How Does Heat Transfer Work
Naturally, heat moves from a hotter body to a colder body. There are three mechanisms of heat transfer, conduction, convection and radiation.
Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the generation, use, conversion, and exchange of thermal energy (heat) between physical systems. Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as thermal conduction, thermal convection, thermal radiation, and transfer of energy by phase changes. Source
We are going to discuss those mechanisms in the following explanation:
1. Conduction
If one end of a metal rod (A) is heated on a fire (Figure 1), then the other end the rod (B) is getting hot. Heat moves from the hotter end to the cooler end through the metalbrod (from A to B). The heated end gets hot because the particles move with a very high energy. Those particles collide with their neighbors, giving them some of their energy. This bumping process continues until the increased motion has been transmitted to all the particles and the entire body has become hot because they have the same energy.
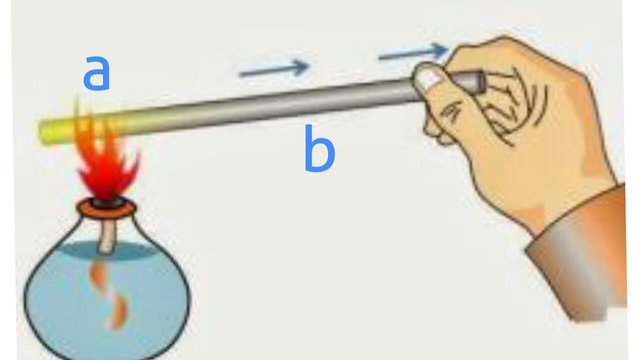
The heat transfer through a medium in direct physical contact without a flow of the medium's material is called conduction. Materials that can transfer heat feels well is called heat conductor, while materials that prevent heat transfer is called heat insulator.
Generally, metals such as iron, aluminum, copper, and brass are good conductors, meanwhile non-metal materials such as wood, plastic, and water are insulators.
2. Convection
Water and air are bad heat conductors (insulators). But, how can you explain why boiling water becomes hot and the air above a flame feels hot? Heat moves through water and air by convection. Thus convection or heat flow is the transfer of heat by particles motion due to density difference.
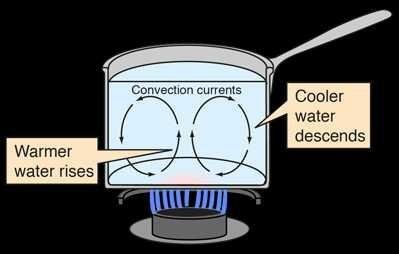
a. Convection on Liquid
Figure 2 shows the convection process in liquid. If the temperature of water increases, then its density decreases. Hotter water with a less density moves upward. Its place is replaced by more dense colder water which moves downward. The water flow can be obviously seen by dropping some coloring substance, such as purple potassium permanganate.
b. Convection on Gas
Convection on gas occurs when hotter air goes up and older water goes down. We can observe the air convection by using an apparatus as shown by Figure 3. If we light up the candle in the box, then the surrounding air is heated, so that the hot air goes up through the smokestack. Then its place is taken by the cold air which enters the box through the other smokestack. This occurs continuously which results an air flows.

The sea breeze and land breeze occur in shores due to air convection. At daytime, the land warms up quicker than the sea. This makes the hot air above the land rises and the cooler air above the sea flows to the land because the air pressure above the sea is higher than that above the land.
Thereby, the sea breeze blows from the sea to the land. Conversely, at night the land cools off quicker than the sea. This makes the hot air above the sea rises and the cooler air above the land flows to the sea. because the air pressure above the land is higher than that above the se Thereby, the land breeze blows from the land to the sea.
3. Radiation
On daytime on a bright and clear weather, you can feel the warmth of the sun. How can you still feel that, although the sun is located very far away from earth and there is a vacuum space between the earth and the sun? Heat transfer can still occur even without a medium. That kind of heat transfer is called radiation (emission).
The quantity of heat radiated or absorbed by a body depends on its color. A shining and bright colored body is a bad heat While darker body is a good heat absorber and emitter.
That is way our body will feel hot faster if we use a black shirt at daytime because black is a dark color which absorbs the heat from the sun well.
The Application of Heat Transfer Concept
We use the concept of heat transfer to build some we use in our every day life, such as flask, irons, etc. We boil water to get hot water. How can we maintain the temperature of the hot water? To keep the water hot, we put it in a vacuum flask. A vacuum flask is an instrument to hold heat. How does it work?
The flask cap is made of a heat isolator, such as cork, to prevent heat transfer by conduction, because cork is a bad heat conductor. Thus the water in the flask remains hot.
An iron is also made by using the concept of heat transfer. It changes the electrical energy into heat. Then the generated heat is conducted to an iron plate placed on the bottom of iron grip is made of heat the iron, because iron is good heat conductor. The isolator materials such as plastic or wood, to prevent the heat transfer on it, so the grip remains cold.
Sources :
Conduction, convection and radiation