Understanding Slip Gauges: Precision Tools for Accurate Measurement
Here’s an enhanced structure for a Steemit blog on Slip Gauges:
Understanding Slip Gauges: Precision Tools for Accurate Measurement
Introduction
In the world of precision engineering and metrology, slip gauges (also known as gauge blocks) are indispensable tools. These finely crafted blocks of steel or ceramic play a crucial role in achieving accurate measurements and calibrations. This post delves into what slip gauges are, how they work, and why they are essential in industries requiring high precision.
What are Slip Gauges?
Slip gauges are rectangular blocks made from hardened steel, ceramic, or tungsten carbide. They come in a set of finely graded sizes, allowing users to stack them together to form precise measurements.
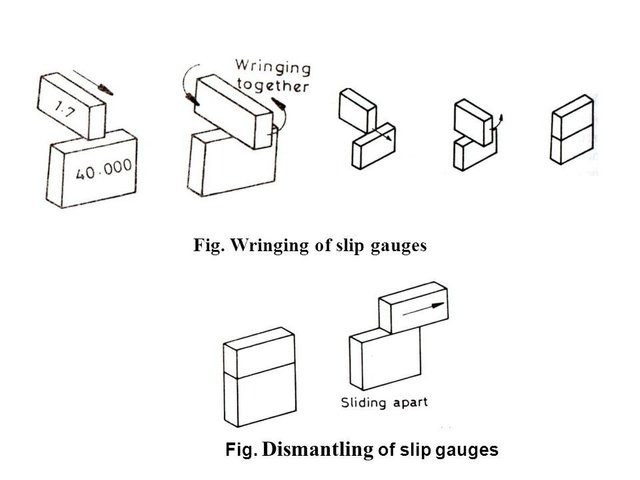
Each slip gauge has an ultra-flat surface, polished to a high degree of accuracy, enabling them to “wring” together without the use of adhesives or clamps. This wringing effect creates a nearly seamless bond between two slip gauges, ensuring measurement stability.
How Slip Gauges Work
Slip gauges are designed to calibrate and check the accuracy of other measuring devices such as micrometers, calipers, and dial indicators. Here’s how they work:
• Combination Stacks: Slip gauges are stacked to create a combination that represents the required measurement.
• Wringing: By slightly sliding two gauges together, they adhere through molecular attraction, creating a stack with virtually no gap.
• Measuring Reference: Once stacked, these blocks serve as a reference point for calibrating various instruments.
Types of Slip Gauges
1. Metric Slip Gauges: Calibrated in millimeters, used in most of the world.
2. Inch Slip Gauges: Based on the imperial system, commonly used in the U.S. and U.K.
3. Grade Levels:
• Grade 0: Used for high-precision standards in labs.
• Grade 1: Used for calibrating instruments.
• Grade 2: Suitable for shop-floor measurements.
Applications of Slip Gauges
Slip gauges find their use in numerous industries, including:
• Manufacturing: Ensuring the precision of components during production.
• Calibration: Calibrating high-precision tools such as micrometers.
• Inspection: Verifying the accuracy of manufactured parts.
How to Use Slip Gauges Correctly
• Cleanliness: Before use, ensure that both the gauges and measuring surface are clean.
• Wringing Technique: Apply slight pressure and twist the gauges to create a wrung stack.
• Proper Storage: After use, clean and store gauges in a protective case to avoid corrosion and damage.
Advantages of Slip Gauges
• High Accuracy: Extremely precise with tolerances in the micrometer range.
• Durability: Made from hard materials, slip gauges maintain their accuracy over a long period.
• Versatility: Can be used with various measuring instruments for different applications.
Conclusion
Slip gauges are vital tools in precision measurement, allowing industries to maintain accuracy across various manufacturing and calibration processes. Whether you’re working in a workshop or a lab, having a good understanding of slip gauges ensures that your measurements are reliable and your tools are properly calibrated.
Call to Action
Do you use slip gauges in your work? Share your experiences or tips on how to use them effectively in the comments below!
This format should make your blog both informative and visually engaging, encouraging readers to learn about slip gauges in a detailed yet approachable way.