Fluorine; risks and benefits?
Fluorine (F), a chemical element of the halogen(*) family, It is in the form of a dual-corn gas (F2) with a yellow color At normal temperature and pressure, this gas has an unpleasant and dizzying odor and it's a toxic gas with a negative impact on living organisms.
fluorine is the most electronegative(*) element with a value of 3.98, that's why it's combines with other elements more easily than any other substance; Interacts with inert gases, forms a strong acid with hydrogen, and interacts with glass and It forms very strong chemical bonds with carbon atoms.

Creditwhat is halogen?:
. Halogens are elements of the seventh group of the periodic table of elements (Chlorine (Cl); Fluor (F); Bromine (Br); Iodine (I); Astatin (At) ).
. The name "halogen" means "salt-producing". When halogens react with metals they produce a wide range of salts, including calcium fluoride, sodium chloride (common table salt), silver bromide and potassium iodide.
. Halogens have seven electrons at the outer level, so they tend to acquire electrons so that electronic distribution is similar to the distribution of electrons in inactive gases.
CreditWhat electronegativity means:?
Electronegativity is the power of attraction of electrons by the nucleus.

Credit
- Historical:
- In 1529, mining scientist Georgios Agricola described fluorite as an additive Suitable during melting of metals, the goal was Reducing their melting point during treatment.

Credit - Giorgios Agricola gave the fluorite rocks the Latin name fluorés , which means flow, then the name changed to fluorspar and fluorite.
- it was discovered after that the fluorite composition is calcium fluoride CaF2.
- Initial experiments on fluorine and its compounds were so serious that many of the nineteenth century scientists who experimented with that element were called fluorine victims.
- In 1764, Andreas Sigismund Marghergh described the process of glass refinement (treated with acid) in detail using fluorite with sulfuric acid.
- Fluorine was first time isolated by the scientist Moissan in 1886.

Chemical properties of fluorine:

Credit
Atomic number = 9
Atomic mass: 18.998403 g.mol -1
Electronegativity according to Pauling: 3.98
Density: 1.8*10-3 g.cm-3 at 20°C
Melting point: -219.6 °C
Boiling point: -188 °C
Vanderwaals radius: 0.135 nm
Isotopes: 2
Electronic shell: [ He ] 2s2 2p5
Energy of first ionisation: 1680.6 kJ.mol -1
Standard potential: - 2.87 V
Fluorine is found in the form of a binary molecule F2; The bond energy in the F2 molecule is much lower than in Cl2 or Br2.
Fluorine belongs to the strongest active oxidants.
It can interact with most materials, even the inert ones.
Wood and water are immediately exposed when exposed to a stream of fluorine gas.
When small amounts of fluorine react in cold water, It produces hydrogen peroxide (oxygen water) and hydrofluoric acid: F2+ 2H2O === H2O2 + 2HF.

CreditWhen excess fluorine is reacted with less water, ice or hydroxides, oxygen and oxygen fluoride are formed as major products.
Fluorine can react with all chemical elements except helium and neon.
The reaction of fluorine with xenon and krypton requires special conditions.
Fluorine combines with hydrogen to give hydrogen fluoride, it is a toxic gas.
Fluorine production:

(Industrial fluorine production cells in Britain)
Credit
The Mawsan method is used to produce industrial quantities of fluorine by electrolysis of a mixture of fluoride of potassium and hydrogen fluoride: 2HF ========= H2 + F2.
Fluorine can be stored in steel cylinder tanks that are lined inside to protect against corrosion.
Fuses and pipes in a fluorine production facility are usually made of nickel.
Laboratory Preparation:
In 1986 Karl Christie was able to design a laboratory method to produce fluorine gas in abundant quantities, despite the availability of the materials used by Karl:
2 KMnO4 + 2 KF + 10 HF + 3 H2O2 → 2 K2MnF6 + 8 H2O + 3 O20
2 K2MnF6 + 4 SbF5 → 4 KSbF6 + 2 MnF3 + F20Moassan used the method of electrolysis instead of direct interaction.
The fluorine gas produced by the industrial or laboratory is so active that it can not be chemically isolated.
Source of fluorine:
- Top 11 Fluorine Rich Foods:
- Water from fresh sources.
- Tea Leaves.
- Pickles.
- Grape Juice.
- Spinach.
- Tomato Products.
- Carrots.
- Orange Juice.
- Asparagus.
- Beets.
- Prunes.

