Signal Modulation and Demodulation
Telecommunication can be defined in a very simple term as the communication between two or more individuals that separated by significant distance(s). Telecommunication is a field with very rapid evolution and a very old history. Though some villages in Nigeria still uses smoke signals and gong to disseminate information to many individuals that a far apart, the reality as of today is that telecommunication is one of the most complex and advanced technology.
[credit: wikimedia. CCv3.0 license. Author: unknown]
Naturally occurring signals are analog in nature and in my previous post on signals and systems, I discussed about how to convert signals between machine readable signals and signals humans can process. The field of telecommunication and electronic communication cannot be complete without modulating and demodulating signals. So what then is modulation and demodulation?
Wikipedia defined modulation as the process of changing the properties of time varying signal known as the carrier signal (usually high frequency signals) with another signal known as the modulating signal (usually very low frequency signals). Most of us make us of postal services to deliver our parcels or just our letter from us to whoever we're sending the letter or parcel to. The process of using the postal services first involves inserting our letter or parcel into an envelop or a container which will later act as an identifier to the letter it contains.
The main purpose of the envelop is to protect the letter as it is on transit. Nearly the same thing happens during modulation. The carrier signal just like the name implies is the envelope that carries the signal while the modulating signal is the signal that contains the actual or needed information.
During the process of demodulation, the modulating signal (message signal) which contains our signal of interest is extracted from the carrier signal. The most popular form of modulation is the frequency modulation and amplitude modulation which are widely used in normal radio broadcasting services known simply as FM and AM. A very popular carrier signal is the sinusoid which contain three parameters known as the frequency, phase and magnitude or simply amplitude.
Why do we need to modulate our communication signals during transmission?
Demodulation is as a result of modulation, hence without modulation, there wont be need for demodulation but to put us through in simple terms why we go through the troubles I will state below just to modulate and demodulate our signals, the reasons are of three categories;
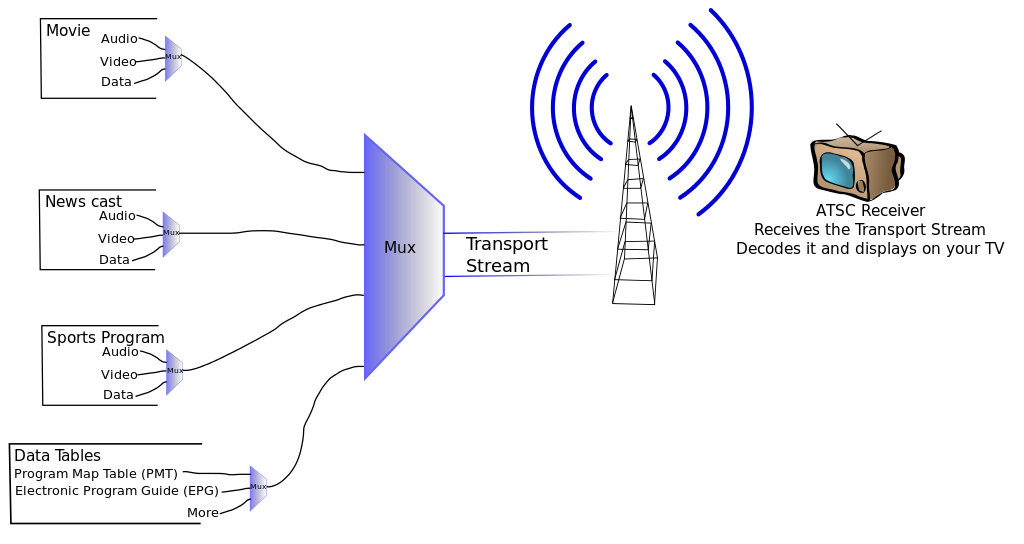
The first reason is to improve transmission distance. If you're asked to throw a piece of A4 paper to a distance of say 100 meters, folding the paper will get you to a reasonable distance but the smartest option would be to increase the weight of the paper or insert the paper in a heavier material before making attempt at throwing the paper. By modulating and demodulating our communication signal, we're able to transmit information to a greater distance.
