Vacuum Blood Collection
Hello Steemit users
Hope you all will be safe and sound. As a medical lab technologist i'am going to share toady about Vacuum Blood Collection.
Introduction:
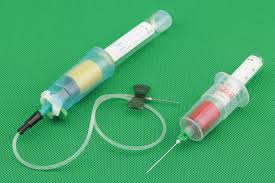
- The vacuum blood collection system consists of a double pointed needle, a plastic holder or adapter, and a series of vacuum tubes with rubber stoppers of various colors.
- The evacuated tube collection system will produce the best blood samples for analysis.
- The blood goes directly from the patient vein into the appropriate test tube.
Multi-Sample Needle
- The bevel is the slanted opening at the end of the needle.
- Needle length (shaft) ranges from 1 to 1 ½ inches.
- Threaded hub screws into needle holder.
- The rubber sheath makes it possible to draw several tubes of blood by preventing leakage of blood as tubes are changed.
Bevel
- Bevel is slanted opening at end of needle.
- Needle must be oriented so that bevel faces up prior to insertion.
Needle Gauge
- The gauge of a needle is a number that indicates the diameter of its lumen.
- The lumen, also called the bore, is the circular hollow space inside the needle.
- The higher the gauge, the smaller the lumen.
- The most frequently used gauges for phlebotomy are 20, 21 and 22.
Holder
- The holder for vacuum blood collection is a plastic sleeve into which the phlebotomist screws the double pointed needle.
- The most current guidelines require that all holders are for single use only.
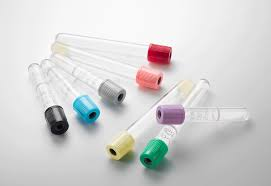
Vacuum Collection Tubes
- Vacuum collection tubes are glass or plastic tubes sealed with a partial vacuum inside by rubber stoppers.
- The air pressure inside the tube is negative, less than the normal environment.
- After inserting the longer needle into the vein, the phlebotomist pushes the tube into the holder so that the shorter needle pierces the stopper.
- The difference in pressure between the inside of the tube and the vein causes blood to fill the tube.
- The tubes are available in various sizes for adult and pediatric phlebotomies.
Additives
- Different blood tests requires different types of blood specimens.
- Most tubes have additives called anticoagulants which prevent clotting/coagulation of the blood.
- Plastic tubes may have an additive to enhance clotting of the blood.
Anticoagulants
- Anticoagulants are already in the tubes in the precise amount needed to mix with the amount of blood that will fill the tube.
- The color of the stopper on each tube indicates what, if any, anticoagulant the tube contains.
- It is important to completely fill each tube so that the proportion of blood to chemical additive is correct, otherwise, the test results may not be accurate or the specimen will be rejected and will need to be recollected.
- It is also important to thoroughly mix the blood with the additive by gentle inversion.
Red
- No additive in glass tube
- Clot activator in plastic tube
- No anticoagulant present
- Tests using serum which include: most blood chemistries, AIDS antibody, viral studies, serology tests, Blood Bank testing.
Red and black mottled (SST)
Hemogard = Gold
- SST = Serum Separator Tube
- silicone/gel (serum separating material)
- All tests using serum except Blood Bank
Red and black mottled (SST)
- Using BD SST Tubes
- Purpose of gel is to separate serum from cells permanently.
(Light) Blue
- Additive - Sodium Citrate
- Tests drawn: Coagulation studies: PT, PTT and fibrinogen
- MUST BE FILLED COMPLETELY!!! NO EXCEPTIONS
Lavender Top Tube
- Additive = EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic)
- Hematology studies: CBC, WBC count, Hemoglobin, Hematocrit, Platelet count, Reticulocyte count, differential.
Green
- One of the following: sodium heparin, lithium heparin or ammonium heparin.
- STAT blood chemistries utilizing plasma.
Green PST
- Additive is heparin
- PST = Plasma Separator Tube
- Has gel which, after centrifugation, permanently separates plasma from red blood cells.
Gray
- Additive (read label):
- Potassium oxalate and sodium fluoride,
- or lithium iodacetate and heparin
- Glucose, Blood Alcohol (ethanol) levels, lactic acid.
Black
- Buffered Sodium Citrate
- Westergren sedimentation rate determination
- MUST BE FILLED COMPLETELY!!! NO EXCEPTIONS.
Yellow
- Sodium polyanethol sulfonate (SPS)
- SPS for blood culture specimen collections in microbiology.
- Tube inversions prevent clotting.
- Acid citrate dextrose additives (ACD)
- ACD for use in blood bank studies, HLA phenotyping, DNA and paternity testing.
Blood Cultures
- Not for laboratory analysis, special collect ion to detect bacteria growing in blood.
- Site preparation VERY important.
- Will be covered later.
Sort: Trending
Loading...