Introduction to Basic Electronics
 Captured by @manuelhooks
Captured by @manuelhooks
Introduction to Basic Electronics
Electronic devices rule today's world and we really can't do without electronics, they are fun, facinating and useful, and have recently become very intelligent. This devices are found everywhere and are doing almost everything. They are made up of small lifeless componentes that work together to create amazing gadgets.
In this basic electronic post, I will be cutting deep into electronics to reveal those components that make our electronics. Follow me as I take a deep dive into the world of electronics and explor the building blocke that brings them to life.

Workshop 1
Electronic Symbology:
Most electronic devices start their life as a concept in someones mind or as an upgrade to an existing system. The idea and working principle is often represented on paper, using universally accepted circuit symbols interwoven to create a circuit diagram which can be interpreted and constructed.
Below are examples of circuit symbols you will likely see in a circuit diagram. They were all designed using PhotoStudio.
Alternating current.
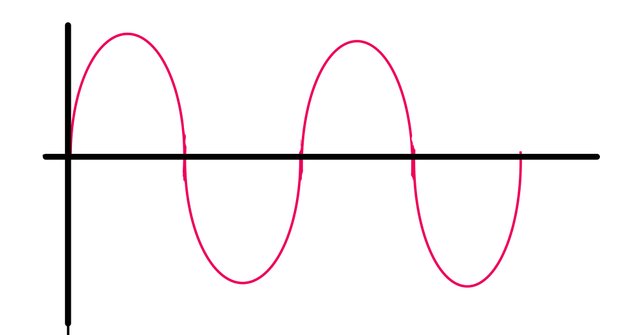 The red wave here represents alternating current.
The red wave here represents alternating current.
 Circuit symbol for AC Voltage and AC Current.
Circuit symbol for AC Voltage and AC Current.
Direct current.
 The red line here represents direct current.
The red line here represents direct current.
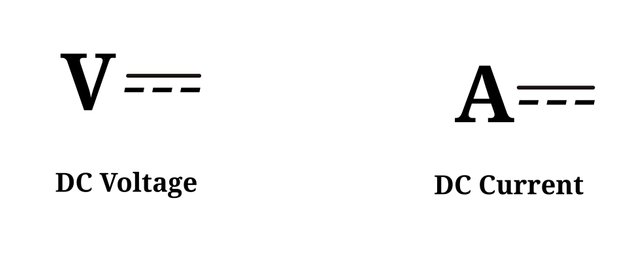 A circuit representation of DC Voltage and DC Current.
A circuit representation of DC Voltage and DC Current.
Amperage.
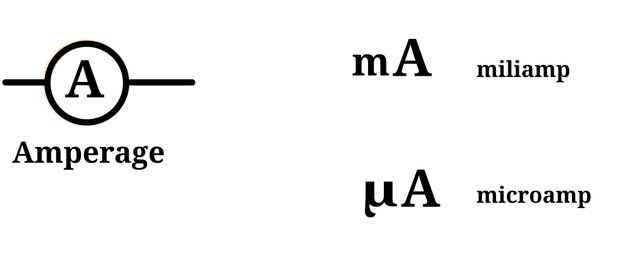 Amperage is sometimes measured in mili or micro amp.
Amperage is sometimes measured in mili or micro amp.
Resistance
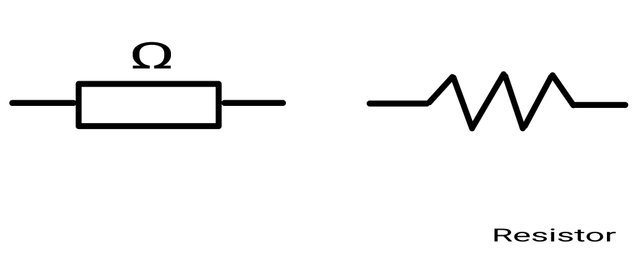 Resistors are represented as a rectangle or a wavy line
Resistors are represented as a rectangle or a wavy line
Potentiometer or variable resistor
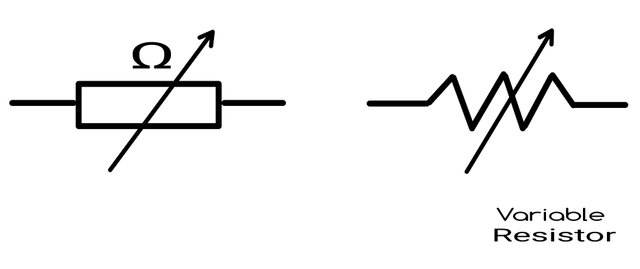 Represented as a resistor with an arrow cutting the middle.
