Plant stress
Plant stresses are the environmental effects that decreases plants growth and development, it implies the adverse effect on the physiology of plant which makes it exhibit one or more metabolic disorder.
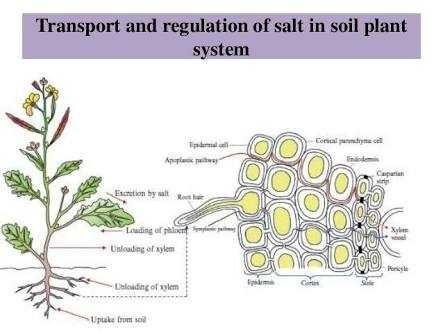 )
)
Source
Allelochemicals and Salinity are abiotic stresses that affect the physiological and biochemical nature of plant, thereby affecting the growth, and survival of crops.
ALLELOCHEMICALS
Allelochemicals are secondary metabolites, which are not required for metabolism (i.e. growth, development and reproduction) of the allelopathic organism. Allelochemicals with negative allelopathic effects are an important part of plant defense against herbivory.
- Allelopathy: Allelopathy is a biological phenomenon where one plant inhibits the growth of another through the release of allelochemicals.
Plant Sources of Allelochemicals.
Rice (1984) and Putnam (1988) observed that allelochemicals are released from the plant roots, rhizomes, stems, leaves, flowers, inflorescence, pollen, fruits and seeds of many plants.
COMMON PLANTS ALLELOCHEMICALS ;
Phenols;
Alkaloids;
Tannins;
Sabronins
Flavournoids
Glycoside
Resins.
Salinity
Salinity is the increase in soil salt content.
Soil salinization is one of the major factors of soil degradation.
Salt stress in soil or water is one of the major abiotic stresses which can severely limit plant growth and yield.
SALINITY AND ALLELOCHEMICALS STRESS ON PHOTOSYNTHESIS, ENZYMES, RESPIRATION AND HOMEOSTATIS.
Salt stress can break down chlorophyll (Chl), the effect ascribed to increased level of the toxic cation, Na+ (Pinheiro et al. 2008, Li et al. 2010,Yang et al. 2011).
Stomata closure in response to salinity stress generally occurs due to decreased leaf turgor and atmospheric vapor pressure along with root-generated chemical signals (Chaves et al.2009).
Allelochemicals exhibit a wide range of mechanisms of action, from effects of alkaloids on DNA, quinones, photosynthetic and mitochondrial function, phenolics on phytohormone activity, ion uptake, and water balance According to Zeng, et al. (2001)
PHYSIOLOGICAL AND BIOCHEMICAL EFFECTS OF PLANTS TO SALINITY
- Plants display shoot growth inhibition during the first phase of salt stress, partly due to a loss of cell wall extensibility.
- Salt stress can lead to stomatal closure, which reduces CO2 availability in the leaves and inhibits carbon fixation, exposing chloroplasts to excessive excitation energy, which in turn could increase the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROSs) and induce oxidative stress (Parida and Das 2005, Parvaiz and Satyawati 2008).
- Salt stress has been shown to impact secondary cell wall formation and structure, as revealed by an altered lignin biosynthesis. Salt treatment increased root lignification and the number of lignified vessels.
SYMPTOMS OF SALT AND ALLELOCHEMICALS STRESSED PLANT
- Poor germination, especially if a soil drench was used.
- Death of seedlings.
- Death of rapidly growing succulent tissues
- Stunting or delayed plant development.
- Misshaped or distorted plants, fruits, or leaves.
- Russeting or bronzing of leaves or fruit.
- Dead spots or flecks on leaves.
- Dead leaf tips or leaf margins.
- Dead areas between the veins of the leaves.
MECHANISM OF PLANT TOLERANCE TO ALLELOCHEMICALS
Plants can employ two general strategies to defend themselves against allelochemicals; they can either reduce the amount of damage they experience (I.e resistance), or they can tolerate the allelochemicals damage.
all chemicals undergo processes such as retention, transport, and transformation, which, in turn, influence their phytotoxic levels (Cheng, 1995). Phytotoxicity of allelochemicals therefore depends on their concentration, movement, fate, and persistence in the soil.
