Heat transfer by radiation through the processes of conduction and convection
Heat transfer is the passage of energy from a body at a higher temperature to one at a lower temperature and takes places by conduction, convection and radiation although evaporation and condensation may play a vital role. In the case of transfer of heat by conduction, heat diffuses through matter from one end of a body to another without a relative motion of the components of the body. During conduction, the molecules vibrate about their mean equilibrium positions with higher frequencies. This vibration is transferred to the nearest neighbours and heat is transferred from one point to another without the movement of the bulk parts of the body.
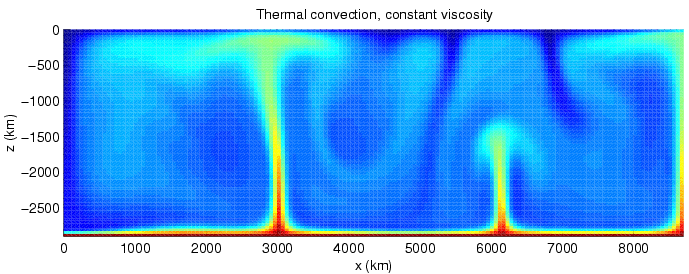
wikipedia: Thermal convection, constant viscosity
Heat transfer by convection, parts of the body responsible for the transfer actually move from the source of heat in order to transport the heat to cooler parts of the body and this means that convection takes place in fluids. The molecules of fluid in close contact with source of heat become less dense as they acquire extra energy. Then the cooler denser parts of the fluid replace the hotter less dense parts. These hotter, less dense parts move away to occupy the space left by the cold denser parts of the fluid. This process continues with the colder denser parts getting heated in turn and giving way for the denser and less hot parts of the fluid. Thus convection currents ensue in the fluid and heat energy is steadily transferred from the heat source to colder parts of the body.
Radiation is a heat transfer that can also take places when the heat travels in free space or vaccuum. Heat transfer in this case is similar to the propagation of electromagnetic radiation through space.
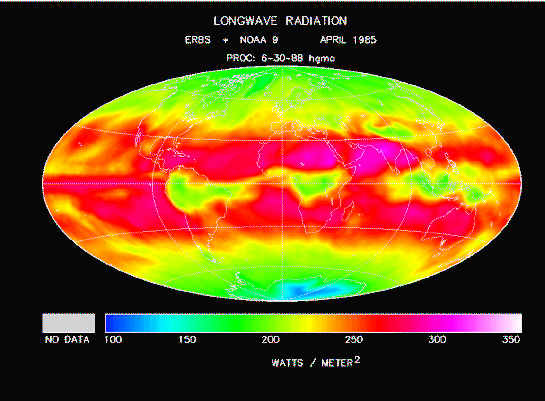
Wikipedia:Earth's long wave thermal radiation intensity
CONDUCTION OF HEAT THROUGH LONGITUDINAL AND LATERAL
In determination of conductivity of a material heat losses are reduced along the directions where measurements are not made.The process of reducing heat losses is known as lagging. In a case of unlagged bar, some of the heat supplied is conducted through the sides of the bar and the temperature along the bar falls rapidly with distance. But in a lagged bar, conduction is just along the length of the bar and in a steady state all the heat supplied is conducted along the bar. Also unlagged bar is associated with longitudinal conduction only.
CONVECTION
Convection refers to transfer of fluids brought about by the actual movement of those masses of the fluid which, being warm by contact with the heat source, expand and so rise through the body of the fluid due to reduction in density. There is an in flow of colder of colder fluid to take the place of the rising heated masses, and the circulating movement so established is referred to as a convection current. And convection occurs in two phases natural and forced convection and Natural convection from a wall.
NATURAL AND FORCED CONVECTION
the molecules of the fluid are set in motion by the gradient in the densities of different sections of the fluid due to the existence of a temperature gradient. For instance the density of the fluid closest to the hot body is less than the density of the fluid far from the hot body. In this regard, if the hot and the cold ends are so oriented that gravitational equilibrium is disturbed, then convection currents could be set up. In forced convection, a convection current is set up in the fluid by a density gradient in the fluid. The fluid is set in motion by some external applied agent. For instance as we blow over a hot body to cool, we force the air around the hot body to move away and colder air takes its place.