Represented as a resistor with an arrow cutting the middle.
Rectifier diode
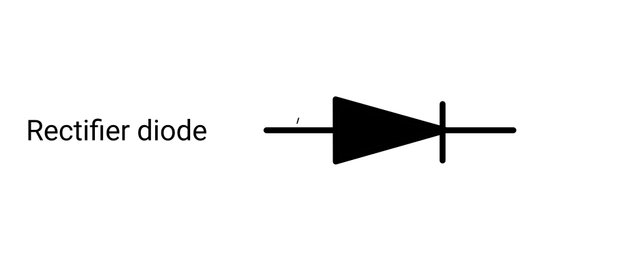 Diode pointing to direction of flow
Diode pointing to direction of flow
Zener diode.
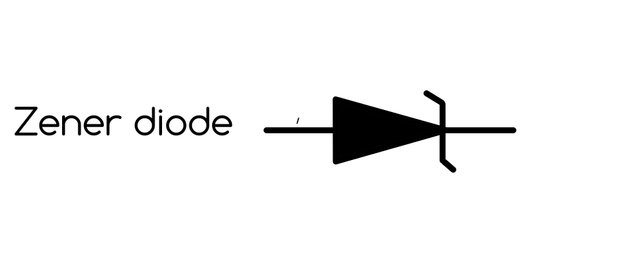 Zener diode with something like a z in front of its symbol
Zener diode with something like a z in front of its symbol
LED diode
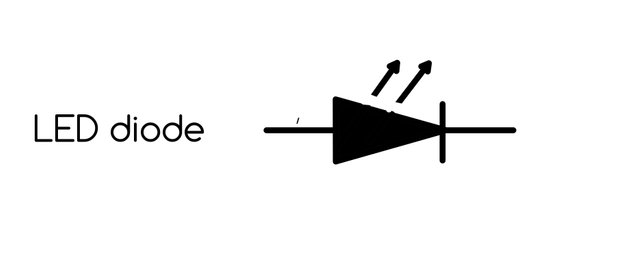 Light Emitting Diode
Light Emitting Diode
Diode bridge
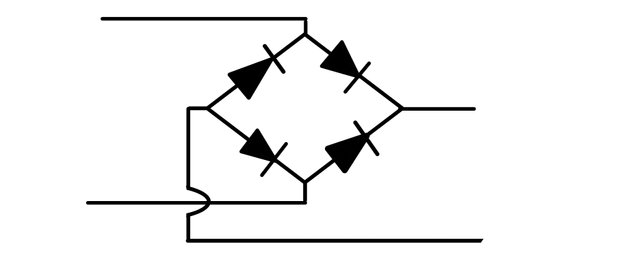 Four diodes arranged as a Rectifier
Four diodes arranged as a Rectifier
Electrolytic capacitor
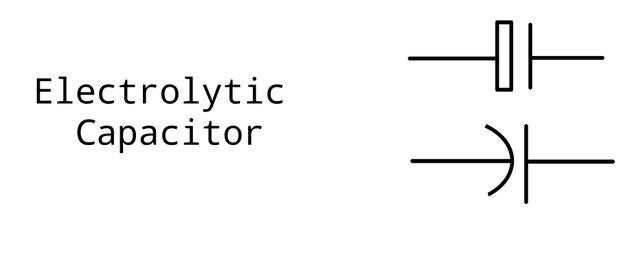 A polarised component with one side being positive.
A polarised component with one side being positive.
