Grassroot Crypto Education | Series 2 Volume 11 - Forks in the Crypto Ecosystem | (#burnsteem25)
Introduction
It all happened like a blink of an eye, the series 2 of our crypto education has entered the 11th volume, and how awesome the journey has been. I appreciate the community, @steemkidss for granting us the space to do the job here and to the Steemit team, the support from time to time is well appreciated. Let's dive into today's topic of discussion, Forks in the Crypto Ecosystem.

Designed with Adobe Photoshop
Forks in the Crypto Ecosystem
The word fork in this ecosystem has no relation to the well-known cooking utensils utilized for consuming your favorite meal, confectioneries (cakes, desserts...), and others, lol, rather it's a special term in the crypto ecosystem that defines the state of a blockchain network, continuing in its old state or taking a new shape.
In essence, forks in the crypto ecosystem simply means a cause for modification of a blockchain network by the miners and developers of the network. It is always aimed to keep things in check on the network either to update for better efficiency, implement new changes/rules, and so on. Forking in the ecosystem looks into if the network continues in the old state or if a new dimension is taking play.
The results from forks are not always in total agreement among the miners and developers as such some may agree on the previous method of operation and others on a new method proposed. In addition, forks in cryptocurrency can be a point of consensus to continue with the network's rules or parting ways between the stakeholders on the network. There are two types of forks which are soft and hard forks, which would be discussed in this lesson.
Hard Forks
Hard forks in the crypto ecosystem is that type of split that occurs on a blockchain network as a result of a disagreement between the miners and developers as regards the propagation of new rules on the network. In this case, two paths or more is created whereby each goes in separate ways due to non-compliance of the nodes with the new rules on the network. Hard forks are often regarded as very intense conflicts on a network.
When hard forks occur, the old protocol and new protocol are now two separate chains that are no longer compatible with each other. In other words, they are backward-incompatible as they would be operating on different chains. Both chains would maintain the same history as it was before the hard fork, equivalent tokens held before would still be available although at different prices now.
In addition, new transactions created would pertain to the individual blockchain as both chains can't communicate with each other again, that's the aftermath of hard forks.
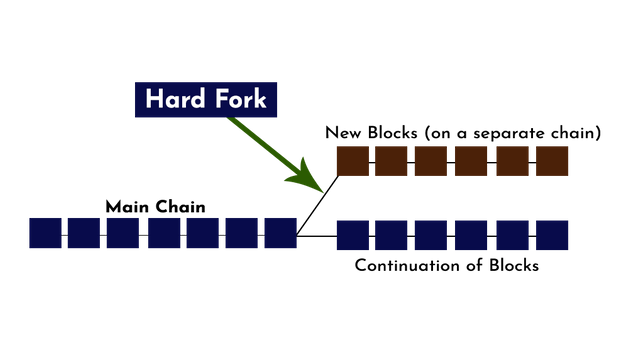
Designed with Adobe Photoshop
Take a look at the illustration above, there exists a hard fork where the nodes that didn't agree with the new rules formed another blockchain network, downloading its history but having its transactions on a new block different to the main chain while the upgraded nodes continued the previous chain.
Soft Forks
Soft forks are the types that are just a mere modification like an added rule which doesn't necessarily break the flow of communication between nodes. In soft forks, an upgrade is a required action on the network, the upgraded and the non-upgraded nodes can still communicate, although the interaction of the old nodes would be limited to the old rules.
In addition, the soft fork is said to be backward-compatible as the new nodes can still communicate with the old nodes, but are a bit limited when it comes to the upgraded rules. In soft forks, all nodes are not required to upgrade to the new rules which are contrary to the hard forks which require all nodes to upgrade, leading to the forced break of chains into separate blockchain networks, the case is different in soft forks where nodes are at the liberty to upgrade or not.
Typically, the non-upgraded nodes are rejected for certain transactions and pass others that conform with the old rules while the upgraded nodes pass transactions that conform with both old and new rules.
What Necessitates Forking in Cryptocurrency?
- When there is a need to enhance the functionality of a network, for example increasing the block size, changing the consensus mechanism, and so on.
- To improve the scalability of a network or tighten up security on a protocol.
- It's sometimes accidental when a transaction is worked on by two or more different miners at a time which causes blocks misalignment, subsequent creation of blocks corrects the occurrence as the longer block continues the chain.
- Settling a dispute between miners and developers when they have not reached common ground on the rules of operation of a protocol, especially when new rules are being proposed where both parties don't quite agree on.
Many cryptocurrencies have undergone hard and soft forks before. Examples are Bitcoin XT, Bitcoin Cash, Bitcoin Gold and so on which are the results of Bitcoin hard forks. In addition, Ethereum Classic, EtherZero, and so on, are results of Ethereum hard forks and the STEEM blockchain hard fork that occurred in 2020 and so many others. We would discuss some soft and hard forks in the future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, forks in cryptocurrency come in two types which could be a hard or soft fork, mostly these forks occur as a result of implementing new rules on the blockchain network, as such requires upgrading the nodes according to the new rules. Soft forks enable flexibility as old nodes can still interact with the main chain while hard forks result in the formation of new chains which have the history downloaded from the former chain. Thanks for reading the lecture today and I look forward to your participation.
Homework Task
- What's your understanding of Forks in the Crypto Ecosystem? List the types of forks in the crypto ecosystem?
- Discuss the two types of Forks in the Crypto Ecosystem. What necessitates forks in cryptocurrency?
Guidelines
- Write an article of at least 300 words. Keep your explanation as simple as possible.
- Include the tag #grassroot-educations2v11, #fintech, #steemexclusive, and your club status among the first 4 tags. Also, tag me @fredquantum in your homework entry.
- The participation in this lecture/homework task is open to everybody (anyone can write, I will leave my comments on your entries) but only entries made by verified kids (not participating in the Academy yet) would be accessed with grades.
- I will check your articles and drop comments on the entries submitted now till 11:59 pm UTC, 26/06/2022.
Cc:-
@steemkidss
Thanks a lot for yet another interesting topic.
Thank you, @steemkidss. I'm glad to have been able to do this in the new week.
Thank you for contributing to #LearnWithSteem theme. This post has been upvoted by @daytona475 using @steemcurator09 account. We encourage you to keep publishing quality and original content in the Steemit ecosystem to earn support for your content.
Regards,
Team #Sevengers
The #learnwithsteem tag focuses on teaching through tutorials and lessons some knowledge, skill or profession that you have. Please avoid using it if it's not about that. Thank you!
Thank you, @daytona475.
interesting lecture teacher . will submit my entry soon @fredquantum
My entry for the homework
https://steemit.com/hive-139765/@ghani12/homework-post-or-forks-in-the-crypto-ecosystem-or-beneficiary-of-this-post-10-to-steemkidss-and-5-to-null-or-by-ghani12
Very intresting and educative one
My entry
https://steemit.com/hive-139765/@habdallah/grassroot-crypto-education-or-series-2-volume-11-forks-in-the-crypto-ecosystem-or-or-by-habdallah
Here is my entry:
https://steemit.com/hive-139765/@david-o/grassroot-crypto-education-or-series-2-volume-11-forks-in-the-crypto-ecosystem