Grassroot Crypto Education (Vol.4) - Cryptography: Private-Key Encryption, Public-Key Encryption and Hash Functions | 10% payout to @steemkidss
Introduction
It's another great time to drop another piece for the kids in the community. From the previous classes, the performance of the users that participated shows that a lot has been learned and it gladdens my heart. So far, kids have been able to learn what is cryptocurrency, understand Bitcoin, Altcoins & Stablecoins,, and Market capitalization. At this point, it's important to teach cryptography, a technology used in cryptocurrency. Join me, kids!
Designed with Adobe Photoshop
Cryptography
Cryptography can be simply defined as the art of solving problems but going deeper into this context, means more than that. Cryptography is the study of the sharing of confidential information between individuals in such a way that only the sender and the intended recipient can see the content or a means of communicating securely in the presence of outsiders without exposing the content of the communication, as such, the details can only be unlocked by the users involved by using certain cryptographic elements.
In short, Joe and Jane can communicate in the presence of Joanna and Jude, while the latter group won't have access to the details of the conversation. This technology is employed in cryptocurrency which brings about many characteristics like confidentially, integrity, authenticity, and so on, in the crypto ecosystem. To understand this technology better, we would talk about the types of cryptography.
Types of Cryptography
In this section, we would be discussing distinctively three types of cryptography, namely; Private-key encryption, Public-key encryption, and Hash functions. And this would open your sight to the application of cryptography in cryptocurrency. Let's take them one by one.
Private-Key (Symmetric) Encryption
It's important to expose you to what encryption means, encryption is the process by which readable messages or plain texts are converted to a code such that it prevents outsiders from seeing the details of the message. Now, Private-key encryption utilizes a single key (private/secret key) to encrypt and the same key is used to decrypt at the destination. Decrypting means solving the code product of encryption back to its original form.
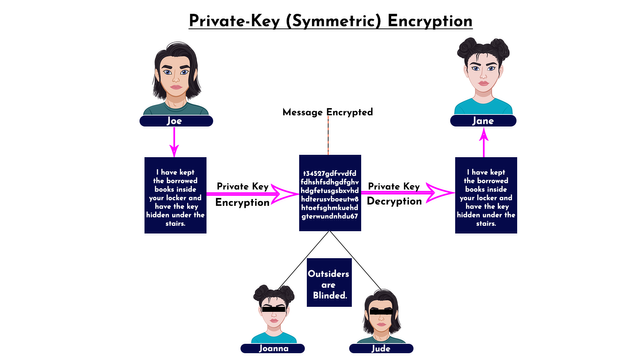
In essence, the sender of the message encrypts with the secret key or private key and shares the same key with the trusted receiver who decrypts at the destination, in that way, the details of the message is not leaked to the outsiders. Take a look at the illustration below.
Designed with Adobe Photoshop
The illustration above shows how Joe sent an encrypted message "I have kept the borrowed books inside your locker and have the key hidden under the stairs" to Jane using the private key. Joanna and Jude are outsiders in the transaction, as such, they were blinded from seeing the details. At the destination, Jane used the same private key to decrypt the message. In short, a single key (private key) is being used for both encryption and decryption in this type of cryptography.
Public-key (Asymmetric) Encryption
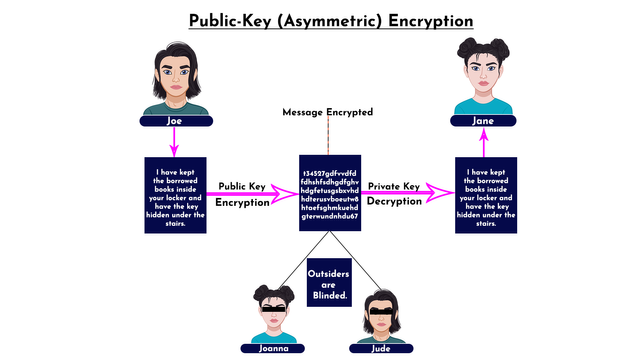
Public-key encryption differs from the first type of cryptography discussed, instead of using the same key for encryption and decryption, two keys are involved in public-key encryption. In essence, one key is used for encryption while the other is used for decryption. In this type of cryptography, the public key is used to encrypt the message by the sender while the private key is used to decrypt the message by the receiver. Let's take a look at the illustration below.
