Industrial Revolution 4.0
Fourth Industrial Revolution, Industry 4.0 encompasses three technological trends driving this transformation- connectivity, intelligence, and flexible automation.

Industry 4.0 describes the growing trend towards automation and data exchange in technology and processes within the manufacturing industry, including- The Internet of Things (IoT), The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Cyber-physical Systems (CPS), Smart Manufacturing, Smart Factories, Cloud Computing, Additive Manufacturing, Big Data, Robotics, Cognitive Computing, Artificial Intelligence & Blockchain, etc.
This automation creates a manufacturing system whereby the machines in factories are augmented with wireless connectivity and sensors to monitor and visualize an entire production process and make autonomous decisions.
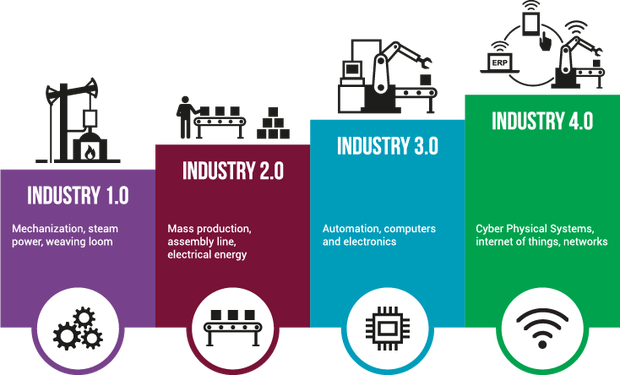
Evolution of the Industrial Revolution?
The first industrial revolution came with the advent of mechanization, steam power, and water power.
The second industrial evolution revolved around mass production and assembly lines using electricity.
The third industrial revolution came with electronic and IT systems and automation.
The fourth industrial revolution is associated with cyber-physical systems.

Impact of Industry 4.0 post-Covid - 19?
Industry 4.0 is not only as relevant as it was before the global COVID-19 emergency; it is actually far more relevant moving forward.
COVID-19 is causing radical shifts in workflow across the globe as millions practice social distancing and comply with self-quarantine recommendations.
The integration of digital infrastructure to streamline public health to respond to the COVID-19 pandemic is very crucial in the context of epidemic forecasting and decision-making,
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has demonstrated the value of IT and digital transformation across industries and businesses and they must utilize this time to speed up the transition.