Credit
- Fluorine is 13th most abundant element found in the earths crust.

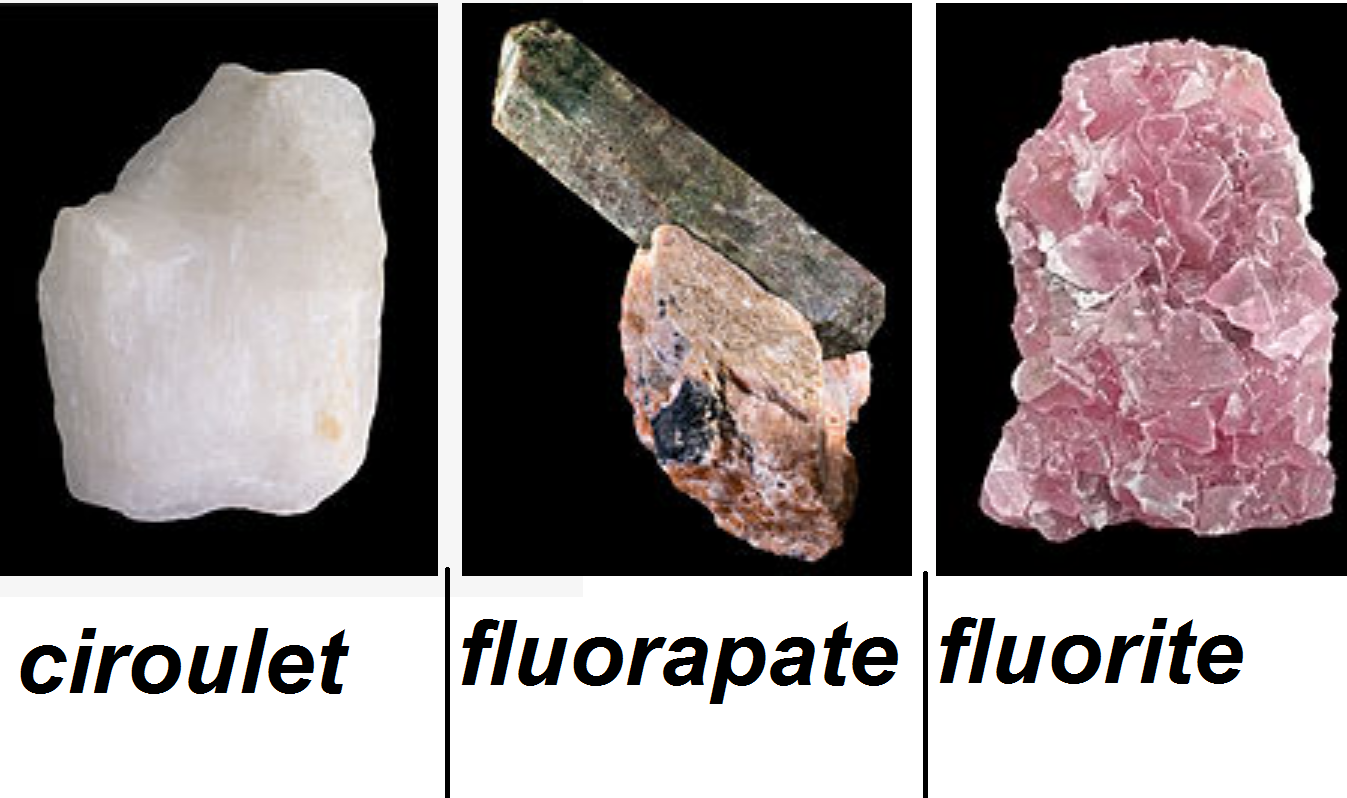
Credit - Because of the large chemical activity of fluorine it is only found in association with other elements in metallic forms such as fluorite (CaF2), fluorapate (Ca5(PO4)3F) and ciroulet (Na3AlF6).

