Science of geology in hydrocarbon exploration
What is geology?
Roles of a geologist in hydrocarbon mining
A geologist is a person whose job is to search, research and explore oil fields whose exploitation is economically profitable.
In my country Venezuela the contribution of the geologist is fundamental, since being an oil country, it needs a geological study that can determine by geological exploration the exact location of where the precious liquid exists, and not only those, but apart from knowing where it is Oil and natural gas, geological studies also provide us with a prediction of the possible pressures that we may find in the oil field.
Study and analysis of the internal and external processes that occur in our planet.
Endogenous processes: Are those that originate in the interior of the earth due to the high temperatures and pressures generated there, and can be classified into two types: orogenic and epirogénicos.
Exogenous processes: They are produced by the action of atmospheric agents (such as wind, temperature changes, rain and ice) on rocks. They include four types of phenomena: weathering, erosion (or erosion of reliefs), transportation of eroded materials and their accumulation or sedimentation in other areas.
It is necessary that when teaching geological aspects, as is the case of these processes that occur in our planet, we can study in detail the existing elements of an endogenous process, which in turn is very different from an exogenous process .
To understand what I want to convey, I quote the following example: "If we analyze a sample of sedimentary rock, for this it is necessary that we understand that for a sedimentary rock could form, had to go through the processes that acted in its formation, these they are of endogenous type like high pressures and temperatures that occur in the interior of the Earth ". The other example that can be cited is the formation of oil: "so that your can deposit organic and vegetable material over long periods of time, it is necessary that there are external factors such as wind, waves of the oceans and others. that drag these materials and remain deposited and buried in the deposition of the strata, to then enter the endogenous processes, with which we can conclude that the oil in its historical process of formation had to go through an exogenous process, necessary for the transport of plant and animal material that is subsequently converted into hydrocarbon.
Examples of endogenous processes:
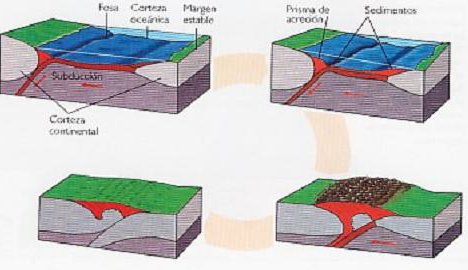
Examples of exogenous processes:

Conclusion
The main objective of this publication is to create and present a small outline of how geological science is applied in the exploration of hydrocarbons, and at the same time, small issues and net aspects of geology that influence the indirect in the exploitation not only of hydrocarbon but mining in general. The seismic and advanced records are the technology that is in progress to detect new oil fields, in a world with so much energy demand. In the search for oil, the petroleum engineers are prepared to provide their geological knowledge, although they always go hand in hand with the geologists to form a team where no aspect is irrelevant in the search for the precious liquid.
Bibliographic reference consulted
General Geology I. INTRODUCTION TO GEOLOGY AND ITS ROLE IN THE MINING WORLD. Author: Carla Navea G.
Source of images used in the publication: The images taken for this article were taken from the same book in pdf format.
Hmm.. Energy.
There's so much research in progress to aid the smooth transmission from hydrocarbons and fossils to sustainable alternative energy sources.
Still, there's no denying the fact that fossils have and will continue to be useful to man in some ways, and getting to understand in part how Geology explores this field is useful.
Thanks for writing.