Top the Greatest Inventions of All Time (from new to old)
PERSONAL COMPUTER and THE INTERNET
Personal computers invented in the 1970s expanded human capabilities. One of the earliest PCs was introduced in 1974 by Micro Instrumentation and Telemetry Systems (MITS) via a mail-order computer kit called the Altair. From there, companies like Apple, Microsoft, and IBM have redefined personal computing.
While the worldwide network of computers has been in development since the 1960s, the Internet as we know it today is an even more modern invention. Global system of interconnected computer networks known as the Internet is used by billions of people worldwide. In the 1960s, a team of computer scientists working for the U.S. Defense Department's ARPA built a communications network to connect the computers in the agency, called ARPANET. It used a method of data transmission called "packet switching" which scientist Lawrence Roberts, a member of the team, developed based on prior work of other computer scientists. ARPANET was the predecessor of the Internet.
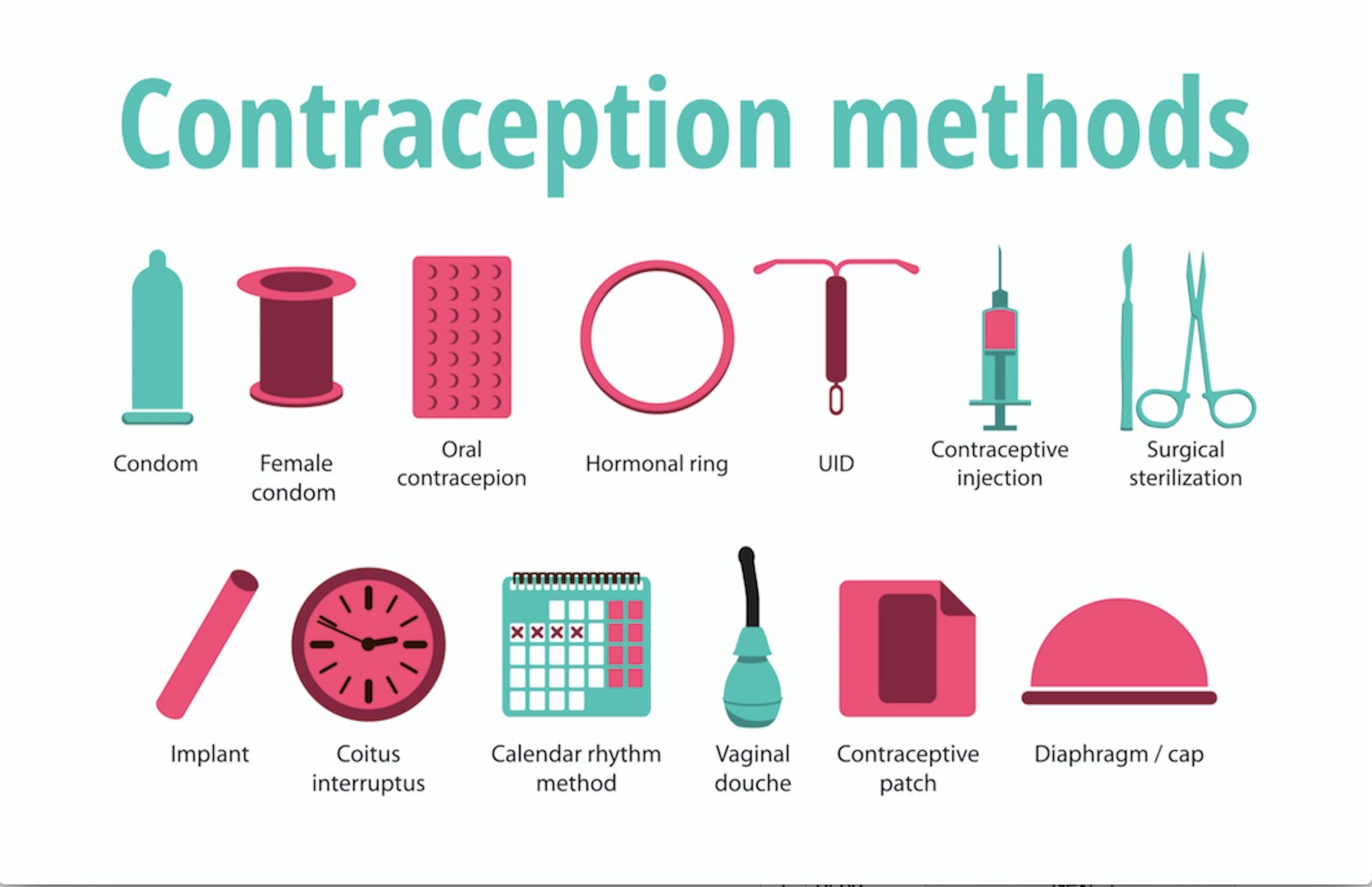
CONTRACEPTIVES
Not only have birth control pills, condoms and other forms of contraception sparked a sexual revolution in the developed world by allowing men and women to have sex for leisure rather than procreation, they have also drastically reduced the average number of offspring per woman in countries where they are used. Certain contraceptives, such as condoms, also curb the spread of sexually transmitted diseases. Condoms came into use in the 18th century. While the earliest oral contraceptive "the pill" was invented in the late 1930s by a chemist named Russell Marker.
VACCINATION and DEVELOPED the PENECILLIN
The first vaccine (for smallpox) was developed by Edward Jenner in 1796. A rabies vaccine was developed by the French chemist and biologist Louis Pasteur in 1885, who is credited with making vaccination the major part of medicine that is it today.
