How Battery Technology Has Evolved & Changed Our Life
You need to charge your phone, but there's nowhere to do so in the immediate vicinity. Is the battery on your laptop on the verge of exploding? The need for batteries that can store more energy, last longer, and are safer to use is becoming increasingly apparent as these situations become more widespread. The good news is that we will soon be able to take use of improved battery technologies .Then be patient because all your worries will go away soon.

Fig 1: Drawing of the three pieces of ancient Baghdad Battery
The future of battery technology has been called "the holy grail", but for now we will explain how batteries were made for the last 200 years, and how our world has recently become much more demanding, sometimes explosively so. The basics of battery technology have not changed significantly since their invention in 1748 by Luigi Galvani and Alessandro Volta. The goal of every battery is to store energy (i.e., electricity), as well as to release it again when required. It is important to realise that batteries are not solar panels, nor anything else in their class. They are batteries.
How Battery Technology Has Changed
Before the advent of modern batteries, many common devices such as lamps and electric cars had to be fitted with mains-powered electrical components. It is actually possible to go back even further than the electric car, and the first practical electrically powered lamps were produced by Martin Heinrich Klaproth in 1801. Lamps could be made from a variety of materials including paraffin wax, oil, or animal fats (the batteries for these would have also had to be mains-powered). Batteries became popular because they could be used in places where mains electricity was not available. The main challenge for battery technologies therefore was to store as much energy as possible for as long as possible – the only other goal being to deliver it safely when required.
Rechargeable Batteries
A major breakthrough came in 1859 when Gaston Planté invented the first rechargeable battery which he called a lead-acid battery, simply because the electrodes were made of lead and acid (sulphuric acid). He managed to avoid exploding batteries by adding a thin layer of pasteboard, soaked in alcohol and manganese dioxide, between the two electrodes. Then , in 1887, Camille Alphonse Faure invented the nickel-cadmium battery. This revolutionised the world of rechargeable batteries and allowed for the development of large-scale electric car and plane industries.
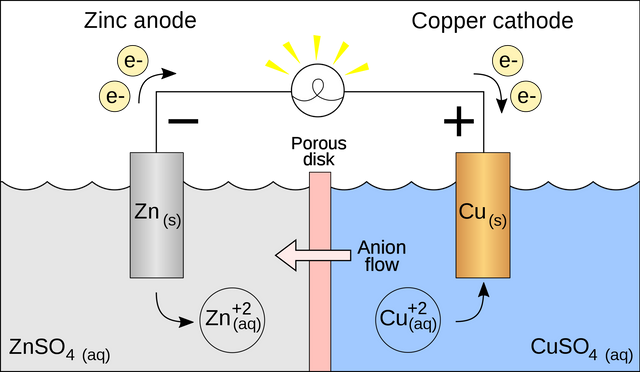
Fig 2: Galvanic cell with no cation flow
Importance of New Battery Technology
Today, electric vehicles are becoming more widely used than ever before. These vehicles will require much more battery power to travel a long way than they currently do, and this has led to several attempts to create a new generation of batteries that are cheaper and last longer than their predecessors. The problem with modern day batteries is that they contain liquids which means they can leak out or even explode under abnormal circumstances. Lithium-ion batteries have come in for particular criticism and it is estimated that a single Boeing 787 Dreamliner contains enough of the rare metal to allow for the production of 1,342 iPhone5. These batteries have also proven to be dangerous in cases where they have overheated and caught fire. For this reason, you will never find lithium-ion batteries on board any aircraft.
The Future of Battery Technology
More research is being put into the power source that can make electric vehicles as viable as their fossil fuelled counterparts. So far, hydrogen fuel cells have been the most successful alternative, being both clean and efficient. However, it is estimated that a single model of Tesla electric car will use approximately twice as much energy than is required to travel just 20 miles in a hydrogen fuel cell car. It is likely that battery technology will need to take a back seat for now.
As you can see from the foregoing, modern batteries do not come cheap. Therefore it is no surprise that many people have tried to come up with an alternative battery that contains no precious metals or rare earths (found in satellite phones and hybrid vehicles). But there is a technology that appeared in the UK in 2014, which is supposedly 80% cheaper than lithium-ion batteries, and all it needs is the help of the global shipping industry. This modern battery can be made out of steel and cardboard.
It will certainly make some people very happy. On the flip side, there are still a lot of people who believe that we should stick with lithium-ion batteries because they are more environmentally friendly. But this argument has already been done to death and modern technology proves that both arguments have been refuted time and time again. The shipping industry is just one example of how commercial viability has outpaced environmental sanity for years now.
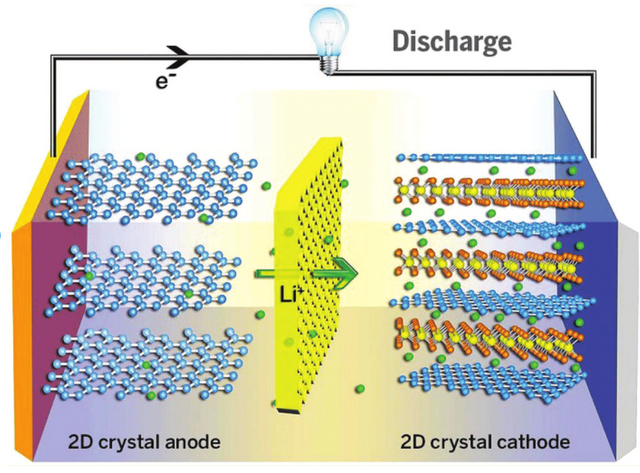
Fig 3: Schematic of showing the working principle of graphene-based electrodes for Li-ion batteries.
Graphene batteries are an emerging technology for future energy storage systems, which may enable a change from the current battery use to a more green technology. The fundamental principle that has inspired many scientists and engineers to develop graphene batteries is the fact that unlike conventional batteries, which utilize electrons for energy generation and are consequently expensive, graphene batteries are based on free electrons in the outer layers of graphene and can be produced easily at low cost.
There is no doubt that graphene can be used to produce high-capacity lithium-ion batteries; however, there is no plan as yet to implement such a system as current technologies are able to deliver energy solutions that are quite sufficient for current applications.
References:
Hello @tanzim2, your post have been supported by @daytona475 using @steemcurator07 account.
Thank you for making a post in the #Technology category. We appreciate the work you have put in this post.
We have analyzed your post and come up with the following conclusion:
Regards,
Team #Sevengers
@steemcurator07 thank you for your support. I will keep writing for better content
It would be great if he could further increase his power to qualify for club5050 and have a higher chance of receiving support. Otherwise, I suggest you don't use the club5050 tag.
Although you have turned on 0.251 that does not represent anything in the system.
With the following link, you can check your status
https://scribe.steemcryptic.me/club5050
@daytona475 thanks for notifying. I wasn't careful. I will further increase power as I don't have prior knowledge about club5050.
how much I need to power up to use the tag club5050 ? I wasn't active for a long time. I checked but didn't understand
Consider turning on a little over 10 steem. It's just a suggestion. Users can turn on whatever they want, however to be in club5050 you need to have a little over 50% turned on with regard to withdrawals.
If you withdraw 20 Steem you must activate at least 21 Steem, always activate a little more
Hey @daytona475,
I powered up as you suggested. Am I eligible now?
Well, keep your power-ups above 50%, and you have a better chance of getting picked. In addition to a plagiarism-free quality publication. I'm going to suggest your post with the guys who will be curating tomorrow. However, I recommend that you place the sources of the images to have more chances of being selected. I also tell you that the votes are not guaranteed.
Thank you very much!