Drilling And Blasting Method of tunelling
The tunnel is the underground passageway for the movement of people or good or water(in case of hydropower, irrigation, water supply and sanitation) and any other material. Nowadays, the tunnel is more in use because of less availability of surface land and also tunnel neither creates the disturbance to the structures in surface nor receives any (e.g. landslide, flood). There are different methods of tunnelling employed some of them are as follows:
• Heading and Benching tunnelling (For weak rock mass or soil)
• Tunnel Boring Machine
• Conventional Drill and blast method
Here we are going to discuss the conventional drill and blast method of tunnelling. It is not suitable for weak rock mass or soil.
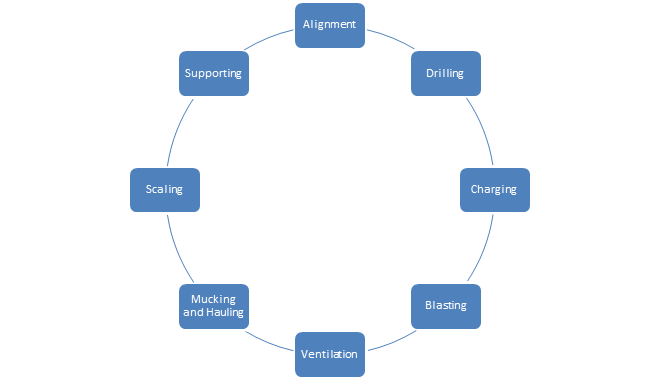
Fig1. Schematic Diagram of Process of Drill and Blast Tunneling
Now let us discuss the different process to get more detail view.
a) Alignment:
At this stage surveyor checks the chainage of the tunnel, verify the alignment of tunnel axis as per drawing and takes the cross-section data to check the opening size in that section.
b) Drilling:
Holes are drill into the face of the tunnel a design of drill pattern. Drill patterns are like v-cut, wedge cut, fan cut, burn cut etc…. Let’s not go into these terminologies in this article. Generally, for the tunnel, the drill hole size varies from 38mm to 58 mm diameter and advancement of these holes depends upon the technical means available for drilling, geological condition.
Drilling can be done manually by the jackhammer, by boomer machine, by the pneumatic driller.
[]
( )
)
Fig2. The pneumatic driller drilling holes at the portal of the tunnel at SHEP headworks
Different types of holes are cut holes, blast holes, buffer holes, contour holes used in drill pattern.
• Cut holes are the centre holes can be open cut holes (where no charge is installed) or filled cut holes (where the charge is installed). Open cut holes are of large diameter (>51mm).
• Contour holes are placed at the circumference of the face of the tunnel for purpose of smooth perimeter blasting. Less amount of charge is used to split the section of excavation to minimize the disturbance created by major blasting. These holes are blasted prior to other major blast holes.
• Buffer holes are the holes that at a certain distance of contour holes inside the tunnel face. Blast holes are distributed at the tunnel face as per design where high-density charging and blasting is done.
c) Charging:
The charging means inserting the explosive inside the drill holes. For charging ANFO( Ammonium nitrate with 5-6% of fuel oil) and 75% of polystyrene beads, nitroglycerine mix-type gel cartridge or pipe charge can be used. For charging, sub-drill is provided and stemming is also provided.
Stemming is packing of the clay or stand material after the explosive is inserted at the open face of drilled holes to minimize the intensity of air pressure induced by blasting.
Generally, for buffer holes, the un-tamped cartridge is used while for blast holes tamped cartridge is used.
d) Blasting:
Blasting is performed with electric equipment or without. For smooth blasting, it is assumed that the blasting is done by without using the electric equipment. The sequence of blasting is provided. First of all, the contour holes are blasted, then cut holes and after that the major blast holes.
e) Ventilation:
After blasting the ventilation is provided to dilute the contaminated air up-to tolerable limit. This done by providing the ventilation duct which sucks or blow the air inside the tunnel. There are different types of mechanism for ventilation. For the large tunnel, two-way ventilation is provided where one ventilation duct blows the fresh air inside and other one suck the contaminated air. Reason to provide the two-way ventilation duct is to decrease the ventilation time in the large tunnel.
f) Mucking and hauling:
Mucking is the process of removing the debris from the construction site while hauling is to dispose the muck (debris) to a place or location. For mucking backhoe loader, trippers are used and hauling rail carts, conveyor belts are used.
g) Scaling:
Scaling means to remove the loose rock pieces from the walls and crown of the tunnel after mucking and hauling. Scaling can be done with two methods:
• Barring
It uses hydraulically powered tooth whose tip is placed at the joint and then twisted. These are done generally for sedimentary rocks.
• Scraping
Initial scaling is commenced by scraping where a special pointed tooth or the teeth of the bucket is used to scrap off the loose rock masses at the surface of the tunnel.
h) Rock support:
The rock support is provided according to the geology encountered in the site. Rock support consists of methods like shot-creting, rock bolting, use of steel ribs etc.