MECHANISM OF TOLERANCE TO SALT STRESS
Osmotic and ionic effects and also the different plant species have developed different mechanisms to cope with the inhibition of salinity of plant growth (Munns, 2002).
The osmotic adjustment, i. e., reduction of cellular osmotic potential by net solute accumulation, has been considered an important mechanism to salt and drought tolerance in plants.
The osmotic adjustment in both roots and leaves contribute to the maintenance of water uptake and cell turgor, allowing physiological processes, such as stomatal opening, photosynthesis, and cell expansion (Serraj and Sinclair, 2002).
ROLE OF BIOTECHNOLOGY TO SALT AND ALLELOCHEMICALS STRESS ON PLANT
Stress induces production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) including superoxide radicals, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and hydroxyl radicals (OH-) and these ROS cause oxidative damage to different cellular components including membrane lipids, protein and nucleic acids (Halliwell and Gutteridge, 1986).
Reduction of oxidative damage could provide enhanced plant resistance to salt stress. Plants use antioxidants such reduced glutathione (GSH) and different enzymes such as superoxide dismutases (SOD), CAT, APX, glutathione-S-transferases (GST) and glutathione peroxidases (GPX) to scavenge ROS.
Biotechnology could be adapted to introduce some antioxidants genes into the plants to reduce oxidants ROS.
To overcome salinity effects, scientists are also using transgenic approaches to obtain genetically modified plants (Ashraf & Akramet al.) .
These approaches include: Increased ROS-scavenging enzymes SOD, POD, CAT and PAL in plants suggest the tolerance capacity of the plant to protect themselves from oxidative damage.
The use of soil bacteria in protecting plants against salinity and Allelochemicals stresses -Rhizosphere microorganisms, particularly beneficial bacteria and fungi, can improve plant performance under stress environments and, consequently, enhance yield both directly and indirectly (Dimkpa et al., 2009a).
Biotechnology can be adapted to produce more of the soil bacteria/fungi which can be genetically modified to reduce the effect of stress on a wide range of of crops.
Modulation of other major plant hormones could improve crop salt tolerance by reducing the toxic effects of salinity (Bianco & Defez, 2009).Over 95% of the Earth plant species.. Generally, C4 and CAM plants are the best adapted to arid environments, because they have higher water-use efficiency (WUE) than that of C3 plants. C4 plants have higher photosynthetic efficiency than C3 plants.
Two approaches are currently used to improve the photosynthetic capacity in different plant species.
Firstly, an effort is devoted to developing transgenic C3 plants with over-expression of Rubisco genes or other enzymes of the C3 pathway.
Secondly, is the transfer the genes of a key C4 photosynthetic pathway to C3 plants.
CONCLUSION
Stress affects agricultural yields hence biotechnologically enhanced crops with the ability to tolerate stress should be adapted.

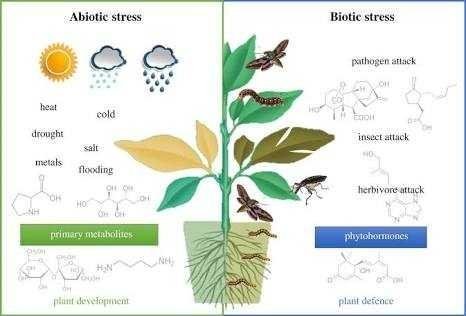
We are so fortunate to have an innovator like you on steemit.
Did you know?
Morphine is named after 'Morpheus', the Greek god of dreams.
Read on and follow @knowledge-portal to find more latest discoveries and interesting related facts on the blog.
Congratulations @bookoons! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on the badge to view your Board of Honor.
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPTo support your work, I also upvoted your post!
If non living things can undergo stress and strain then the living must confess lol. Amount of Stress in plants detrrmines their productions also.
Congratulations! this post got an upvote by @steemrepo and was manually picked by the curator @yanosh01 to be added on STEEM REPOSITORY, simply comment "YES" and we upload it on STEEM REPO Website.
Want to know more about the Steem Repo project? Contact us on Discord