[credit: wikimedia. CC3.0 license. Author: Tiger66]
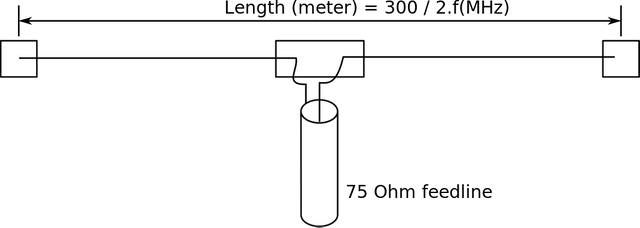
The second reason for modulating signals is to cut down on the size of transmission and reception antennas. A signal with very low frequency would require a big antenna to transmit it to its destination. Practically, when choosing antenna for transmissions of signal, a suitable antenna is one with length of about one tenth of wavelength of desired signal. By modulation, we increase the frequency of the target signal thereby requiring smaller antennas for transmission.
Finally, modulation allows us to make the most out of available transmission channel. For instance, consider a channel made up of band pass filter which allows signals of certain frequency to pass, without shifting our signal of interest to this particular allowed frequency, transmission would be impossible. By modulating signals that were not initially up to a transmission frequency into a transmissible frequency, many signals can be transmitted simultaneously over the same channel leveraging on different frequency ranges.
Signal Modulation
There are basically two broad method of signal modulation which are Digital and Analog Modulation methods. Modulation as defined earlier is the process of changing the properties of a carrier signal with respect to target signal or message signal. During analog modulation, the carrier signal is a sinusoid giving us three different component for changing the carrier signal, mathematically, the general sinusoidal function is given as:
f(t) = Acos(2πft +ϕ)
where A is the amplitude component of the equation
f is the frequency component of the equation and
ϕ is the phase component of the equation.
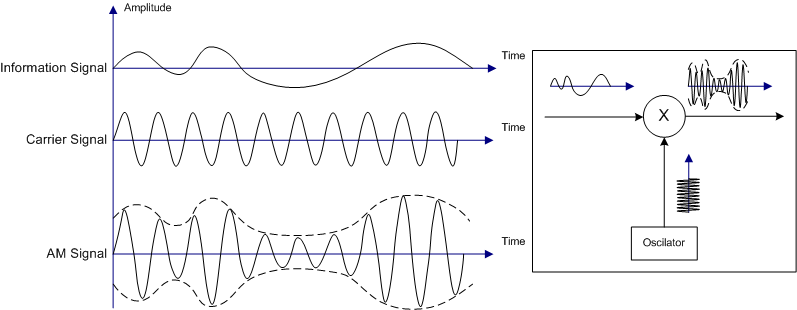
[An amplitude modulated signal. Credit: wikimedia. CC3.0 license. Author: Ivan Akira]
In amplitude modulation, the phase component and frequency component of the carrier signal is kept constant while the amplitude varies. Amplitude modulation is the oldest form of modulation and is used mostly in voice and radio systems. It is widely used in very high frequency aircraft radio systems and also in commercial modems. Filtering amplitude modulated signals are always very difficult and modulation requires higher energy and bandwidth.
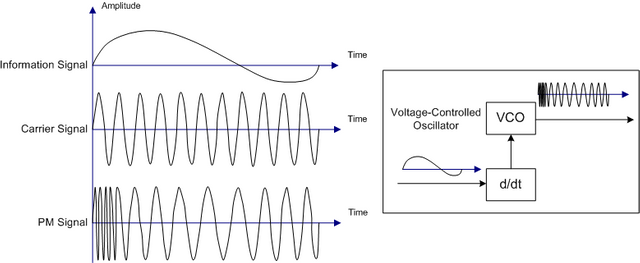
[A phase modulated signal. Credit: wikimedia. CC3.0 license. Author: Ivan Akira]
In phase modulation, the message signal is encoded into the carrier signal by changing the real-valued component of phase of the carrier signal also known as the instantaneous phase of the carrier wave. When the phase component of the carrier signal is varied, the frequency component also changes which makes some people classified both frequency modulation and phase modulation as angular modulation. Phase modulations are not just applied in voice signal transmission but also in data transmissions like the satellite and general system for mobile communication.