Ceramic Capacitor
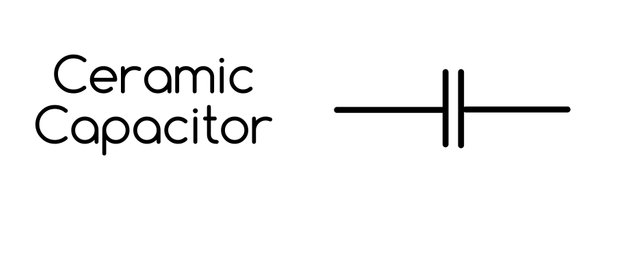 A non polarised component with no polarity.
A non polarised component with no polarity.
Coil
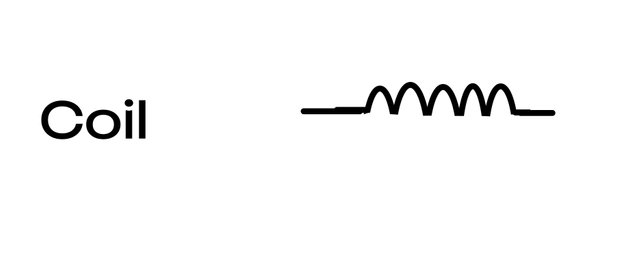 An inductor coil.
An inductor coil.
Fuse
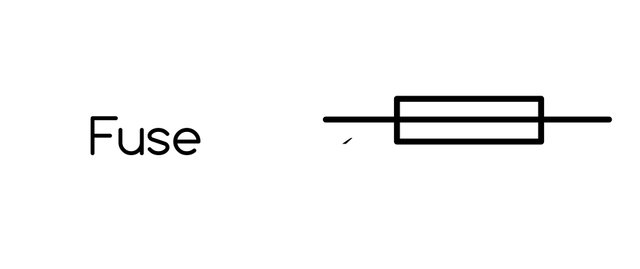
Transformer.
 An iron core transformer
An iron core transformer
Battery.
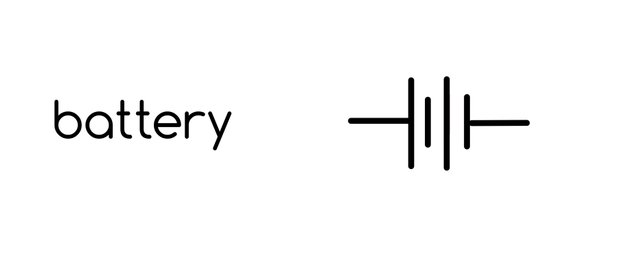 A two cell battery
A two cell battery
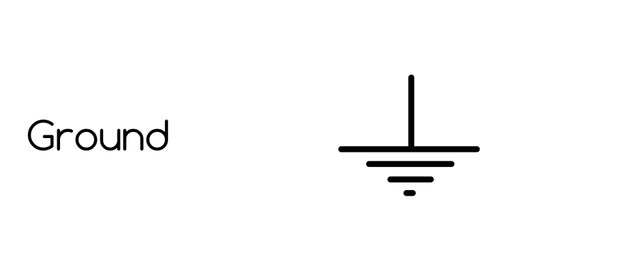
Ground.
NPN and PNP transistor
Motor
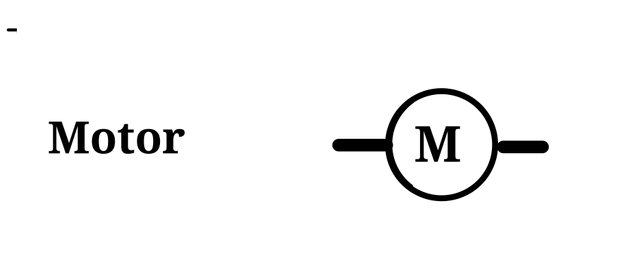

Workshop 2
**Alternating Voltage. **
This is a type of electrical energy that switches polarity between positive and negative continously, it is the type of power that comes from generator. In nigeria the power grid provides 140 voltes of alternating current.
Direct Voltage
This type of electrical energy maintains its polarity at all time and travels in one direction such that one cable is positive and the other remains negative without switching.