In 1928, the Scottish scientist Alexander Fleming noticed a bacteria-filled Petri dish in his laboratory with its lid accidentally ajar. The sample had become contaminated with a mold, and everywhere the mold was, the bacteria was dead. That antibiotic mold turned out to be the fungus Penicillium, and over the next two decades, chemists purified it and developed the drug Penicillin, which fights a huge number of bacterial infections in humans without harming the humans themselves. It began the era of antibiotics.
The TELEPHONE
Though several inventors did pioneering work on electronic voice transmission , Alexander Graham Bell was the first to be awarded a patent for the electric telephone in 1876. The invention quickly took off, and revolutionized global business and communication. When Bell died on Aug. 2, 1922, Scottish-born inventor Alexander Graham Bell got the first patent for an electric telephone in 1876. Certainly, this instrument has revolutionized our ability to communicate.

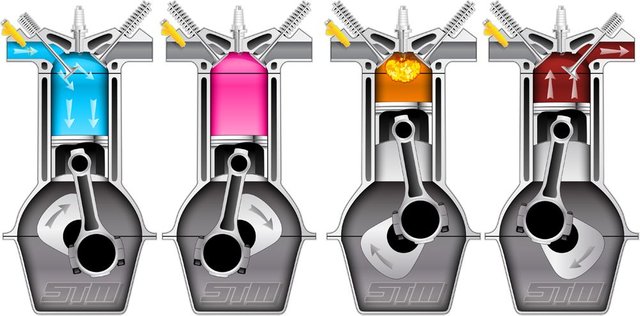
ELECTRICITY and The INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE
It’s hard to overestimate how important electricity has become to humanity as it runs the majority of our gadgetry and shapes our way of life. The invention of the light bulb is certainly a major extension of the ability to harness electricity. It has profoundly changed the way we live, work as well as the look and functioning of our cities.
The 19th-century invention (created by Belgian engineer Etienne Lenoir in 1859 and improved by Germany's Nikolaus Otto in 1876) the engine ushered in the Industrial Age, as well as enabling the invention of a huge variety of machines, including modern cars and aircraft.