Credit - Fluoride (F-) is also present in many drinking water sources arround the world, fluoride concentrations may appear in groundwater when rocks or soils containing fluoride disintegrate and dissolve.
So important:
- he maximum acceptable concentration of fluoride in drinking water is 1.5 mg / l
- small amounts of fluorine are added to the drinking water treatment system in some countries to prevent tooth decay (0.7 mg/l).
How can fluoride protect teath?

Credit - Fluoride can kill or inhibit bacteria and make them less able to produce acids from carbohydrates
- fluoride is embedded in crystals on the surface of the tooth, which makes this surgace more resistant to acid that's why
- fluoride favors the remineralization of enamel, the process of demineralization and remineralization of enamel is observed, fluorine increases the speed of the process and the incorporation of fluorine into the mineral makes it less soluble in acid.

Credit
Due to the great benefit of fluoride in tooth protection, manufacturers use it to make toothpaste

Credit
People who are at risk of decay more than others, benefit from fluoride drinking water treatment, those people are:
. People who eat fast food frequently.
. People whose teeth are in poor condition and who can not visit a dentist.
. People with a diet of many sugars and starches.
. People who have calendar hoops and tooth restoration in their mouths.
. People with a history of dental necrosis.
. People who have dry mouth.Important:
. Teeth need rest, avoid eating between meals, reduce sweets, drink water when you feel thirsty, and do not use toothpaste too much.
Fluorine and risks to health!???

Credit
the health risks associated with fluoride depend on the duration and level of exposure. at a low dose, fluoride is beneficial.
. ingestion of high concentrations of fluoride may induce fluorosis in children younger than 8 years of age.

Credit
. For adults, high fluoride intake for a very long time may result in skeletal fluorosis:
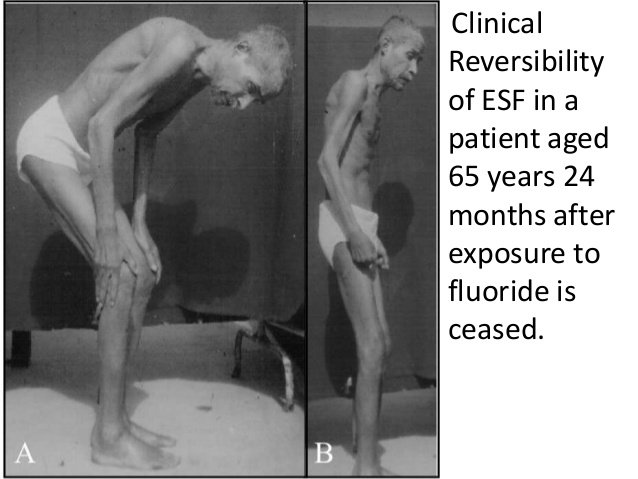
Credit

Credite
Fluoride, an international problem:

Credit
. UNICEF considered fluorine a global problem, with at least 25 countries suffering from fluorosis.
. Tens of millions of people suffer from fluoridated skeletal toxicity arround the world, the world Health Organization estimates that 2.7 million people in China have been paralyzed and disabled as a result of the disease.
. Not all studies on fluoridation have yielded positive results. Some studies have shown that fluorine may reduce IQ in children.
. Scientists have found that fluorine causes periodontal disease.
- Warning of fluorine during pregnancy*:

Credit
Women who avoid fluoride are less likely to develop anemia during pregnancy, fluorine may also cause premature birth and children with light weights.
- Why did not these countries find a solution?

