Cryptocurrency formation
Crypto! Crypto! Crypto!
What is the cryptocurrency?
In the running world where ever you go. you can hear this sound crypto or cryptocurrency.
If you ask any one 95% people says don't know.
4% or above said digital currency means BITCOIN or NETELLER or Skrill etc.
and rest of % , less than 1% or .10 % actually knows about cryptocurrency.
believe it or not, 90% of those knowledgeable person who actually know about cryptocurrency are not to ready to share this other person.
rest of 10% ready to share it whole world. I respect them.
Now a days world became small by technology. you can find definition of cryptocurrency though internet.
but it is not at all knowledge.
Today i am going to tell you about cryptocurrency in my little knowledge.
Now see the begging history of cryptocurrency
Since 1983, One American cryptographer, name David Chaum. He conceived an pseudonym cryptographic electronic money, and called it e-cash. after 12 years in 1995, he implement it. and named Digicash.
This is the Starting path of cryptocurrency
In the following years, 1996,1997, 1998, its activities increased day by day.
at last the result came out in 2009, first decentralized cryptocurrency, bitcoin, was created by using Hash function SHA-256. This is the breakthrough invention created by Satoshi Nakamoto.
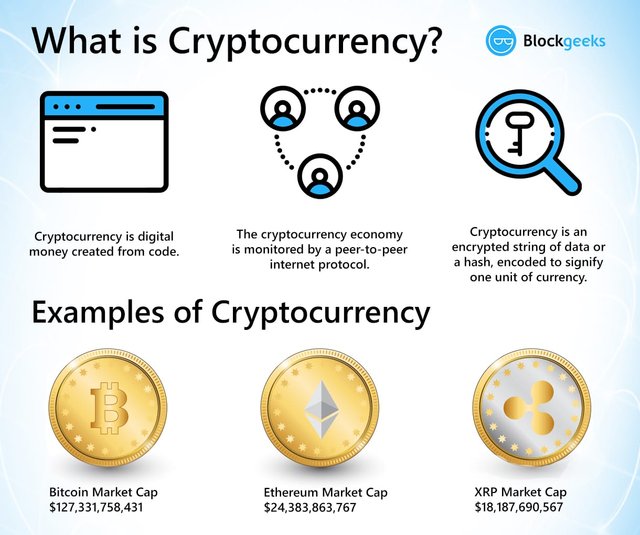
What is cryptocurrency?
cryptocurrency is best thought of digital currency for the digital age. cryptocurrency is similar to regular money — think $ or € . it used cryptographical functions and conduct financial transactions. but, it’s only digital, So, here is no money or coins to carry out.
Formal definition of Cryptocurrency
According to Jan Lansky, a cryptocurrency is a system that meets six conditions:
- The system does not require a central authority, its state is maintained through distributed consensus.
- The system keeps an overview of cryptocurrency units and their ownership.
- The system defines whether new cryptocurrency units can be created. If new cryptocurrency units can be created, the system defines the circumstances of their origin and how to determine the ownership of these new units.
- Ownership of cryptocurrency units can be proved exclusively cryptographically.
- The system allows transactions to be performed in which ownership of the cryptographic units is changed. A transaction statement can only be issued by an entity proving the current ownership of these units.
- If two different instructions for changing the ownership of the same cryptographic units are simultaneously entered, the system performs at most one of them.
Source of this information
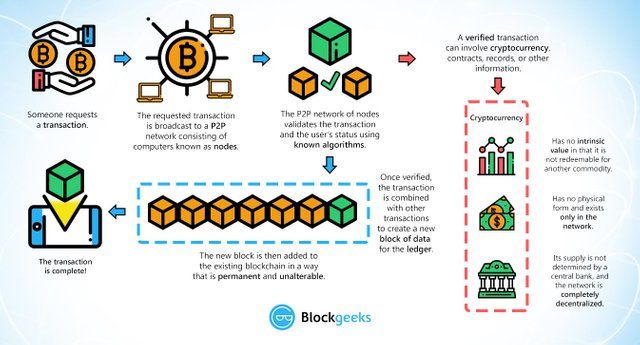
How cryptocurrency work?
