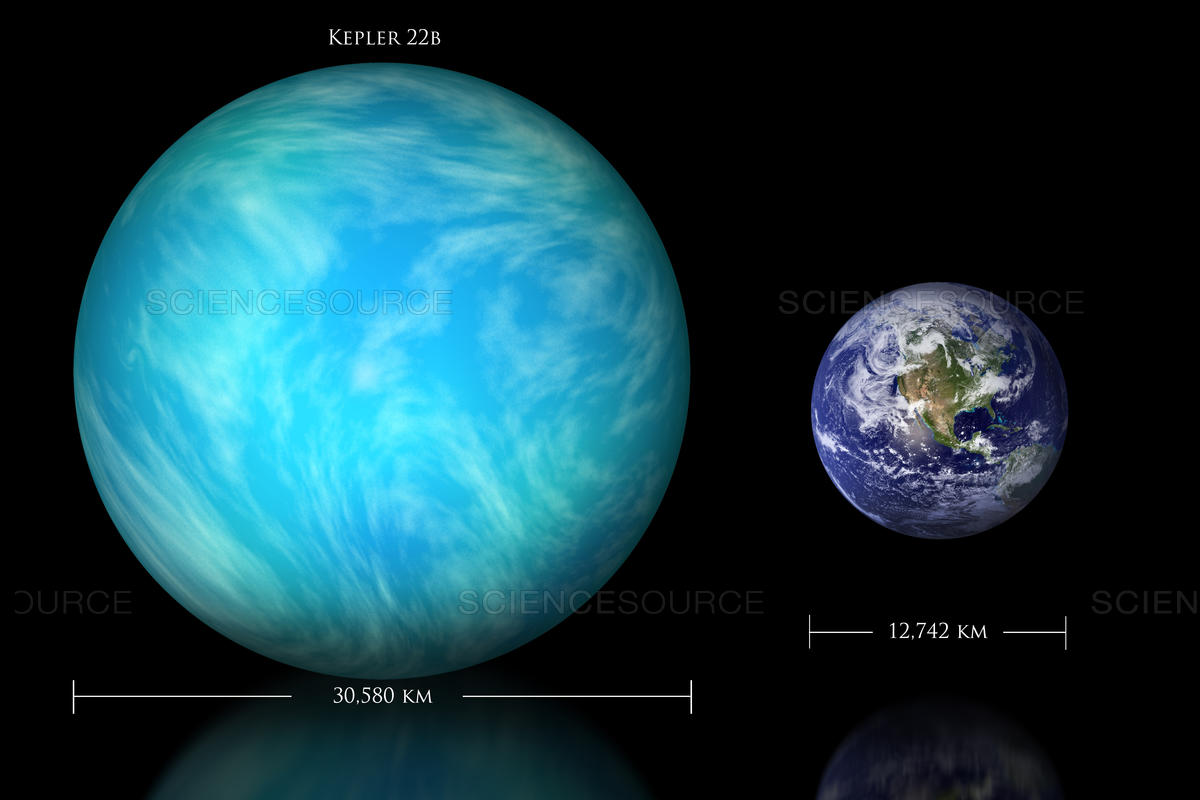

The Kepler space telescope confirmed the existence of 26 new exoplanets, all of them orbiting too close to their stars to house life and scattered across 11 planetary systems. Their temperatures would be too high for survival since they all orbit their stars closer than Venus, the second planet from the Sun, which has a surface temperature of 464 degrees Celsius.

In January 2012, NASA scientists announced that the Kepler satellite had found three tiny planets that had not been detected until then, orbiting a star. The planets were called KOI-961. The planetary catalog that Kepler elaborates will be very useful for good statistics and obtain a reliable estimate of the total number of planets similar to the Earth in the Milky Way.

Our universe is undoubtedly immense and it hides many secrets, the scientists are closer and closer to unveiling part of these mysteries, but the question still reigns, what is there beyond? Is there life in these worlds? For now there is a lot of questions to answer, as for example, in the case that some of these planets have life, how are we going to be able to reach them ?, we would have to start answering these questions and start evolving in our means of transport, how to support a so long ? or how to make an engine that can travel at speeds that allow distances are not a problem ?, there are a number of questions that arise at the time of just imagine that a planet that we have just seen sustain life
For more information visit this pages:
https://www.ecured.cu/Sat%C3%A9lite_artificial
https://www.univision.com/noticias/planeta/adios-cassini-las-mejores-imagenes-tomadas-por-la-sonda-antes-de-desintegrarse-en-la-atmosfera-de-saturno-fotos
http://enciclopedia.us.es/index.php/Observatorio_espacial
http://www.rtve.es/noticias/20170619/telescopio-kepler-localiza-otros-diez-planetas-candidatos-albergar-vida/1567240.shtml
Saludos amigo! de verdad muy interesante tu publicación. Me gusta mucho tu enfoque. Me parece interesante como la carrera espacial fue el resultado del posterior desarrollo de la tecnología nazi de Werner Von Braun con sus V2 y luego catapultada por la guerra fría entre Occidente y la URSS. Te felicito!