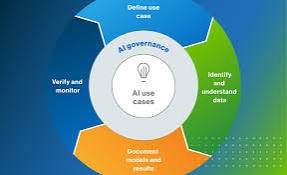
AI Governance Framework
An AI Governance Framework is a structured approach for managing and regulating the development, deployment, and use of artificial intelligence systems. It aims to ensure that AI technologies are safe, ethical, transparent, and aligned with societal values. A comprehensive AI Governance Framework typically includes a variety of components to manage risk, compliance, accountability, and stakeholder engagement across the lifecycle of AI systems.
Key Components of an AI Governance Framework
Ethics and Values Alignment
- Establish principles for ethical AI use, including fairness, transparency, accountability, and privacy.
- Define societal and organizational values to guide AI development and applications.
- Ensure AI systems respect human rights and avoid discrimination or bias.
Risk Management
- Identify potential risks related to AI applications, such as operational risks, reputational risks, and privacy risks.
- Implement strategies to assess, mitigate, and monitor risks throughout the AI lifecycle.
- Set up escalation procedures for handling risks as they arise.
Accountability and Transparency
- Define clear roles and responsibilities for AI governance, including accountability structures.
- Document AI decision-making processes to allow for transparency in automated decisions.
- Implement explainability measures to clarify AI models and their decision logic.
Data Governance
- Establish policies for data collection, processing, storage, and usage that comply with privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA).
- Ensure data used for AI is accurate, relevant, and representative.
- Implement controls to prevent misuse or unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Compliance and Regulatory Adherence
- Monitor evolving regulations and standards (e.g., EU AI Act, NIST guidelines) to ensure compliance.
- Develop policies to align with regulatory requirements for data protection, transparency, and AI safety.
- Set up audit mechanisms to verify compliance and address non-compliance issues.
Stakeholder Engagement
- Include diverse stakeholder perspectives to guide AI development, including customers, employees, and impacted communities.
- Create mechanisms for stakeholders to provide feedback and express concerns.
- Ensure that AI deployments consider the interests and rights of those affected by AI-driven decisions.
Model Performance and Monitoring
- Develop metrics and benchmarks to monitor AI system performance, accuracy, and reliability.
- Implement ongoing monitoring processes to detect model drift or performance degradation.
- Establish thresholds for retraining or modifying models as necessary.
Security and Privacy
- Integrate cybersecurity best practices to protect AI systems from malicious attacks or tampering.
- Use privacy-preserving techniques, such as differential privacy or federated learning, to safeguard user data.
- Conduct regular security assessments to address vulnerabilities in AI systems.
Lifecycle Management and Change Control
- Develop protocols for managing the AI lifecycle, including development, deployment, and decommissioning.
- Implement change management policies to oversee updates or changes in AI models or data sources.
- Ensure that AI systems are retired responsibly, considering data retention and system archiving needs.
Bias and Fairness Audits
- Conduct periodic audits to assess potential biases in AI algorithms and data.
- Implement corrective actions when biases or disparities are detected.
- Promote inclusivity in data collection and model design to ensure equitable outcomes.
Steps to Implementing an AI Governance Framework
Define Scope and Objectives
- Identify the types of AI systems in use and their impact on the organization and stakeholders.
- Set objectives for AI governance based on organizational goals, regulatory requirements, and ethical considerations.
Establish Governance Structure
- Create a governance committee or assign roles for oversight, compliance, and risk management.
- Designate a Chief AI Officer (or equivalent role) to oversee AI governance.
Develop Policies and Procedures
- Draft policies covering data management, risk assessment, ethical standards, and compliance.
- Provide clear guidelines for AI system development, deployment, and monitoring.
Implement Training and Awareness Programs
- Train employees on AI ethics, governance policies, and responsible AI practices.
- Conduct awareness programs to ensure stakeholders understand AI impacts and governance standards.
Monitor and Evaluate
- Set up mechanisms to regularly assess the effectiveness of governance practices.
- Adjust the framework as necessary to respond to new risks, technologies, and regulatory changes.
Benefits of an AI Governance Framework
- Reduced Risk: Helps identify and mitigate risks before they impact the organization.
- Improved Trust and Transparency: Builds stakeholder trust by providing clarity on AI use and decision-making.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures adherence to legal standards and reduces the risk of fines or sanctions.
- Ethical Assurance: Supports the development of AI that aligns with ethical principles and social values.
- Operational Efficiency: Provides clear guidelines, reducing confusion and enhancing consistency across AI projects.
Implementing an AI Governance Framework is essential as organizations increasingly rely on AI-driven decisions. The framework can evolve to keep up with technological advances, allowing for responsible innovation.