Designed with Adobe Photoshop
From the illustration above, Joe sent a message "I have kept the borrowed books inside your locker and have the key hidden under the stairs" to Jane, the message was encrypted with a public key and that blinded Joanna and Jude from seeing the details of the message. At the destination, Jane decrypted the code with a private key and the details were revealed to her. Notably, two keys were used in this case which differs from the first type of encryption.
Hash Functions
Hash functions are the cryptography type employed in cryptocurrency, which is an irreversible and one-way function, such that data stored about a particular cryptocurrency transaction cannot be reversed. In that case, the originally inputted data can't be recovered through tweak or editing or any form of altering.
That said, Hashing is a product of the function such that the data of an entire transaction is converted into fixed-length string "Hash" which is an alphanumeric (alphabets and numbers) combination. In hashing, each input gives different outputs which means it becomes hard or impossible to cook up a fake transaction. Let us take an example below.
- The website I will be using for the example is https://andersbrownworth.com/blockchain/hash, it's a demo website for study. Now I will input two different inputs, consider inputs as transactions. Let's see how it goes.
- For the first one, I inputted School as the input and for the second one, my input is Town. Let's see the result below.
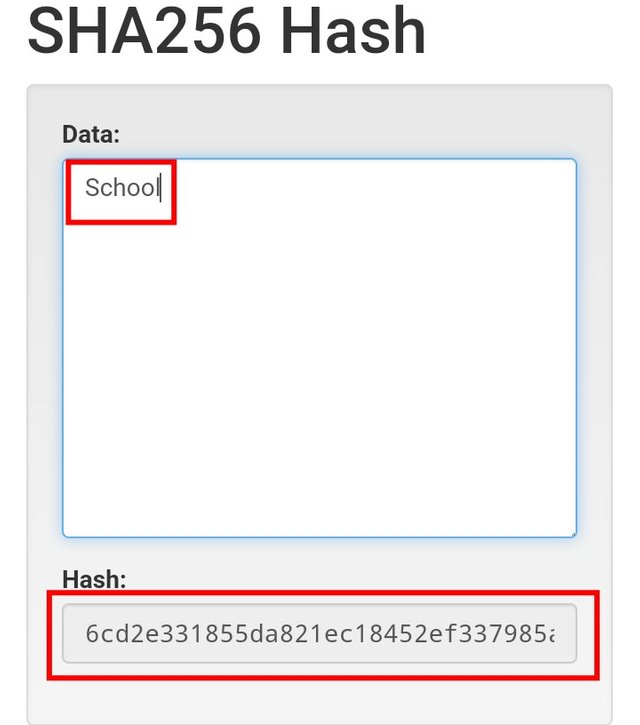
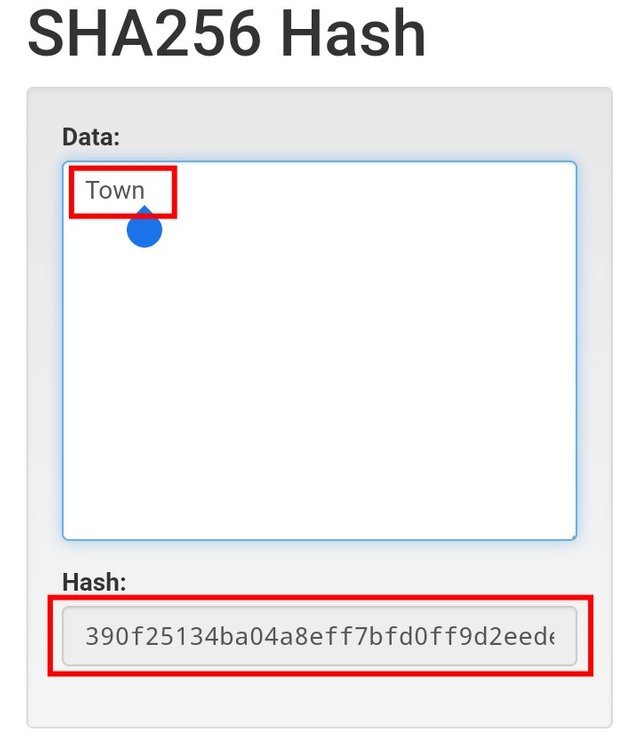
The School input has the output hash "6cd2e331855da821ec18452ef337985a5dc2f2ee6eb0bc2b0c894768d5a95c32" while the Town input has the output hash "390f25134ba04a8eff7bfd0ff9d2eede5f8b139fb6af326732f2f57c2b210e83". From the result;
- Both input have different Hash which means two different inputs will always have different hash and in that way, it's not possible to reverse the input that produced the hash.