Announcing the first release of Bitcoin, a new electronic cash system that uses a peer-to-peer network to prevent double-spending. It’s completely decentralized with no server or central authority. – Satoshi Nakamoto, 09 January 2009, announcing Bitcoin on SourceForge.
Source
Transactions are sent between peers using software called “cryptocurrency wallets.” The person creating the transaction uses the wallet software to transfer balances from one account (AKA a public address) to another. To transfer funds, knowledge of a password (AKA a private key) associated with the account is needed. Transactions made between peers are encrypted and then broadcast to the cryptocurrency’s network and queued up to be added to the public ledger. Transactions are then recorded on the public ledger via a process called “mining” (explained below). All users of a given cryptocurrency have access to the ledger if they choose to access it, for example by downloading and running a copy of the software called a “full node” wallet (as opposed to holding their coins in a third party wallet like Coinbase). The transaction amounts are public, but who sent the transaction is encrypted (transactions are pseudo-anonymous). Each transaction leads back to a unique set of keys. Whoever owns a set of keys, owns the amount of cryptocurrency associated with those keys (just like whoever owns a bank account owns the money in it). Many transactions are added to a ledger at once. These “blocks” of transactions are added sequentially by miners. That is why the ledger and the technology behind it are called “block” “chain.” It is a “chain” of “blocks” of transactions.
TIP: I’ve just described how Bitcion works and how many other coins work too. However, some altcoins use unique mechanics. For example some coins offer fully private transactions and some don’t use blockchain at all.
Source of this information
Another time I try to told about blockchain.
List of Market Leading cryptocurrency
1.Bitcoin (BTC) – It allows for online payments without depending on third parties.
Ethereum (ETH) – It introduced smart contracts to the blockchain. It processes transactions quickly and inexpensively and runs smart contracts.
Ripple (XRP) – Ripple aims to improve the speed of financial transactions. It is considered one of the biggest cryptocurrencies in the world as it currently comprises of more than 150 people.
Stellar lumens (XLM) – This network uses blockchain to speed up international payments for a small transaction fee.
Bitcoin Cash (BCH) – It enabled the block size to be increased from 1 MB to 8 MB. Its goal is to increase the number of transactions.
EOS – While ethereum involves a fee for every interaction or modification with the network, the DAPP (Decentralized app) creator foots the bill, and the user doesn’t pay anything.
LiteCoin (LTC ) – It is a peer-to-peer platform designed to handle a larger number of transactions for a lower cost.
Cardano (ADA) – It focuses on interoperation with other cryptocurrencies by fixing issues such as scalability and democratized voting.
Monero (XMR) – It implements cryptonic hashing of receiving address thereby separating the coin from the address it is going to.
Tether (UDST) – It aims to fix legal issues and protects people from market volatility.
Dash (DASH) – Short for digital cash, it instantly sends funds through double-send-proof security.
TRON (TRX) – It enables users to freely publish, store, and own data thereby vesting them with the power to decide where and how to share.
NEO – It aims to digitize many types of assets and aims to make it possible for use in smart contracts.
Binance Coin (BNB) – It uses its cryptocurrency platform, Binance, to process 1.4 million orders per second.
IOTA (MIOTA) – When issuing a transaction in IOTA, two previous transactions are validated. This saves computing power and coins, rather than when done by miners.
Ethereum Classic (ETC) – It helps implement decentralized apps and smart contracts.
NEM (XEM) -New Economy Movement (NEM) aims to help companies create customizable blockchains with their ‘smart asset system.’
VeChain (VET) – It focuses on eliminating counterfeiting in industries such as automobiles, food, and fashion.
Zcash (ZEC) – It is a value transfer protocol which shields the amount transferred and the senders, thereby making transactions anonymous.
