The formula thermodynamics entropy
Thermodynamics
 Image credit : Wikimedia
Image credit : Wikimedia
In the language of Greece: thermos = 'hot' and dynamic = 'changes'.
On the system where occurs the process of changes in the form or exchange of energy, thermodynamics classical is not associated with the kinetics of the reaction (the speed of a reaction process takes place). Because this reason, the use of the term “thermodynamics” usually refers to thermodynamic equilibrium. With this relationship, the main concept in thermodynamics is the process of kuasistatik, which is idealized, the process of “super slow”. The thermodynamic process depending on the time studied in thermodynamics no the equilibrium.
Understanding Entropy
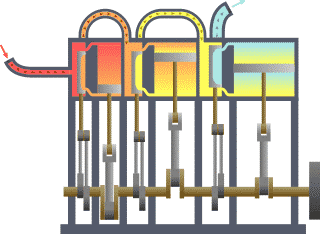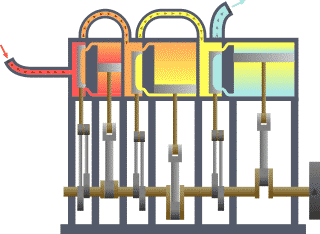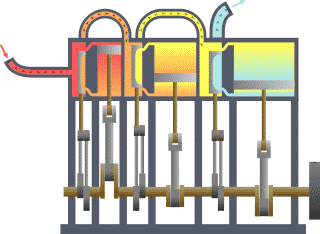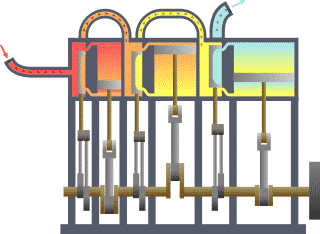 A system of thermodynamics. Engine expansion three-fold.
A system of thermodynamics. Engine expansion three-fold.
The formula thermodynamics
The law of Thermodynamics
- ΔU = Q − W
Description :
ΔU = The changes in energy (joules)
Q = Heat (joules)
W = Business (joules)
The process of the Process :
Isobaris → Fixed Pressure
Isotermis → The temperature stays
Isokhoris → The volume of fixed (or isovolumic or isometric) → W = 0
Adiabatis → Does not occur exchange heat → Q = 0
Cycles → Cycle → ΔU = 0
Equation of State of gas
The law Gay-Lussac
- The pressure remains → V/T = Constant → V1/T1 = V2/T2
The law Charles
- Volume remains → P/T = Constant → P1/T1 = P2/T2
The law Boyle
- The temperature stays → PV = Constant → P1V1 = P2V2
P, V, T Changed (non adiabatis)
- (P1V1) / (T1) = (P2V2) / (T2)
Adiabatis
- P1V1 γ= P2V2γ
- T1V1 γ − 1= T2V2γ − 1
γ = Comparison of heat type of gas in the pressure remains and the volume remains → γ = Cp/Cv
Business
W = P(ΔV) → Isobaris
W = 0 → Isokhoris
W = nRT ln (V2 / V1) → Isotermis
W = − 3/2 nRΔT → Adiabatis (monatomic gas)
Description :
T = temperature (Kelvin, do not Celsius)
P = pressure (Pa = N/m2)
V = volume (m3)
n = The number of mol
1 liter = 10-3m3
1 atm = 105 Pa (Or join the question!)
If not known in question take the value ln 2 = 0,693
Carnot Machine
η = ( 1 − Tr / Tt ) x 100%
η = ( W / Q1 ) x 100%
W = Q1 − Q2
Description :
Η = efficiency of the Carnot engine (%)
Tr = low reservoir temperature (Kelvin)
Tt = high reservoir temperature (Kelvin)
W = (business joule)
Q1 = heat enter / absorbed reservoir high (joule)
Q2 = heat out / cast reservoir low (joule)
The formula thermodynamics black hole entropy
The second law of thermodynamics requires that black holes have entropy. If the black hole does not bring entropy, allows to be breaking the law by throwing the masses into the black hole. Increasing entropy black holes more than compensate for declining increases entropy which brought by the object that had swallowed.
Similarities to entropy black hole is usually given with the formula : Bekenstein-Hawking suspect that entropy black holes it.
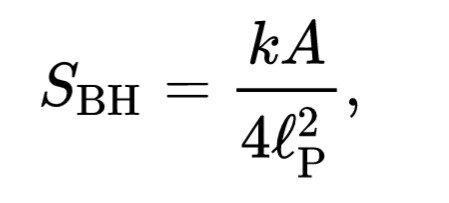 Image credit : Wikimedia
Image credit : Wikimedia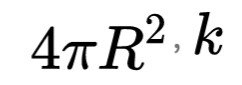
Is the Planck Boltzmann, and 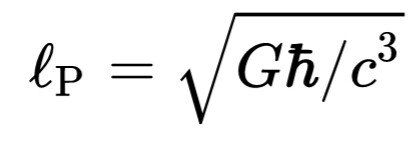
Is the length of Plancks. This is often referred to as the formula Bekenstein-Hawking. BH subscriptus stands for "black hole" or "Bekenstein-Hawking". Entropy black hole commensurate with the vast expanse of occurrence 🅰.
The fact that entropy black hole is also entropy maximum can be obtained by the Bekenstein which is bound (Where the Bekenstein bound become equation) Is the main observation that lead to a holographic principles (A principle of the theory of the string and properties that should be owned by quantum gravity that states that the description of the volume of a space can be considered as a limit on encoding a lower dimension to the region of the most likely a similar limit of light like horison gravitation).

That's post I this time, hopefully useful. And #steemSTEM has cool people who like, create, and support nerd stuff like Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics related content and activities on the STEEM blockchain. If you want to be a part of it you can contribute relevant STEM content with the #steemstem tag, support and vote on steemSTEM authors, join the curation trail, hop in the Discord Channel

w usually stands for work…
Quasi- static ; almost static, reversible, infinitely slow process.