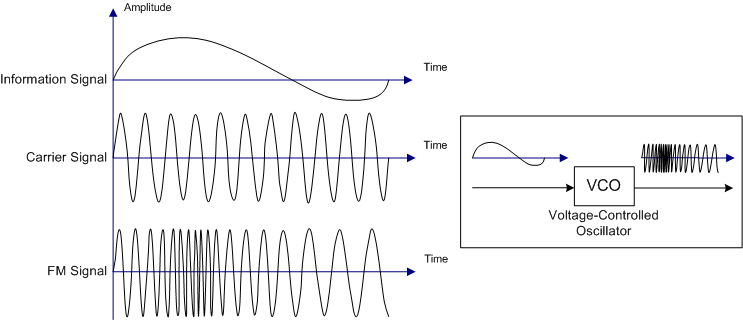
[A frequency modulated signal. Credit: wikimedia. CC3.0 license. Author: Ivan Akira]
In frequency modulation, the phase and the amplitude component of the carrier signal are kept constant with only the frequency changing with respect to the message signal. Some of us at one point or is currently tuned to a radio station or made us of car MP3 set which makes us of FM for transmitting voice signals. It is also applied in EEG which is use to monitor the electrical activities in the brains of newborn babies.
Digital Modulation.
Generally, digital signals are less susceptible to noise and very easy to reproduce. In digital modulation, modulation is done in form of keying. When shaping a carrier signal in order to convey a digital message signal, keying is the act of representing digital message in an analog waveform. Hence digital modulation helps us to convey digital information (which are in the form of streams of bits) using a analog channel, allowing us to transmit the resulting signal from a digital circuit like our cell phones across a physical medium (like air).
There are three major techniques of digital modulation, these are;
There are other digital modulation techniques like the quadrature shift keying, the continuous phase modulation, the spread-spectrum modulation, and many more but a grasp of the above three basic modulation techniques ensures the understanding of other modulation techniques which are subset of the basic techniques.
))
[An FSK credit: wikimedia CC3.0 license. Author: Demm]
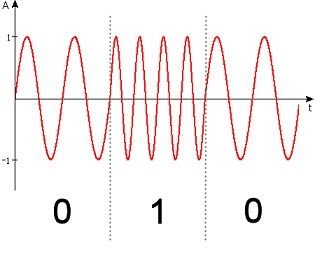
In frequency shift keying, the digital input signal (message signal) which is discrete in form (containing values of either zero (0) or one (1)) are represented in analog form by having the logic 1 represented by analog signal (like the sinusoid) at certain frequency and the logic 0 represented by the same analog signal but at different frequency.
An example of a system that makes use of frequency shift keying (FSK) in its data operations is the tiny computer modem which converts its bit streams into analog form using the FSK and then transmits this analog signal to the nearest base station which then performs demodulation and extracts the message signal and carries out other require processing or encoding.
In amplitude shift keying, the amplitude of the carrier wave is made to change instantaneously with respect to the message signal. Here, each discrete message signal has a matching amplitude in the carrier wave. Though this type of modulation is characterized by a good noise resistance (which it inherited from its analog counterpart), it is rarely used in reality because compared other digital modulation technique, its noise to signal ratio is low.
Lastly on the digital modulation technique, the phase modulation shift keying (PSK) is based on varying the phase of a carrier wave to represent the digital logic of a message signal. The PSK is further divided into quadrature phase shift keying and binary phase shift keying.
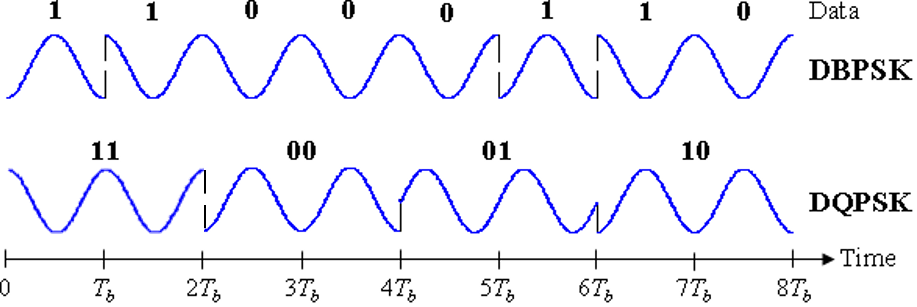
[Binary phase shift keying (top) and quadrature phase shift keying (buttom). credit: wikimedia. CC4.0 license. Authour: Salty Orange]
The binary phase shift keying is the simplest form of PSK in which two bits of a message signal is represented using two phases of carrier wave. Quadrature phase shift keying functions just like the binary phase shift keying but this time, the two binary bits of digital message signal are encoded using four phases of the carrier signal.
