The Organization Procariota // Cellular Theory

Mattias Schleiden ( 1804-1881),source of image of mastery of wikimedia commons
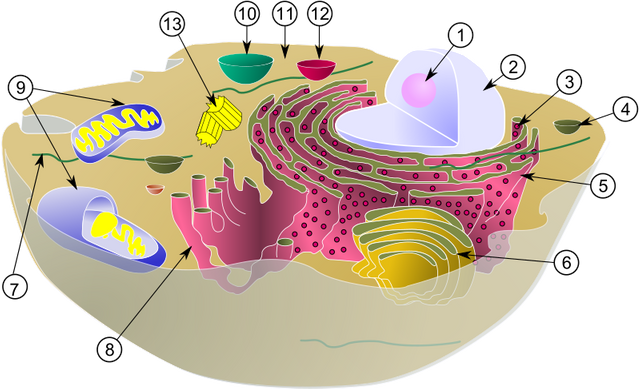
two types Exist cells, which it differs according to his complexity: the cells procariotas, simpler and the cells eucariotas, one believes that it is the first one as counterfoil that they gave for evolution to the second, the term procariota, that it means before of the nucleus, is used to define those cells in, that the genetic material is not structured isolated of rest of dela cells by an eucariota the remaining cells. For the opposite the term eucariota means built well nucleus and is used to describe cellular, the majority of the cells procariotas present a covering or cellular wall, which wraps it forming for a complex called molecule mureína, in contrast to the cellular wall of the vegetable cells eucariotas, which is formed by celluloses.
The principal system of division used by the procariotas is the bidivision, process in which, using a cell mother forms two cells genetically equal daughters, thinking that also the cells procariotas can trasferir genetic material from one to other one, but they never present the division mitótica.
The cells eucariotas have orgánulos exclusive, the device of Golgi, the nucléolo, the reticulum endoplasmástico and the lisosomas. The group of the organisms procariotas is formed by the bacteria and the cianofíceas, also call cianobacterias or seaweed procariotas.
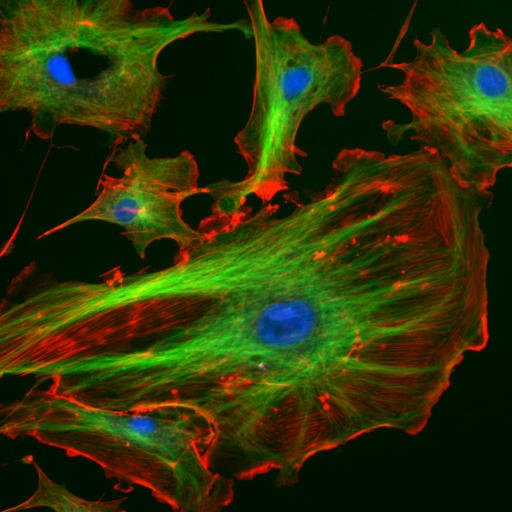
Cells endoteliales under the microscope. The nuclei are dyed of blue with DAPI, the microtúbidos are marked with green color with an antibody joined FITC and the filaments of actina are marked of red with the faloidina joined TRITC. Cells endoteliales of the pulmonary bovine artery, source of image of mastery of wikimedia commons
recent Discoveries make to think, that one can subdivide the bacteria in two groups: the archaic bacteria and the eubacterias, you differentiate it it is based that the cellular wall of the archaic bacteria is not presented by you mureína, the absence of this one molecules, it is of point of view filogenético, of such importance, that they consider to the archaic bacteria like the only ones, representatives of a group independent from the rest of the procariotas.
Also we have the cianofíceas they differ from the bacteria for presenting the aptitude to realize the photosynthesis, the cells procariotas to thinking about his simplicity, have considered throughout the time due to his efficacy. The later appearance of the organism eucariotas did not mean the disappearance of the procariotas, since they could occupy these of form more specializing in the ambiences from the eucariotas they they cannot compete, the test of them is that the procariotas, even if 2000 million years have appeared before the eucariotas cells, are still the alive organisms more abundant in the ground.
Realizing well that two types of cells exist: the procariotas and the eucariotas, where the cells procariotas has no nucleus and in the eucariotas, on the other hand one distinguishes two zones, the nucleus and the citoplasma, separated by the nuclear membranes.
It important that all is cells, structures are surrounded by one as: the membranes plasmatic, formed for lípidos and proteins, it is membranes is permeable and it has the function to regulate the entry and exit of the water and other substances of the cells. In the majorities of the vegetable cells so-called cellular primary wall observes a cellulose covering, which surrounds the plasmatic membrane.
The citoplasma is limited externally by the plasmatic membrane and internally, by the nuclear membrane, the citoplasma that the orgánulos surround calls citosol, it is formed by water, proteins, different types of ribonucleic acids, sweeten, amino acids. The principal orgánulos citoplasmáticos are the reticulum endoplasmástico, the device of Golgi, the lisosomas, the peroxisomas, the mitocondrias, cloroplastos.
The nucleus of the cells eucariotas is placed by the common thing in the center of the cells, most of the cells has only one nucleus, although in some types cellular they can be in major number and the nucleus consists of nuclear membrane, genetic material, nucleoplasma and several nucléolos.
Source Bibliographical.
Cellular biology for Marc Maillet - 2002.
Biology the IIIrd. The codes of the life for David Aljanati - 2004.