How does optical fiber work?
Hello Steemians, how you doing? Hope All is Well. Today, I want to share my knowledge about "Optical Fiber" though this post.
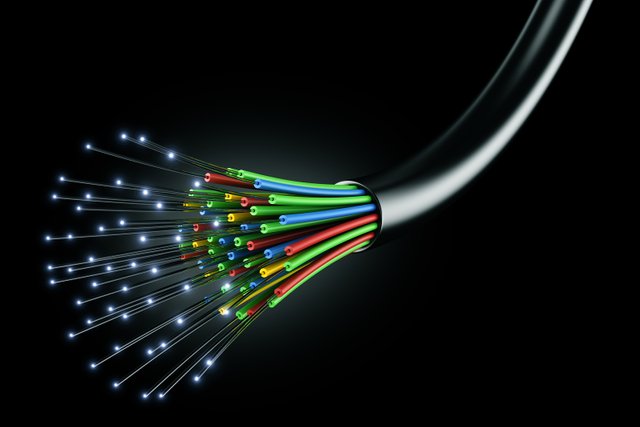
Optical means related to light and the fiber means thread or filament. The optical fiber is a thread like structure in which light can travel even in the bent path. It is used to transmit signals over long distances. For transmitting signals, we have been using copper wires for many centuries. But, the data transmission is economical and efficient using optical fiber than traditional wire transmission. Other reasons to chose the optical fiber transmission are:
i. It has low attenuation. Attenuation means the decrease in strength of signal over the transmission.
ii It has high bandwidth. Bandwidth is the measure of how much data can be transmitted in a given time. It is measured in bytes per second.
iii.It has a small size and low weight.
iv. There is no electromagnetic interference.
v. Manufacturing material is Silica. It is abundant and economical than copper.
vi. The transmitting data are secure in optical transmission.
With the advantages may be you are motivated now. Let's go into structure and physics of transmission.
Construction
The optical fiber is cylindrical in shape. It has a diameter of about 250 µm, which is around the size of human hair. These small fibres arranged in bundles called which then is called optical cable. Mainly, it has three parts: Core, Cladding and Buffer Coating.
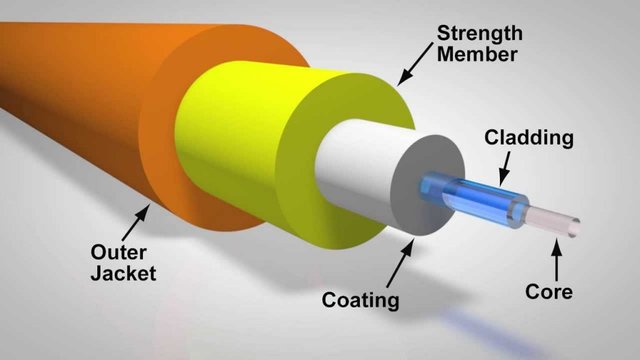
Core is the thin glass center and it light transmitting part. It is made up of glass or plastic, generally SiO2. Cladding is also made up of glass or plastic but it has lower refractive index than that of core. It helps to reflect light back in core. Buffer Coating is made up of plastic to protect core and cladding from moisture and other environmental effects.
Principle
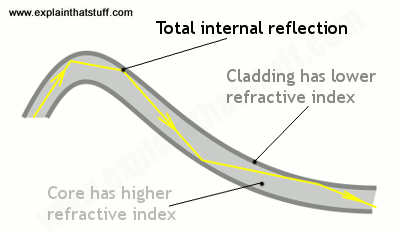
Transmission of light in optical fiber is based on Total Internal Reflection of Light. When the light travels from denser medium to rarer medium, if its angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle then the light reflect back to denser medium instead of refraction. It is called total internal reflection of light.
Explanation
Light travels in vacuum with the speed of 3*10^8 m/s. Its speed decreases in other medium. The ratio of speed of light in vacuum to the speed of light in that medium is called refractive index of the medium. Refractive index of water is 1.33 means the speed of light in vacuum is 1.33 times of the speed of light in water.
The angle made by the incident ray with the normal is angle of incidence and the angle made by refracted ray with the normal is called angle of refraction.
Let 'i' be angle of incident from denser medium with refractive index n1 to the medium with refractive index n2. Angle of refraction be 'r'.
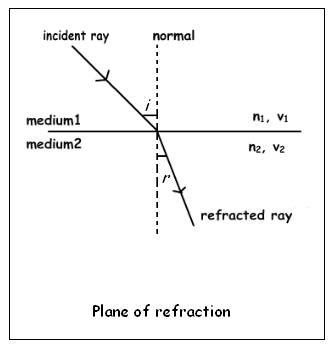
Then, from Snell's law
(n2/n1) = sin i /sin r
when angle of refraction is 90 degree,
sin i = n2/n1
i = arc sin(n2/n1);
This is called the critical angle. If we increase incidence angle then, there will be total internal reflection of light. The light signal travels though core by the process of continuous total internal reflection of light.
Conclusion
In the information age, we want large data transmission that too in short time. We want those data to be secured without any interference. Hence, optical fiber transmission is best suited for transmission of data in present scenario.
Sources:
The Science and Engineering of Materials
Fundamental of Physics
Explainthatstuff
Encyclopedia
#introduceyourself/#introducemyself
The “introduceyourself/introducemyself” tag is for creating one introductory post that tells us about you. Users are encouraged to use this tag exclusively for that, and not to reuse it.
Without optic fiber, I woudn't be able to see that post! Hahahaha!