Dye sensitized Solar cell, DSSC
Being a scientist is fun but it quite challenging when conducting experiment. Here is my final year project on DSSC
Image 1: Fabrication of DSSC
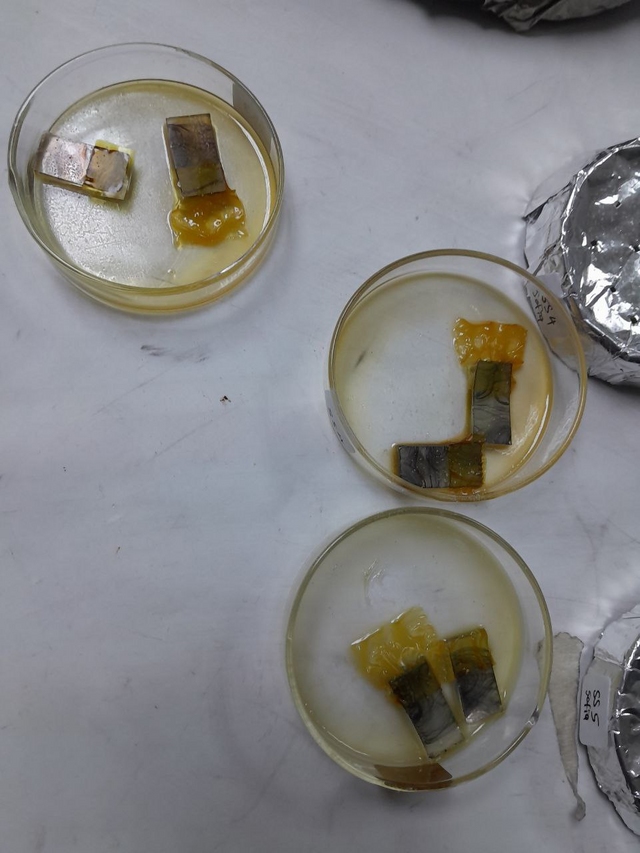

Image 2: Solar cell layer preparation.
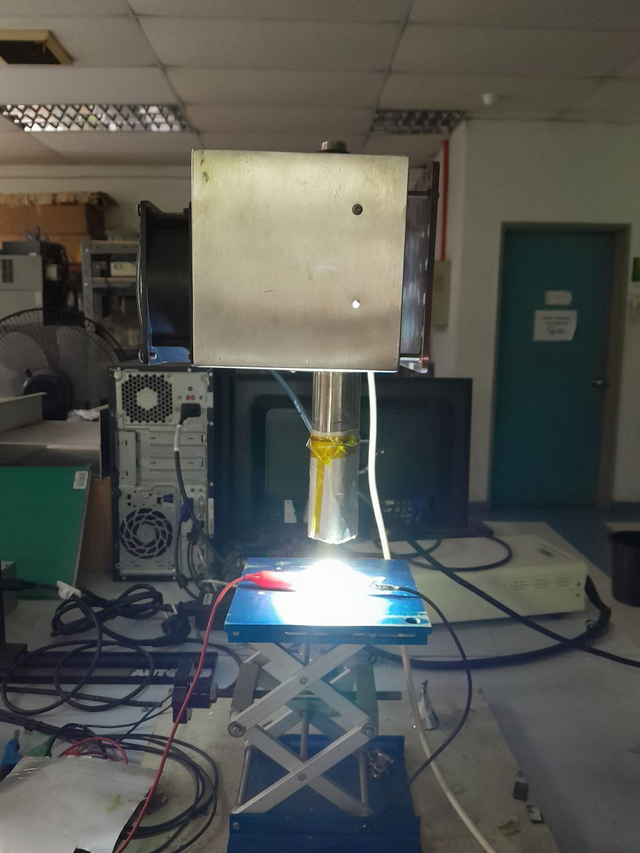
Image 3: Characterization of Solar Cell
A solar cell, also known as a photovoltaic cell, is an electronic device that converts sunlight directly into electrical energy. It is a type of semiconductor device that uses the photoelectric effect to generate electricity. When sunlight (photons) strikes the surface of a solar cell, it excites electrons in the material, causing them to move, and creating an electrical current.
The basic structure of a solar cell consists of a layer of silicon or other semiconductor material sandwiched between two electrodes. The top electrode is typically a thin, transparent layer of conducting material, while the bottom electrode is a thicker layer of metal. When light strikes the top electrode, it creates a flow of electrons between the two electrodes, generating an electrical current.
Solar cells are commonly used in solar panels, which are used to generate electricity for a wide range of applications, including residential and commercial power systems, remote power systems, and spacecraft. As solar energy is a renewable and environmentally friendly source of energy, the use of solar cells is becoming increasingly popular as a means of reducing our reliance on fossil fuels.