Thus, combustion engines convert chemical energy into mechanical work. Elon Musk's electric car company Tesla, among others, is currently trying to revolutionize technology in this arena once again
PAPER and PRINTING PRESS
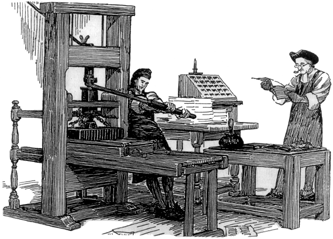
PAPER - invented about 100 BC in China, paper has been indispensible in allowing us to write down and share our ideas. The German Johannes Gutenberg invented the printing press around 1440. This revolutionized the spread of knowledge and religion. Because this movable type process, printing presses exponentially increased the speed with which book copies could be made, and thus they led to the rapid and widespread dissemination of knowledge for the first time in history.
The COMPASS
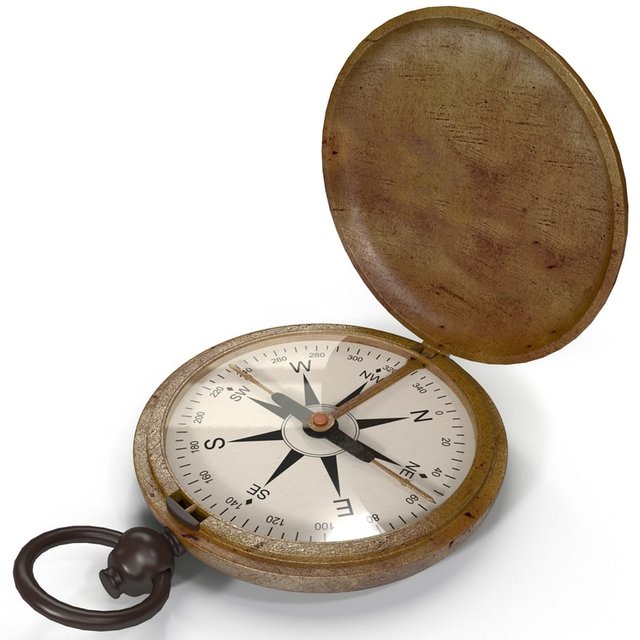
Ancient mariners navigated by the stars, but that method didn't work during the day or on cloudy nights, and so it was unsafe to voyage far from land. Compass- this navigational device has been a major force in human exploration. The earliest compasses were made of lodestone in China between 300 and 200 B.C. The compass enabled mariners to navigate safely far from land, increasing sea trade and contributing to the Age of Discovery.

OPTICAL LENSES
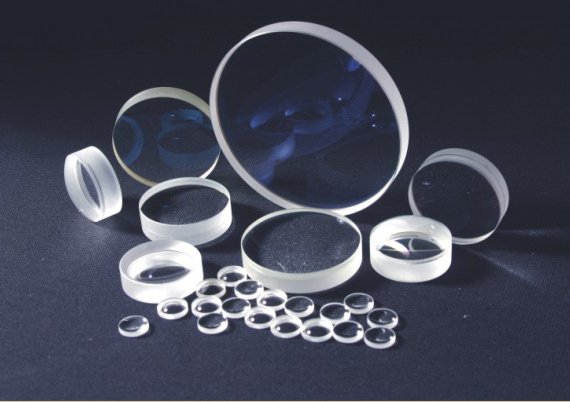
OPTICAL LENSES - from glasses to microscopes and telescopes, optical lenses have greatly expanded the possibilities of our vision. Optical lenses were also instrumental components in the creation of media technologies involved in photography, film and television.

The WHEEL
Before the invention of the wheel in 3500 B.C., humans were severely limited in how much stuff we could transport over land, and how far. It to be used in the creation of pottery. About 300 years after that, the wheel was put on a chariot and the rest is history. Wheels are ubiquitous in our everyday life, facilitating our transportation and commerce. Wheeled carts facilitated agriculture and commerce by enabling the transportation of goods to and from markets, as well as easing the burdens of people traveling great distances

Really good list!
could have added 'fire' down the bottom too :p
Thanks!:) I had been thinking about fire but the other things are are more materialistic. I mean fire is natural thing and human just found how to tame and to use it )
Haha too true :)
Great answer