Resistance
This is anything that restricts the free flow of electric current. A resistor is a component that creates resistance to the free flow of electric current in a circuit.
Potentiometer
This is a type of variable resistor that has a nub which can be used to vary the resistance across its terminals.
Rectifier diode:
This is an electronic component that restricts the flow of electronic current to a single direction.
Diode bridge:
This is mostly made up four Rectifier diodes arranged in such a way that it directs the flow of electric current thereby converting an alternating current into a direct current in a process called rectification.
Capacitor:
This is an electronic conponent that stores charges and can quickly discharge the stored charges, some capacitors are used as filters and are also used to create resonance and timing.
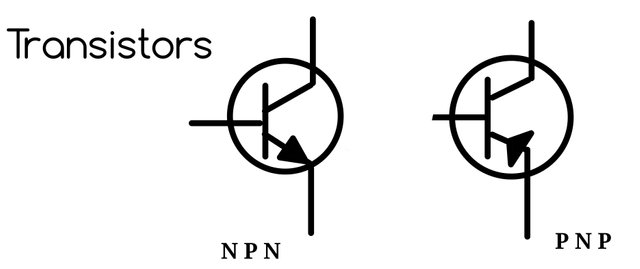
Transistor:
This is an active component in an electronic circuit that acts as an amplifier or as a switch in digital electronics.
Transformer:
A transformer is a coupled device that either steps up or steps down voltage or current. They are also used to isolate sections of a circuit. Transformers work using the principle of induction.
Fuse:
A fuse is a safety mechanism that is design to protect a circuit for excessively high power.
Lithium battery:
This is a type of reservoir that holdes power and used Lithium-Ion as one of its key component.

Workshop 3
Resistors:
Resistors are basically devided into Fixed Resistors and Variable resistor.
When looking at their make-up, we can have metal film resistors, wirewound resistors, metal oxide resistors, Carbon Composition Resistors etc.
Capacitors:
Capacitors can be grouped as fixed and variable capacitore, we can also arrange them as electrolitic capacitors that have polarity and those that have no polarity like ceramic capacitor.
Diodes:
Power diodes
Zener diodes
Diode bridge
Light Emitting Diode
Tunnel diodes
Photo diodes
PN junction diode
Transistor according to their encapsulation:
Through-Hole transistors are the usual transistors with legs that gets into holes on the board and are soldered on the other side.
Surface-Mount transistors are solderd on top of the board, they don't go out of the other side of the board.
Dual-In-Line transistors (DIL) have connectors on two opposite sides of the transistormuch like the regular IC.
Small-Outline transistors (SOT) small rectangular transistors that are surface mounted with short legs.
Power Transistors transistors with huge metal heat sinks to cool it down.
BGA (Ball Grid Array) Transistors these are surface mounted rectangular chip with small connectors on one side. After soldering to the board its connectors are not visible.
Coils
Iron core: a coil with iron in the middle.
Air core: only coil with no iron in the middle.