Demodulation
Demodulation is the opposite of modulation. Here, the message signal is extracted from the carrier signal, but further signal processing like amplification and filtering are required to extract information that is reasonably noise free. Just like there are many types and techniques of modulation, there are also many types of demodulators which are basically a program or a circuit which can extract information from a carrier wave. The output of a demodulator can be anything ranging from raw information (data), acoustic signals and video/image signal.
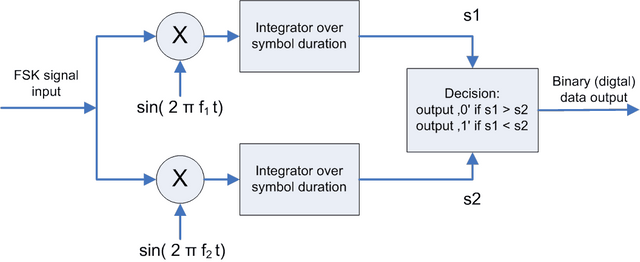
[A block diagram of a typical FSK demodulator. Credit: wikimedia. CC3.0 license. Author: wdwd]
When a particular technique is used to encode information to a carrier signal, usually a reverse operation is required at the demodulating end to either extract the message signal or cancel out the carrier signal leaving behind, the message signal. For example, a linearly modulated carrier signal would require a synchronous demodulator at the receiving end of the channel to extract the message signal.
Summary
Without modulation and demodulation, wireless communications won't be a reality because digital signal cannot directly make use of air-interface.
))
[credit: wikimedia CC3.0 license. Author: .Prolineserver]
Also most transmitted signals are very weak and cannot travel far on its own, thereby for a signal to safely land at its required destination, the message signal can be wrapped in another "stronger" (carrier) signal which can then transmit it to the required destination, this process is known as modulation.
At the receiving end, the message signal is extracted from the carrier signal in a process known as demodulation.
A good example of a device that constantly performs these operations is the popular electronic piece called "modem" which is a short form of modulation-demodulation and its activities are as described in this post.
REFERENCES
- Modulation -wikipedia
- Demodulation -wikipedia
- Phase modulation -wikipedia
- Amplitude modulation -wikipedia
- Frequency modulation -wikipedia
- FSK modulation and demodulation -elprocu
- Amplitude shift keying -technoeverywhere
- Phase shift keying -tutorialspoint
If you write STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) related posts, consider joining #steemSTEM on steemit chat or discord here. If you are from Nigeria, you may want to include the #stemng tag in your post. You can visit this blog by @stemng for more details. You can also check this blog post by @steemstem here and this guidelines here for help on how to be a member of @steemstem.

I you.
you.
@henrychidiebere, you are rightly on point and always consistent in dropping quality posts.
Well done bro
High chief I greet you sir😅. I try my best to follow the footsteps of great guys like you. I feel my posts don't even measure up but I'll keep getting better. Thanks for stopping by.
Disorienting and reorienting me to a devastating effect on modulation and demodulation of signals.
Nice one bro.
This post brings back many memories! 😀
Happy I could offset some balance 😂
Nice explanation @henrychidiebere. Can you explain about VCO?
A voltage controlled oscillator is a type of oscillator whose output signal is controlled by an input voltage. Generally oscillators are active electronic circuits which produces varying electrical signals.
Thanks @henrychidiebere
I will upvote and resteem your last blog post to my 36,000+ followers for free if you reply to this comment. Follow @a-0-0
Congratulations! this post got an upvote by @steemrepo and was manually picked by the curator @horpey to be added on STEEM REPOSITORY. Simply comment "YES" and we upload it on STEEM REPO website.