How much does it cost to 3D scan an object?
3D scanning technology has become an important tool in many industries, whether in product design, digital cultural heritage protection, or customized medical devices, it has shown great value. So, for individuals or companies that need 3D scanning services, the issue of price is undoubtedly a key consideration. So, how much does it cost to 3D scan an object?
First of all, it should be clear that the price of 3D scanning will be affected by many factors:
1 The size and complexity of the object
The more complex the size and geometry of the object, the longer the scanning time will be. Large and complex objects often require higher resolution scanners and require more computing resources to process, which increases the cost.
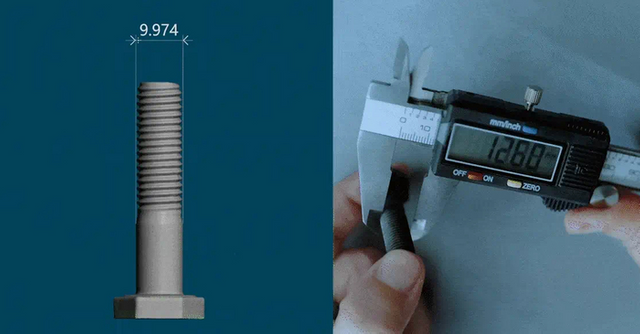
2 Scanning accuracy
Accuracy requirements are also an important price factor. For industrial-level applications that require high precision, such as reverse engineering of mechanical parts, higher-specification scanning equipment is usually required, and the cost will naturally rise. Scanning of works of art and everyday objects may not require such high precision, so the cost is relatively low.
3 Service Type
Customers can choose to purchase 3D scanning equipment and operate it themselves, or choose professional 3D scanning services. The cost of purchasing a 3D scanner depends on the type and brand of equipment. For example, Revopoint's portable 3D scanner has a relatively affordable starting price, which is very suitable for individual users or small businesses. If you choose a scanning service provided by a third-party company, the cost is generally calculated based on the number and size of objects and the difficulty of scanning.

https://www.revopoint3d.com/products/all-in-one-3d-scanner-miracoplus
4 Post-processing
After the 3D scan is completed, data processing is usually required, such as noise filtering, model repair, and texture addition. These post-processing are also important factors affecting the price. Some high-demand projects may require professionals to perform long-term post-processing, which will increase the cost.
5 Industry demand
The price difference between different application fields is also very large. For example, in the film and television industry, it usually costs more to make high-precision 3D models for visual effects. In education, medical and other fields, the requirements for scanning are relatively different, and the cost may be more flexible.
There is no uniform standard for the cost of 3D scanning, and its final price depends on the above factors. Generally speaking, a simple scan of a small object might cost between $50 and $100, while a large or complex project could cost $500 or more. If you need to use it for a long time, buying the right 3D scanner is also a cost-effective choice.