Steemit Learning Challenge-S21W4: Physical Therapy Intervention: Asthma
Let's say you're running through a field in the morning and the cool air brushes against your face, making your breath shallow, your chest tightened, and that uneasy feeling that makes you bend and stop running. This feeling is as if the world is closing in and you begin to gasp for air heavily in such a way that others around you can hear.
This is a real scenario for those suffering asthma. Breathing becomes a battle for millions around the world to the extent that some struggle to breathe through a straw, and if the air that passes through this straw to their nose vanishes, it becomes a big problem as they are susceptible to death.
One may ask what exactly causes this asthma, how it starts, and how it can be managed. The real-life situations I'll narrate will serve as self-explanatory examples.
What's Asthma? Write in your own words after getting knowledge from the lesson post. |
|---|
Before talking about asthma, let's start from its roots. In summary, it's related to difficulty breathing, but what's its origin? How does breathing become a chronic respiratory disease? We as humans are created to breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide, which is called breathing, while respiration is the breakdown of glucose to release energy used by the body cells.
Now, we have respiratory organs, which include our lungs, alveoli, bronchi, etc., which aid respiration. Those noses are the door or pathway for sending out waste products and taking in air to the lungs. Now, let's understand something here.....
- The Airways, or the bronchi, are tubes that carry air from the nose and mouth to the lungs. It serves as that track lined with smooth mucus-producing layer that keeps these tubes moist and clean. As the air from the environment to the nose passes through the bronchioles, the lungs receive the air.
- The lungs are responsible for the exchange of oxygen. Now, when these airways within the lungs become inflamed or stiff, it brings about difficulty in the exchange of oxygen.
- The alveolus are small sacs where oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide and then moves out of the nose. Now, in a situation where there's obstruction of the airways by inflammation, mucus, or possible constriction around the airways, breathing becomes so difficult that people depend on oxygen or inhalers to minimise the inflammation rate. It tightened the chest, which houses the lungs and airways, which brings about a condition called asthma attack.
Asthma
Asthma is derived from the Greek word "ásthma," which means panting or shortness of breath. Asthma is used to describe a medical disorder that's related to a chronic respiratory disease, characterised by inflammation of the airways in the lungs and stiffness, which makes breathing very difficult.
This results in consistent wheezing, chest tightness, breathlessness, etc; when something triggers it. It is a long-term condition that begins with simple body mechanisms to complex contributions of genetics, the human environment, and the immune response in the body. Now, what causes these inflammations? It's obvious that triggers cause inflammation of the airways and hyperresponsiveness of the body, which leads to an increased panic reaction to stimulus like allergens, etc.
Factors that cause asthma
You can't just wake up one morning and say you have asthma without tracing its roots. Something triggers it. The factors include;
- Environmental Factors: This is an extensive factor that characterises a lot of things. It could be weather conditions, dust, smoke, etc. What do I mean by weather conditions? Weather conditions like harmattan or extreme cold can increase the risk of asthma as it irritates the airways and triggers panic breathing as a result of the cold.
Dust and smoke work hand-in-hand as they serve as allergies to humans suffering from this disease. If they encounter smoke or dust, they'll begin coughing and sneezing painfully, which triggers difficulty breathing well. I know of a lady who died because of a trigger from smoke. She wasn't close to her inhaler when she got triggered by the smoke from the plantain she was frying. The smoke triggered her asthma and positioned her in a place she was battling to breathe and couldn't bear it anymore.
Crowded environment can cause trigger asthma. Someone suffering from asthma shouldn't be found in a crowded place, as the trigger comes with the tightness and difficulty in breathing during the crowd. It tightens your chest and airways, which makes it difficult to breathe.
This can be so violent and can throw you to the ground to struggle there. My schoolmate died in this crowded place because he wanted to write an examination. The atmosphere of the examination triggered his asthma, and before he could reach out to his inhaler, he kicked the bucket. Very painful news.

Allergens is another factor that can cause triggered asthmatic attacks. These includes molds, cleaning damp areas and the likes. One may be allergic to pollens or a particular food.
- Physical Triggers: These include activities like running, jumping, exercise, etc. In most cases, it's usually seen among racers who breakdown because of an increased pent rate when they run. People with asthma are not allowed to run in national competitions because, even for me, that's normal; I do pant a lot, and something has increased my breathing rate due to running. Exercise too triggers it. It's not as if it's completely bad to do these physical activities. You shouldn't use up your energy on them to avoid triggering your asthma.