Tezos (XTZ) – It works to create a cryptocurrency ‘commonwealth’ where holders have the ability to vote in new protocols.
Bitcoin Gold (BTG) – It allows users to employ Graphic Processing units (GPU) and lower the entry barrier for new miners.
OmiseGo (OMG) – It seeks to speed up the way money is sent and received, both nationally and internationally.
Maker (MKR) – It is a revolutionary approach to digital money which eliminates large price volatilities in coins.
Dogecoin (DOGE) – It is used for microtransactions and for tipping on articles.
Ox (ZRX) – It is a decentralized, open-source smart contract system which acts as an infrastructure.
QTUM (QTUM) – It is a value transfer platform which focuses on mobile decentralized apps.
Decred (DCR)– It aims to solve the problem of blockchain governance. It uses a unique PoW and PoS to decentralize the decision-making process.
Ontology (ONT) – It creates an integrated protocol system with its main focus on trust, date exchange authorization, and identity. Users can easily find protocols that help with transactions.
Zilliqa (ZIL) – It aims to solve the issue of scaling in public blockchains. As nodes increase, its ability to handle high transaction volumes will increase.
Lisk (LSK) – It helps developers deploy their own side chains which are fully customizable.
BitShares (BTS)– It uses a decentralized exchange for dealing with transactions and funds.
NANO (Formerly RaiBlocks) – It aims to tackle scalability issues. It helps in increasing transaction speed and minimizing overheads.
Bitcoin Diamond (BCD) – It is a currency which focuses on private transactions.
Aeternity (AE) – It keeps security and efficiency intact through creating a consensus mechanism to process information.
BAT – Basic Attention Token (BAT) rewards advertisers and publishers who provide high-quality content to users.
Bytecoin (BCN) – It offers unlinkable transactions, resistance to blockchain analysis, and untraceable payments.
Pundi X (NPXS) – It is hardware, Point-of-Sale system to enable payment using wallet apps.
ICON (ICX) – It is a high-performance blockchain which provides real-time transactions based on enhanced smart contracts.
SiaCoin (SC) – It allows users to rent out their unused hard drive thereby reducing the overhead costs of cloud storage.
Digibyte (DGB) – Its uses five secure and advanced cryptographic mining algorithms for preventing centralized mining.
Steem (STEEM) – Its platform incentivizes users to create high-quality content. Micro-rewards are provided for upvoting, liking, and sharing.
Aurora (AOA) – It is a smart contracts platform which aims at facilitating easy creation of Dapps.
Verge (XVG) – It is designed for private transactions. The public addresses of the transactions are not visible.
Bytom (BTM) – It was created to transfer assets to the byteworld from the atomic world.
Populous (PPT) – It is a global invoice trading platform which connects business owners and invoice buyers through security, speed, and transparency.
Chainlink (LINK) – It applies smart contracts to the outside world by creating APIs which are compatible with off-chain-based software.
Metaverse ETP (ETP) – It helps users create their own identity and also to create and store digital assets.
Waves (WAVES)– It helps even a person without coding experience to create their own blockchain token.
Golem (GNT) – Its plans to create an open-source, global supercomputer which can be used by anyone with internet access. It lends out unused computational power for a fee.
Augur (REP) – Using the concepts of game theory and wisdom of the crowd, it achieves greater forecasting accuracy.
© All rights reserved for this References Blog
https://blockgeeks.com/guides/what-is-cryptocurrency/
https://www.genesis-mining.com/how-cryptocurrency-works
https://cryptocurrencyfacts.com/how-does-cryptocurrency-work-for-beginners/
https://www.blockchain-council.org/blockchain/the-top-50-cryptocurrencies/




because of Participate @sbdpotato beneficiary experiment
10% beneficiary of author on this post will go to @sbdpotato account.

Find this article on twitter with tag #steem #steemit #posh #ocdb #photo #my2020 #steemonboarding #NewYork #crypto for promoting #steemit to other social media.
https://twitter.com/ShaikAkram2470/status/1216717222367899649