Exploring Classical Conditioning, A Behavioral Training Technique
Exploring Classical Conditioning, A Behavioral Training Technique

Image Source
Classical conditioning is a kind of finding that affected the school of thought in psychology known as behaviorism. Found by Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov, classical conditioning is a learning technique that occurs through connection between a natural stimulus and a really happening stimulus. But classical conditioning was not found by a psychologist by any methods, it had a giant effect over the school of thought in psychology known as behaviorism.
Classical conditioning includes setting a nonpartisan flag before an actually happening reflex. In Pavlov's great explore different avenues regarding canines, the unbiased flag was the sound of a tone and the actually happening reflex was salivating in response to sustenance. By partner the unbiased stimulus with the natural stimulus, the sound of the tone alone could create the salivation response.
Stages of classical conditioning
Stage 1: Before Conditioning
The initial segment of this procedure requires a normally happening stimulus that will consequently inspire a response. Salivating in response to the resemble sustenance is a decent case of a normally happening stimulus. Amid this period of the procedures, the unconditioned stimulus brings about an unconditioned response.
For instance, showing nourishment normally and naturally triggers a salivation response.
Now, there is additionally an unbiased stimulus that creates no impact - yet. It isn't until this impartial stimulus is matched with the unconditioned stimulus that it will come to inspire a response. We should investigate the two basic segments of this period of classical conditioning. The unconditioned stimulus is one that unequivocally, normally, and naturally triggers a response. For instance, when you notice one of your most loved sustenances, you may instantly feel exceptionally ravenous. In this case, the possess a scent reminiscent of the nourishment is the unconditioned stimulus.
Stage 2: During Conditioning
Amid the second period of the classical conditioning process, the beforehand impartial stimulus is more than once matched with the unconditioned stimulus. Accordingly of this blending, a relationship between the already impartial stimulus and the unconditioned stimulus is shaped. Now, the once nonpartisan stimulus ends up noticeably known as the molded stimulus. The subject has now been molded to react to this stimulus.
The molded stimulus is beforehand impartial stimulus that, in the wake of getting to be related with the unconditioned stimulus, in the end comes to trigger an adapted response. In our prior case, assume that when you noticed your most loved nourishment, you additionally heard the sound of a shriek. While the shriek is irrelevant to the possess an aroma similar to the sustenance, if the sound of the shriek was matched different circumstances with the odor, the sound would in the long run trigger the adapted response. For this situation, the sound of the shriek is the molded stimulus.
Stage 3: After Conditioning
Once the affiliation has been made between the unconditioned stimulus and the adapted stimulus, displaying the molded stimulus alone will come to inspire a response even without the unconditioned stimulus. The subsequent response is known as the molded response. The adapted response is the educated response to the already impartial stimulus. In our case, the molded response would be feeling hungry when you heard the sound of the shriek.
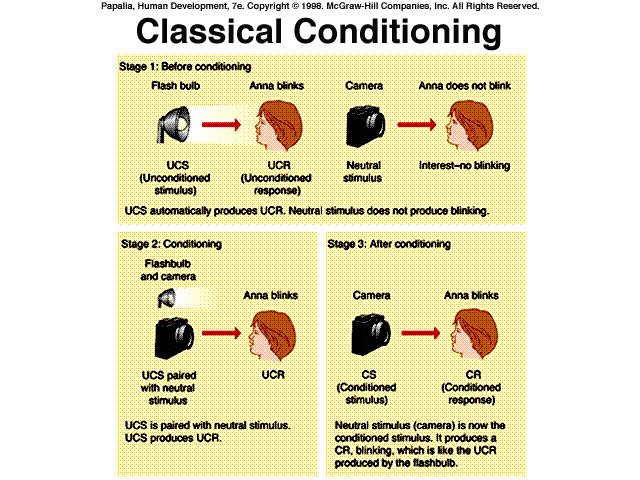
Image Source
Standards of Classical Conditioning
Acquisition
Acquisition is the underlying phase of realizing when a response is first settled and steadily fortified. Amid the acquisition period of classical conditioning, a nonpartisan stimulus is over and over matched with an unconditioned stimulus. As you may review, an unconditioned stimulus is something that actually and naturally triggers a response with no learning. After an affiliation is made, the subject will start to transmit a conduct in response to the already unbiased stimulus, which is presently known as a molded stimulus. It is now that we can state that the response has been gained.
Extinction
Extinction is the point at which the events of an adapted response diminishes or vanishes. In classical conditioning, this happens when an adapted stimulus is never again combined with an unconditioned stimulus.
Spontaneous Recovery
Now and again an educated response can all of a sudden reemerge even after a time of extinction. Spontaneous Recovery is the return of the adapted response after a rest period or time of diminished response. For instance, envision that subsequent to preparing a pooch to salivate to the sound of a ringer, you quit fortifying the conduct and the response in the long run winds up noticeably terminated. After a rest period amid which the adapted stimulus is not displayed, you all of a sudden ring the ringer and the creature spontaneously recoups the beforehand learned response.
Stimulus Generalization
Stimulus Generalization is the propensity for the molded stimulus to inspire comparable responses after the response has been adapted.
Stimulus Discrimination
Discrimination is the capacity to separate between a molded stimulus and other boosts that have not been combined with an unconditioned stimulus.

Image Source
References:
Principles of Psychology, Breedlove, SM.
Psychology: Concepts and Applications, Nevid, JS.
They sell clicker noise makers for dogs using this very approach. I have watched dogs as puppies grow up hearing this clicker and will automatically come running. However, I found that dogs that are in bred from a puppy mill have a learning disorder and no matter what you do, they just cannot grasp the concept, not just with the classic conditioning, but in most things such as walking, healing, etc. I studied this concept in my Psych 101 class at University. Thanks
You have an impressive thoughts about the topic but Im sorry, I was just using the picture of a dog but the content is intended for human behavior development. I don't know if this techniques also works with dog.
It totally does work for dogs. So much so that they made this clicker tool. I have seen first hand it work.
Good to know that. Thanks for the share.