- Psychology factors like stress and anxiety can cause triggered asthma. What do I mean? There are times when someone is overly stressed due to doing tedious work. It could trigger such a person if overly stressed. Factors that trigger asthma are not far from the causes of asthma.
Causes
Most asthma is genetic in nature, implying that if the parents are asthmatic, so is the child. The disorder passes through the gene and is inherited by the children. Sometimes it may not be direct, but allergies as a genetic trait can cause asthma.
- Environmental factors, such as exposure to chemicals or irritants in your workplace or school, can cause asthmatic attacks. I can remember a young boy who suffered from this as a result of being exposed to ammonia, which has a choking smell in the laboratory. Obesity too, which is a medical disorder increases chances of breath obstruction and increased panting because of being overweight.
- Immune deregulation: When the immune system of a person becomes so hypersensitive to harmless stimulus, it becomes a problem. This is characterised under the risk factors and triggers mentioned above. So these are the major causes of asthma, but what are its symptoms?
One shouldn't confuse asthma with pneumonia as they are two distinct terms They are two different respiratory diseases, as asthma is a chronic respiratory disease while pneumonia is acute. Asthma is caused by environmental factors, allergies, and genetics, while pneumonia is caused by infections like viruses, fungi, etc.
Symptoms
Asthma usually begins with mild symptoms that can be easily overlooked or assumed to be normal respiratory problems. It can start with severe coughing at night or after an exercise or body activity. Then you'll notice this wheezing sound anytime you breathe out air. You'll also notice an inability to breathe properly; there's shortness of breath.
Most of these symptoms would be mild initially until they were triggered. Some people experience tightness of the chest after an activity like running or coughing. There's a break whenever the person reads, as he's not able to read a full sentence at once. These are some mild symptoms though, as it starts like this.
Types
We have various types of asthma based on what triggers it and the symptoms that accompany it. One can have asthma and still do activities like exercise comfortably, but another can have a restricted life.
- Allergic Asthma: This is a type of asthma that's triggered by allergens, which include dust mites, pollens, and pet dander. This occurs when a person sneezes and wheezes every spring when flowers bloom. It could also be present in food for some causes.
- Non allergic asthma* is one that involves being exposed to irritants like smoke, strong doors, perfumes, or pollution rather than allergens.
- Seasonal asthma is one that comes with season. Anytime it's winter season where there's extreme cold and dryness of air, one gets triggered and finds it difficult to breathe.
- Occupational asthma is one that involves being exposed to certain things in your workplace, like dust, chemicals, or other irritants. It could be exposure to irritating chemicals that causes you to sneeze or choke. Or it could be dust particles.
There are various types of asthma. These are just a few described above. We have nocturnal asthma, eosinophilic asthma resulting from high levels of blood cells, exercise induced asthma, difficult asthma, mild asthma, severe asthma, etc.
Stages
- Intermittent stage: This is a brief and mild asthma, and nighttime symptoms are rare. There's no significant hindrance in daily activities and exercises, and the king functions normally. It occurs less than twice in a week compared to mild.
- Mild Stage: This is the stage where nighttime symptoms are seen four times in a month and it occurs more than twice in a week. There's a slight reduction in the expiratory flow rate by the lungs, which limits daily activities as to some exercises.
- Moderate stage: This occurs when there's a moderate limitation in physical activities and there's an 80% normal flow of the lungs. The symptoms are daily and require the use of drugs to suppress.
- Severe stage is one where the symptoms are persistent during the day and cause nightly awakenings. Hospital visits may be frequent due to difficulties breathing.
Phases
Note that asthma doesn't have fixed age range as it can occur in children and adults. These are the phases of asthma.
- Early phase comprises mild chest tightness and coughing. It occurs within minutes of being exposed to triggers, and this trigger activates what we call mast cells, releasing histamine to aggregate the attack.
- Late phase occurs after 4–12 hours of exposure. There's a persistent cough and incredibly tight chest. The inflammatory cells in the body after the trigger infiltrate the airways and cause mucus production to clog the airways.
- Severe phase is prolonged, and there's complete obstruction in the airways due to excessive mucus production and tightening of muscles around the airways. This always requires severe medical intervention as patients find it difficult to breathe and even speak. These are the phases that accompany the silent killer disease, asthma.
