Science Experiment : How Does Cohesion and Adhesion Work
Cohesion and Adhesion
Did you learned about attractive force between particles as one of the particles properties???. Those forces may be classified as cohesion and adhesion.
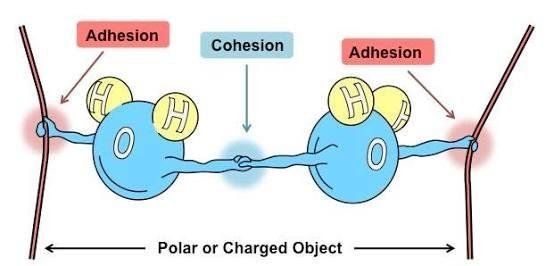
Cohesion is the tendency of certain similar particles to cling together due to attractive forces; while adhesion is the tendency of certain dissimilar particles to cling together due to attractive forces.
1. Concave Meniscus and Convex Meniscus
Do the following activity to help you understanding the concave meniscus and convex meniscus!
Activity 1
Objective
To demonstrate cohesion and adhesion on matter.
Equipment and Materials
Water, mercury, and glass tube.
- Pour the water into the first tube and the mercury into the second one!
- Watch the waters surface especially around the tube wall! Is it curving?
- Watch the mercury's surface especially around the tube wall! Is it curving?
- Is there any difference between the waters and the mercury's surface from steps (2) and (3)?
- What is your conclusion?
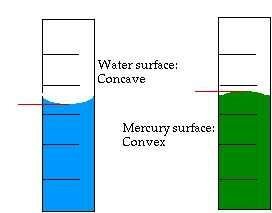
From the observation resulting from Activity 1, you can see that the surface of water and mercury is not flat, but it is curving around the tube wall. The water's surface is curving upward and it wets the tube wall because the attractive force among the water's particles is smaller than the attractive force between the water's particles and the tube wall (cohesion is smaller than adhesion).
On the other hand, the mercury's surface is curving downward and does not wets the tube wall because the attractive force among the mercury's particles is greater than the attractive force between mercury's particles and the tube wall (cohesion is greater than adhesion).
The upward curve of liquid's surface is called concave meniscus while the downward curve is called convex meniscus.
2. Capillarity
How is kerosene absorbed and goes up through the oil stove fuse? Do you know why a rag is able to absorb water when you wipe spilled water on the floor? To understand it, do the following activity!
Activity 2
Objective
To observe capillarity.
Equipment and Materials
A container, water, mercury, and two capillary tubes with different diameter.
- Pour some water into the container, and then plunge both of capillary tubes into the container!
- Observe the waters surface on both capillary tubes! Do they have the same heights?
- Replace the water with mercury, and then do the same step as before!
- 0bserve the mercury's surface on both capillary tubes! Do they have the same heights?
- What is your conclusion?
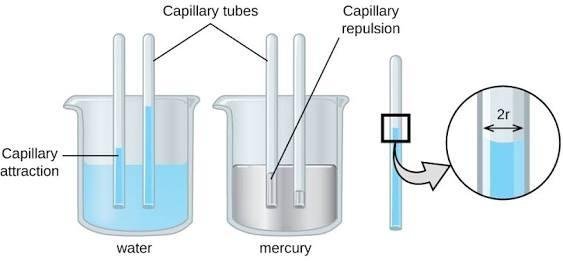
From Activity 2, you have found out that the water's surface height in the capillary tube was higher than that in the container. The smaller the tube diameter, the higher the water surface height will be. What about mercury? The mercury's surface height in the capillary tube was lower than that in the container. The smaller the tube diameter, the lower the mercury surface height will be. Those phenomena are called capillarity. Capillarity is the rising of liquid up or down in a capillary tube.
The Benefits of Capillarity Capillarity is very useful for us, for example the kerosene could be absorbed and goes up through the fuse of oil stove or oil lamp so that we can use the stove to cook or turn on the lamp. Find other benefits of capillarity in our everyday life!
3. Surface Tension
Surface tension is the elastic tendency of a fluid surface which makes it acquire the least surface area possible. Surface tension allows insects (e.g. water striders), usually denser than water, to float and stride on a water surface. Source
Do the following activity to help you understanding the surface tension!
Activity 3
Objective
To observe the surface tension of liquid
Equipment and Materials
Container, a razor blade, and some water.
- Fill the container with water
- Put the razor blade slowly in the position as shown in the picture!
- What happens with the razor blade? Is it sinking?
- What is your conclusion?
Why does not the razor blade sink? It does not sink because there are attractive forces (cohesion) between the water particles at the surface. As a consequence, the water surface will form an elastic sheet that able to hold objects like razor blades, needles, insects, etc. The phenomenon is called surface tension.
Sources :
Concave Meniscus and Convex Meniscus

Congratulations @draw-art! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Do not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!