Workshop - Chemistry of happiness - DOPAMINE
Hello again dear @steem.skillshare friends,
I would like to publish, from now on, in a form of workshop my studies about happiness.
I'm trying to follow a scientific approach and not purely psychological or spiritual, this doesn't mean that I give less importance to the last two approaches but for now I would like to get deep into the first one!
Previous posts
- https://steemit.com/hive-197809/@vik24/how-to-build-a-food-plan-to-regain-a-good-mood
- https://steemit.com/hive-197809/@vik24/how-to-live-a-healthy-and-happy-environment-at-home
Main chemicals of happiness
- Dopamine
- Ossitocine
- Serotonin
- Endorfine
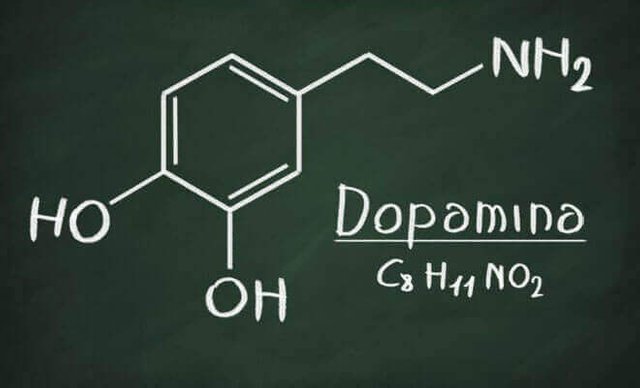
DOPAMINE
What is it
Dopamine is an organic molecule, an important neurotransmitter (substances defined as chemical messengers because they allow the cells of the nervous system, neurons, to communicate with each other) of the catecholamine family, which performs a function of control over different physical and psychic processes at the level of the Central and Peripheral Nervous System.
For example: movement control, working memory, reward and pleasure mechanisms, prolactin production, sleep regulation mechanisms, some cognitive faculties and attention span, mood control, basis of learning, but dopamine also acts as a vasodilator, stimulating the excretion of sodium through the urine, promotes intestinal motility, reduces lymphocyte activity and insulin secretion.
It is the precursor molecule from which cells also derive two other important neurotransmitters of the catecholamine family: norepinephrine (or noradrenaline) and epinephrine (or adrenaline).
In the human body the production of dopamine is mainly due to the neurons of the dopaminergic area, which are located in different regions of the brain between the telencephalon and the midbrain: nucleus accumbens, substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area (which includes the prefrontal cortex, the amygdala and hippocampus), posterior hypothalamus, pituitary and, to a lesser extent, the adrenal glands.
How does it work
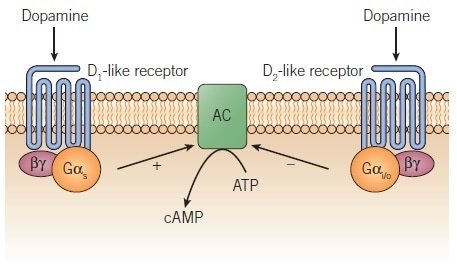
After its release into the synaptic space, dopamine exerts its effects by interacting with the so-called dopaminergic receptors, present on the membrane of different nerve cells.
In mammals, and therefore also in humans, there are 5 different types of dopaminergic receptors.
Among the many functions that it performs, it has been seen how dopamine is a mediator of pleasure and reward: the brain of the human being releases dopamine when he "experiences" pleasurable activities, such as eating good food or having satisfying sexual activity.
Because it is released from the brain when we feel gratification and satisfaction, it is able to affect behavior.
The reward
This is the dopaminergic reward circuit: that is, a mechanism that consists in repeating what produces feelings of gratification and well-being and discarding what does not.
Our brain, every time we experience moments of pleasure, releases dopamine, which works as a reinforcement.
Precisely because we are led to seek and recreate the sensations that made us feel satisfaction, dopamine sets up what is called the reward circuit, or the reward circuit, pushing us to repeat the behaviors that have given us pleasure and triggering the well-known mechanism of addiction.
The reward circuit works precisely with the release of dopamine, in order to seek gratification again, both physical and psychological.
It is safe to say that dopamine is therefore the neurotransmitter responsible for motivation, associative learning, positive emotions, especially those involving pleasure as a fundamental component (joy, euphoria and ecstasy) and the reward-seeking behavior, essential for neuroblastic change, which is the process that allows the formation of a habit or an addiction.
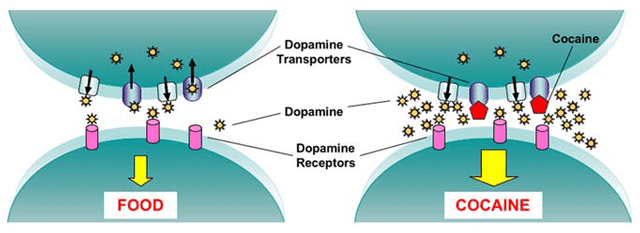
An excessive dosage of the hormone, a predisposition to the so-called "addiction": essentially an excessive dose of dopamine alters the control system in the mechanisms that regulate pleasure, gratification and reward.