Coupled Inductor: two coils side by side
Soft Ferrite Core Inductor: coil with black material in the middle
Hard Ferrite Core Inductor: coil with hard ferrite

Component Identification
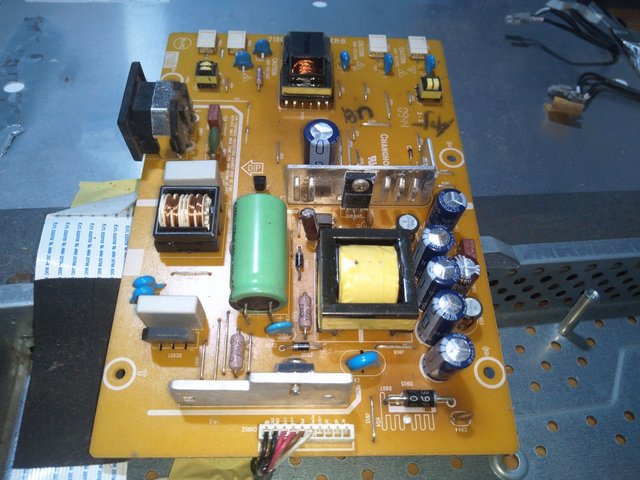 Image from Electronics Academy
Image from Electronics Academy
Identifing the various components on this board,
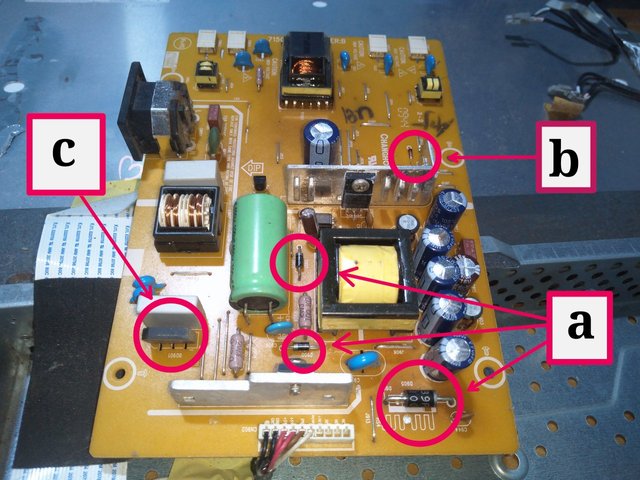 Image from Electronics Academy edited with PhotoStudio
Image from Electronics Academy edited with PhotoStudio
a = Power diode
b = Zener diodes
c = Diode bridge
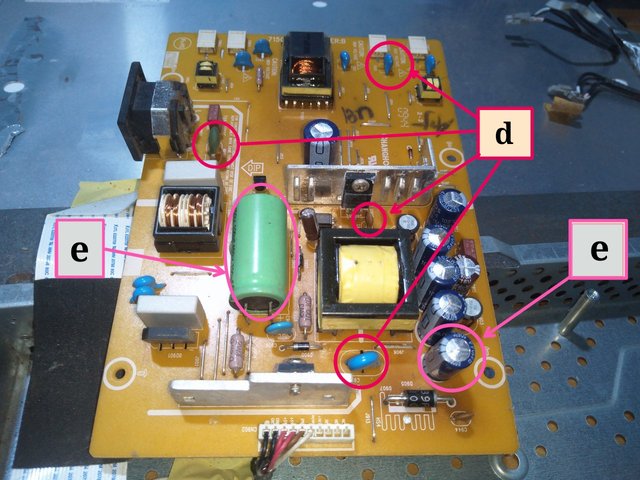 Image from Electronics Academy edited with PhotoStudio
Image from Electronics Academy edited with PhotoStudio
d = Ceramic Capacitors
e = Electrolitic Capacitors
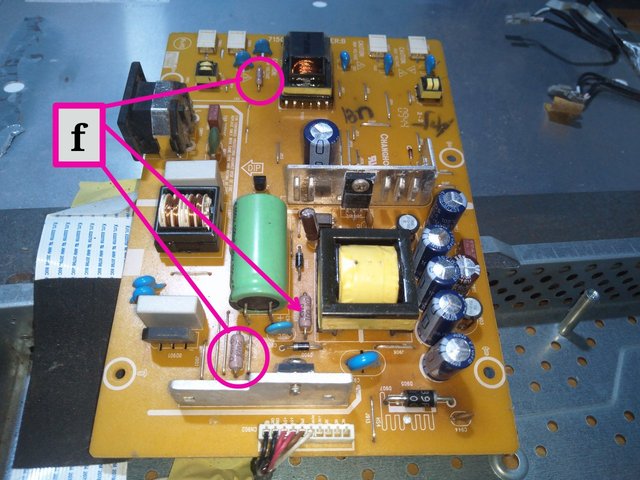 Image from Electronics Academy edited with PhotoStudio