Credit
. The suffering caused by fluorine water can be prevented, but the removal of excess fluorine from drinking water is a difficult and costly task, and low-cost solutions do not exist.
Sources of excessive exposure to fluoridation:
. Fluorination of drinking water in water treatment plants.
. The presence of high concentrations of fluorine in freshwater in some parts of the world.
. Fluorescent toothpastes that children can ingest.
. Bottled water that has not been examinated.
. Improper use of some fluorine supplements.
Industrial uses of fluorine:
companies produces at least 17,000 metric tons of fluorine annually, and costs US $ 5-8 per kilogram when produced in the form of uranium hexafluoride or sulfur.
1)Fluorine gas:
- Used to prepare uranium hexafluoride UF6, Used in the nuclear fuel cycle.

Credit
2)Inorganic fluorides:
- Fluoride salts are mainly used in smelting, steelmaking and steel.

Credit
3)Crystallization materials:
- (R-11), Dichlorofluorocarbons (R-12) and 2,1-dichloro-tetrafluoroethane (R-114) control the chemical fluorine industry for high demand in the manufacture of refrigerators, air conditioners and feeders, The industry reached its peak in the 1980s.
4)Polymers:

Credit
- About 180,000 metric tons of fluorine polymers have been produced between 2006 and 2007, which generated revenues of over $ 3.5 billion annually.
5)Surface treatment:
- Fluorescent surface-effective fluoride has great effectiveness in pushing water and stains.
6)Agrochemicals:

Credit
- About 30% of agrochemicals contain a fluorine component in their composition.
7)Pharmaceutical drugs:

Credit
- About 20% of modern pharmaceuticals contain fluorine in their composition.
8)PET tomography:

Credit
- Fluor-18 is used in the installation of radioactive tracer for PET positron imaging.
References:
La géochimie récréative, G.Fresman
Utilisation du fluor dans la prévention de la carie dentaire avant l'age de 18ans, agence francaise de sécurité sanitaire des profuits de santé, octobre 2008
FOLKTANDVARDEN, arabiska- Rad och information om karies och fluor
Le fluor et la santé des dents chez l'enfant, Héléne Roy, CHU sainte-justine
Chemistry and Pharmacy, Fluorine Series, Second Seminar, Syrian Researchers
Health effects of fluorine
Fluorine Rich Foods For Children
Fluorine, wikipedia
Search for fluorine element, forumthe middle
dear steemians, thank you for reading i hope you will like this post.
If you like this post upvote and follow To be informed of upcoming posts.
Accept my greetings and wishes for your health and wellness.
@Benainouna


I had always hated chemistry, but this your post has made me change my mind. I appreciate the time you put in to make this elaborate post on flourine and have made me less ignorant ;) This post is brilliant! You're good!
i appreciate that, thank you for finding time to read this post and for your opinion :)
Resteemed to over 10800 followers and 100% upvoted. Thank you for using my service!
Send 0.200 Steem or 0.200 Steem Dollar and the URL in the memo to use the bot.
Read here how the bot from Berlin works.
We are happy to be part of the APPICS bounty program. APPICS is a new social community based on Steem. The presale was sold in 26 minutes. The ICO will start soon. You can get a account over our invite link: https://ico.appics.com/login?referral=1fRdrJIW
@resteem.bot
Hi! Love the post. I feel it worth mentioning that flourine and flouride are different in every way, yet they are misunderstood and exchanged for one another quite often. Flourine is natural to our earth and by extension occurs naturally.
Sodium flouride however is dangerous. It would be futile to discuss any benefit, as there are none. The science justifying the chemical being added to things we consume simply does not exist. It is a nuclear waste byproduct that is responsible for our dental flourosis ( we maintain highest in the world) , as well as furthering the cancer epidemic.
It is crucial that these are identified and not confused.
I am following you! Thanks for the post!
thanks for reading and for the addition :)