Wikipedia: Forced convection by a fan in a snow machine
NATURAL CONVECTION FROM A WALL
in consideration of a fluid contact with a wall whose temperature is higher than that of the main body of the fluid, experiments show that though the fluid may be in continuous motion, a thin film exists which remains in permanent contact with the wall. The thickness of this film depends on the nature of the wall and fluid.Therefore, Heat transfer through the fluid is by conduction through this film of fluid, and then by convection.
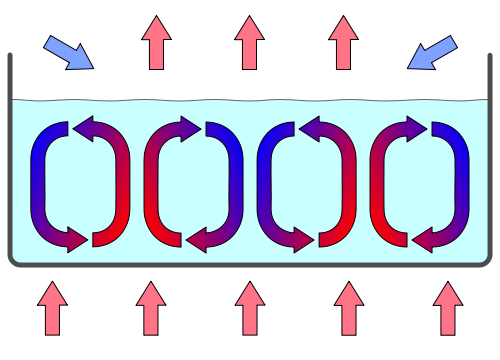
wikipedia: Convection cells in a gravity field
RADIATION AND RADIANT ENERGY
Heat from the sun travels through vast distances of empty space before reaching the earth. Radiant heat therefore can be transmitted through a vacuum, or through an intervening material medium without affecting the temperature of the medium. Radiant energy and light are closely related. Actually, radiant energy has the same nature as light. The similarities between radiant energy and light suggest that the mode of generation and transmission are the same, and both forms of radiations are propagated by transverse waves in the electromagnetic waves. The only difference between them is their wavelengths.
DETECTION OF RADIANT ENERGY
radiant energy can be detected with an instrument known as thermopile which depends on the change in e.m.f of a circuit when radiant energy falls on a blackened junction. The thermopile consists of a number of thermocouples connected in series. One set of junctions of the thermocouples is covered with lamp black and can be exposed to radiant energy. The other set of junctions is shielded from all radiant energy. A metal cone screens the sensitive set of junctions from all radiation except those lying within the angle of the cone. When radiant heat falls on the sensitive set of junctions the e.m.f produced may be measured by a sensitive galvanometer or a potentiometer, providing a measure of the radiant energy contained in the radiation.
wikipedia: Sunlight carries radiant energy
BLACK BODY AND THERMAL RADIATION
black body as a body which absorbs all the radiations of every wavelength falling on it. Black body is often referred to as a full radiator and a good emitter. Thermal radiation in the other hand refers toss energy that travels as electromagnetic waves, having been produced by a source because of its temperature. In a case of thermal radiation it's major component is usually infra-red radiation but light and ultraviolet may also be present. This is regarded as heat because it is energy in the process of transfer.
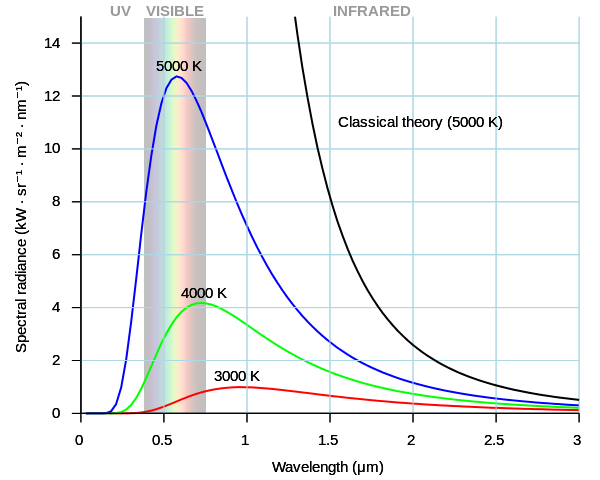
wikipedia:black body radiation
REFERENCES
what is heat?
wikipedia:heat transfer
Wikipedia : Heat transfer coefficient
wikipedia:Convective heat transfer
Thermal conduction
Thank you for stopping by

well put together article
Thank you