Image from Electronics Academy edited with PhotoStudio
f = Fixed Resistors
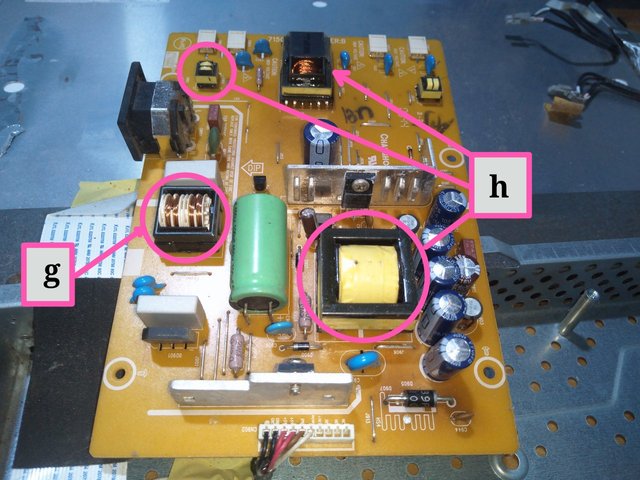 Image from Electronics Academy edited with PhotoStudio
Image from Electronics Academy edited with PhotoStudio
g = Coupled Inductor
h = Transformer
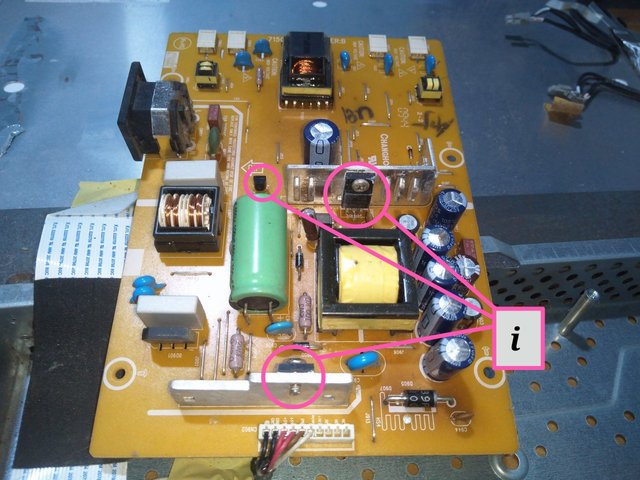 Image from Electronics Academy edited with PhotoStudio
Image from Electronics Academy edited with PhotoStudio
i = Transistor
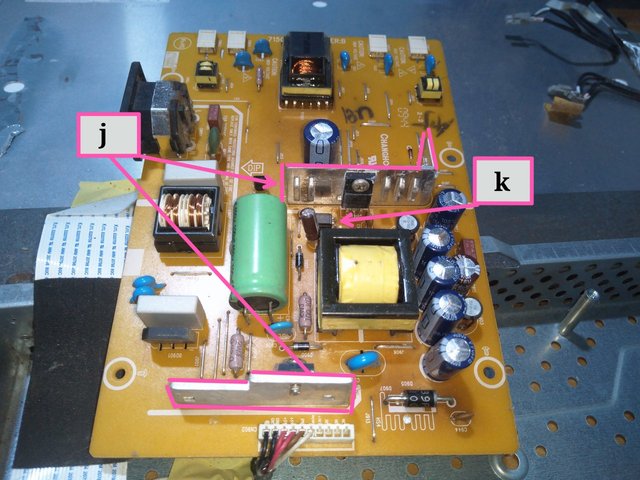 Image from Electronics Academy edited with PhotoStudio
Image from Electronics Academy edited with PhotoStudio
j = heat sink
k = Opto isolator
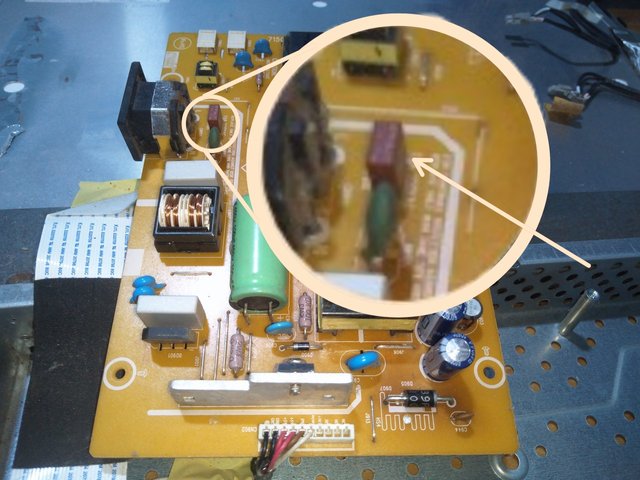 Image from Electronics Academy edited with PhotoStudio
Image from Electronics Academy edited with PhotoStudio
fuse
I got this board from an old Logik television for the purpose of identifing some components on it.
