DC motors.
DC motors are used mainly in cases where it is intended to control the speed of rotation in a continuous, accurate and simple way, they are also widely used where only have access to direct current through batteries as the case of automobiles . The number of magnetic poles of the stator (coils that generate the fixed field) must be the same as the rotor or the armature.
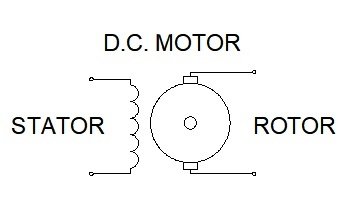
The control of the speed in these motors is done by varying the voltage applied to the stator, while torque is varied with the current flowing through the rotor.
Types of motor excitation according to their connection.
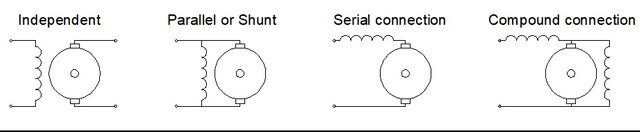
• Motor with independent excitation:
The stator and rotor windings are connected to two independent voltage sources to achieve independent control of motor speed and torque.
• Motor with parallel excitation:
The stator and rotor windings are connected in parallel to the same source, the motor speed remains constant. When the demand for torque increases due to the load, the current through the stator increases also causing the torque supplied by the motor to increase, ensuring great stability in its operation with variable mechanical loads.
• Motor with series excitation:
The windings of the stator and rotor are connected in series to the same source, the speed of the motor decreases as the excitation current increases, ie when the mechanical load increases. For very small currents the motor reaches very high speeds. It has a high starting torque since it varies with the square of the excitation current. Its main application is in motor machines of trains and cranes mainly
• Motor with compound excitation:
This type of configuration combines the advantages of the connection in series and the connection in parallel, is not used much due to the great possibility that the engine accelerates and increases its speed without control.