- No matter the length of the input, the output comes with a fixed length hash even though the length of the inputs differs. If you count both generated above, it is 64.
Conclusion
In the first volume of the grassroot crypto education, we have talked about cryptography as a technology employed in cryptocurrency which makes many curious about what the technology is. In today's volume, I have exposed you to cryptography which is a secure communication technology to keep details of a message hidden from outsiders. I believe you have something tangible added to you today and I will be waiting for your participation. Thank you.
Homework Task
- Define Cryptography. Explain Private-Key Encryption, Public-Key Encryption, and Hash Functions. What is the distinctive difference between Private-Key Encryption and Public-Key Encryption? .
- What happens to outsiders if a message is encrypted? Give a brief example. Visit https://andersbrownworth.com/blockchain/hash, enter two different inputs, and show your observation. (Screenshot required).
Guidelines
- Write an article of at least 250 words. Keep your explanation as simple as possible.
- Include the tags #grassroot-education4 and #crypto among the first 4 tags. Also, tag me @fredquantum in your homework entry.
- For Verified Steem kids alone.
- I will check your articles and drop comments on the entries submitted now till 11:59 pm UTC, 12/02/2022.
Cc:-
@steemkidss
@steemitblog
@steemcurator01
@steemcurator02
Wonderful lesson again from you @fredquantum. The kids are really very lucky to have you as their crypto professor. Cryptography is very important in crypto education. I wish the kids success as they are going to take part in this lesson
Thanks for acknowledging this piece of work, @ngoenyi. Yes, it's important to teach the kids the technology behind cryptocurrency, as such, they would properly understand how some of the characteristics of crypto are achieved through this technology. Thanks once again, ma'am.
My entry sir
https://steemit.com/hive-139765/@ronindboss/3m4js3-homework-task-or-or-grassroot-crypto-education-vol-4-cryptography-private-key-encryption-public-key-encryption-and-hash
Unfortunately, I won't be able to rate your homework entry at this moment as the community found out you have been involved in content farming. Maybe some other time when you have the case settled. Thank you.
I am glad to be able to take part in this homework task.
Here is my assignment sir:
https://steemit.com/hive-139765/@madilyn02/grassroot-crypto-education-vol-4-cryptography-private-key-encryption-public-key-encryption-and-hash-functions-or-or-assignment
Hi @fredquantum
Here is my entry. Sorry for the delay, the post did not go through till this morning
https://steemit.com/hive-139765/@chimeroselam/4swty-grassroot-crypto-education-vol-4-cryptography-private-key-encryption-public-key-encryption-and-hash-functions-or-10-payout-to
https://steemit.com/hive-139765/@bossj23/grassroot-crypto-education-vol-4-cryptography-private-key-encryption-public-key-encryption-by-bossj23-or-or-10-payout-to
👍🏼