 Captured with Galaxy-A15
Captured with Galaxy-A15
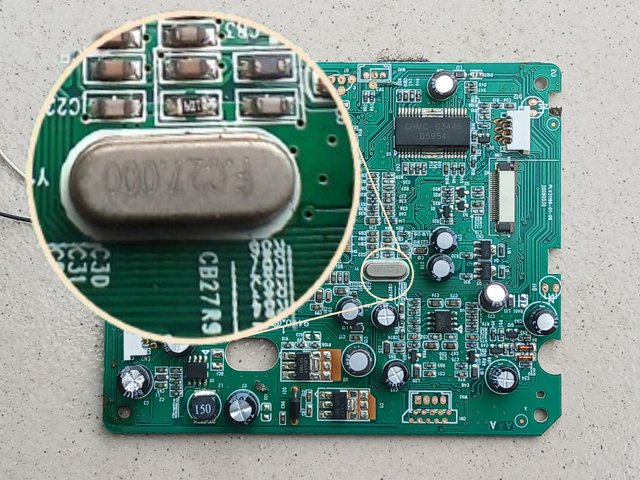 Captured with Galaxy-A15 and edited with PhotoStudio
Captured with Galaxy-A15 and edited with PhotoStudio
Oscillator
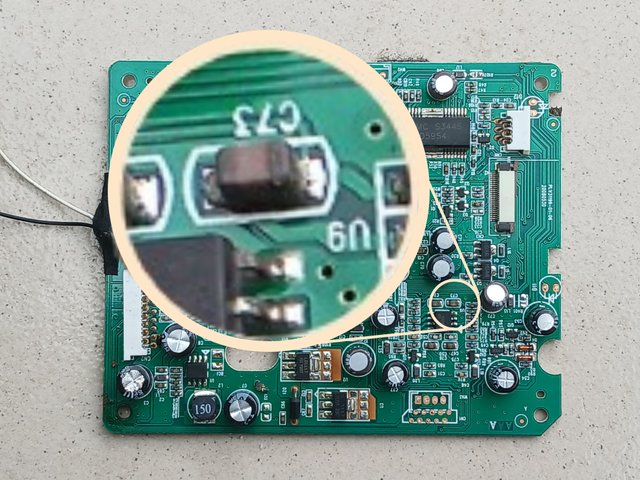 Captured with Galaxy-A15 and edited with PhotoStudio
Captured with Galaxy-A15 and edited with PhotoStudio
Surface mounted capacitor
#electronicss19w1 #steemexclusive #nigeria #burnsteem25 #electronics #club5050
My husband studied short term in electronics and I found notes like this.
Thank you for sharing
Saludos amigo, al principio de las tareas tuviste pocos desaciertos pero te ha ocurrido esto por no seguir al pie de la letra las actividades.
Cómo técnicos debemos leer bien, seguir las instrucciones para no desviarnos o hacer maniobras erradas. Paciencia, buena visión y organización.
Las definiciones fueron claras y concisas, directo al punto.
En la identificación de componentes también tuviste una buena actuación, viste componentes que otros no habían logrado detectar.
Sin embargo me hubiese gustado que identificaras más elementos en tu tarjeta SMD ya que los de montaje superficial suelen ser físicamente distintos a los de hueco pasante.
Tuviste un buen comienzo, esfuérzate más. Recuerda somos Las Águilas de la Electrónica.
I appreciate the correction and comendations, i will read between the lines of the instruction and adhear to it. I love electronics, i have got most of the recommended tools and belive i will really benefit a lot from this class.
Greetings @manuelhooks
What an awesome post it is! You have done all the worksheets extraordinary. I am so much surprised after seeing your post. Keep us the good work like this. Wishing you many more successes in life.