SALT BRIDGE AND ITS SIGNIFICANCE
SALT BRIDGE AND ITS SIGNIFICANCE
Salt bridge is usually an inverted U-tube filled with concentrated solution of inert electrolytes. An inert electrolyte is one whose ions are neither involved in any electrochemical change nor do they react chemically with the electrolytes in the two half-cells. Generally salts like KCl, KN03, NH4N03, etc., are used. For the preparation of salt bridge, gelatin or agar-agar is dissolved in a hot concentrated aqueous solution of an inert electrolyte and the solution thus formed is filled in the U-tube. On cooling the solution sets in the form of a gel in the U-tube. The ends of the U-tube are plugged with cotton wool as to minimize diffusion effects. This is used as a salt bridge.
Significance of salt bridge:
The following are the functions of the salt bridge:
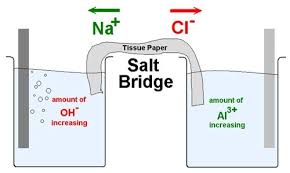
(i) It connects the solutions of two half-cells and completes the cell circuit.
(ii) It prevents transference or diffusion of the solutions from one half-cell to the other.
(iii) It keeps the solutions in two half-cells electrically neutral. In anodic half cell, positive ions pass into the solution and there shall be accumulation of extra positive charge in the solution around the anode which will prevent the flow of electrons from anode. This does not happen because negative ions are provided by salt bridge. Similarly, in cathodic half-cell negative ions will accumulate around cathode due to deposition of positive ions by reduction. To neutralize these negative ions, sufficient number of positive ions is provided by salt bridge. Thus, salt bridge maintains electrical neutrality.
(iv) It prevents liquid-liquid junction-potential, i.e., the potential difference which arises between two solutions when in contact with each other.
Salt bridge can be replaced by a porous partition which allows the migration of ions without allowing the solutions to intermix.