Addictions are therefore a question of dopamine: addiction to any substance of abuse (natural such as food, sport, sex or artificial, which procure a release of dopamine starting from something unnatural, for example alcohol and drugs, nicotine, sucrose contained in junk food or even the approval seeking mechanism created by social networks), is the result of a change in neuronal plasticity, i.e. modifications in the normal physiology and biochemistry of cells of the brain.
Dependence on a substance causes the person to search for the substance to perceive its effect. And it has such an effect as to push those who use it to take it more and more and more often, that is, to abuse it. By regularly taking a substance of abuse, the release of dopamine is stimulated, transmitting a feeling of pleasure and well-being that leads to repeat the experience.
The chronic and prolonged activation of the dopaminergic neurons of the "reward system" (due to the continuous intake of drugs of abuse) can lead to changes in the functions of this system that cause an alteration of the perception of pleasure. All this translates into the perception of a strong and urgent need, in English craving, to take the substance, to restore a feeling of well-being that you feel you have lost.
But the dopaminergic neural circuits of the Central Nervous System are not only involved in generating the sensation of pleasure characteristic of hedonistic experiences. In reality, the function they perform is much more complex and not associated only with the sensation of pleasure: scientific studies underline that the dopamine circuit linked to the mechanism of gratification, so important for understanding our motivational system and behavioral choice, is a structure of "dependent experience" learning.
Who is able to "shape" our motivations in obtaining positive hedonistic or eudaemonic experiences ("high" experiences of seeking well-being and happiness that include the hedonistic feeling but are not limited to it).
In the human brain the neural networks involved in this motivational process realize the learning "dependent experience" which in fact modifies epigenetically the neurons that include dopamine receptors in their structure.
The evolution of the studies of Epigenetic Psychology is therefore leading to a distinction between the neural circuits of pleasure (defined as “like” circuits) from those relating to the motivation to pursue a reward (“want” circuits). In a nutshell, the dopaminergic circuit functions as a fundamental apparatus for research aimed at the replication of experiences that also involve pleasure but not only: the perception of oneself, recognition, the sense of one's own existence.
After the foregoing, it is easy to understand how anyone who is able to control the "dopamine market" can produce loyal consumers and secure significant economic income: it is estimated that the total dopamine business (alcohol, legal and illegal drugs, junk business food) amounts to hundreds of billions of dollars. Not to mention the stratospheric income of the business that revolves around the dysfunctional behaviors generated by social networks.
Defense against addiction
The only defense mechanism against addictions, against dopaminergic addiction, remains the awareness that comes from information, from knowledge.
Be aware, for example, that dopaminergic circuits do not only influence hedonistic behaviors linked to addiction but also those that promote the establishment of positive habits for our health: good practices in sport, nutrition, the use of technology.
If it is true that all forms of addiction are characterized by a specific configuration of the dopaminergic circuit, it is equally true that this does not in itself mean a greater probability of developing addictive behaviors: in fact the greater activation of dopaminergic neurons in correspondence with hedonistic emotions can also lead to the promotion of positive behaviors for health and psychophysical well-being.
The functional aspect
Finally, it should not be forgotten that all hedonistic experiences also have a functional aspect relating to the management of the stress experienced at that moment, due to the effect of the activation of the neural circuits that release endorphins.
If a person is perceiving a situation of distress (i.e. negative stress), the main motivation in seeking (and obtaining) an experience linked to the sensation of pleasure, by activating the neurons that contribute to the production of endorphins, may be precisely this: the consequent lowering of negative stress perceived at the moment, even if this effect will be short-lived.
This concept clarifies how the dynamics of behaviors linked to the reward system, both pathological and not, are so strongly integrated in the psycho-neuro-endocrine-immunological systems, which mutually influence each other in our organism.
Conclusions
Much remains to be understood about the way in which molecules, dopamine in the first place, structurally and functionally change the neural reward circuits and this understanding will be crucial for the development of areas of psychology such as Epigenetic Psychology, which studies the influence of psychoemotional aspects. on the cellular level of our organism.
The advancement of scientific research will therefore be fundamental to effectively promote interventions to promote psychophysical well-being as well as for the treatment of pathological situations.




Wow, we often pay attention to anything but not to our mental condition which is so important to us humans. You do great to write so informative and interesting content!
It is an awesome tutorial! Thanks for this contribution!
That was a nice write up,it really in understanding human system and mode and go it work hand in hand with our physical out look,i must say am really interested in the area of neurons because it one of my best subject in school
This is such an informative post, and quite a coincidence because today I was listening to a podcast of Tom Bilyieu interviewing Dr Andrew Huberman and he was talking about exactly this topic. He was saying that for people to be successful, they have to understand Dopamine has to be used for motivation. It's not something we can appreciate solely as a reward. Thanks @Vik24