How would you diagnose a asthma? Any clinical investigation or assessment tests? |
|---|
It's easy to diagnose asthma, but you must go through several processes, like clinical evaluation, checking the medical history of the patient, doing physical examinations, and assessment tests. These are the steps in detail.
Checking patient medical records or history
This is very important to know certain symptoms, genetic traits, or allergies. You can get this by kindly interrogating the patient to see if he has had any occupational exposure to chemicals or smoke thereabout, if he smokes, or if there are things that irritate him in his environment. Your questioning will help you know what type of asthma the person has.

You can also check the presence of asthma or allergies in his family by asking if any member of the family has a series of symptoms corresponding to recurrent episodes of coughing and chest tightness. If the patient tells you that he has persistent wheezing, most especially at night, breathlessness, severe coughing, and pain in the chest when done with any activity or so, you can tell he has symptoms of asthma.
You can also ask to be sure it's not other forms of respiratory diseases that trigger these symptoms. If he says it's cold air, exercise, or allergy to something that can be pollen, you can then know what to do next. Asking how persistent this has been going on will help you know the phase. Aside from patient history, it's important to examine the patient.
Physical Examination
Observations will help you to know if he's suffering from asthma. You can tell if he has shortness of breath or difficulty speaking. When he breathes out, there's a possibility that he'll be whistling through his nose. That wheezing sound will help you know it's an auscultation in the lungs. You can also examine the skin of the patient to check for signs of atopic dermatitis, which is a cause.
This atopic dermatitis is often associated with eczema......When the chest auscultates, it reveals wheezing sounds, which implies that the airway is obstructed.
Assessment Tests
The following tests are used to diagnose asthma. These are the tests and how they're carried out.
- Spirometry: This is a test that involves measuring the functionality of the lungs by assessing the speed and amount of air the person can inhale and exhale. The patient should breathe out into a device. If he does so forcefully after a deep inhalation, one can determine signs. Using the spirometry, Forced Vital Capacity and Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 second are measured. If there's a reduction in the ratio of these two, below 70%, there's the presence of an obstruction in the airways of the patient.
- Peak Expiratory Flow Monitoring: This form of test measures the fastest speeds of air released from the lungs to monitor the variability in airway obstruction. Variability greater than 20% between mornings and evenings indicates the presence of asthma. The use of a Peak Flow Meter to record the PEF readings is essential.
- Methacholine Challenge Test: This is carried out to test the airways for hyperresponsiveness when the results from the spirometry tests aren't conclusive. This test is used when initial tests aren't conclusive. If the patient shows a percentage greater than 20% in FEV1 after being exposed to methacholine, there's a presence of asthma.
- Allergy skin prick Test: This involves the introduction of small amounts of allergens into the skin of the patient using a prick to identify which allergens trigger the asthmatic effect of the patient. When a red bump is observed, there's a positive reaction.
- Bronchodilator Reversibility Test: This is used in confirming if the lungs function well to confirm the presence of asthma through the use of bronchodilator medication. Spirometry is the first thing to be done before administering this. An increase in FEV1 by 12% confirms the presence of asthma. This test helps differentiate asthma from other conditions. It helps in confirming asthma.
- Cold Air Challenge Test: This is used to evaluate the airway's hyperresponsiveness to cold air when exposed. The patient inhales cold or dry air, and spirometry is performed to detect if there's any decline in the FEV1. A 20% decline shows the presence of asthma.
Other tests include; Exercise challenge test, IgE blood test, Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide Test etc......The first two tests are very effective in the diagnosis of asthma.
Imaging Studies
The use of a CT scan to assess the airways and rule out other lung diseases that may be involved and a chest X-ray to help rule out other medical conditions or infections like pneumonia has proven effective for the diagnosis of asthma.
The Lung Function Test is used in monitoring asthma to measure how well the lungs are functional and also help identify limitations in the airways. In this test, a spirometry test is carried out, and if there's a reduction in FEV1 and FVC, it indicates the presence of an obstruction in the airways of the patient.
- Sputum Analysis and Arterial Blood Gases are used in assessment. For sputum, it helps identify inflammation and possible triggers in asthma.
Try to practice at least 3 exercises that you have learned from the lesson. Share images, gifs or videos while practising. |
|---|
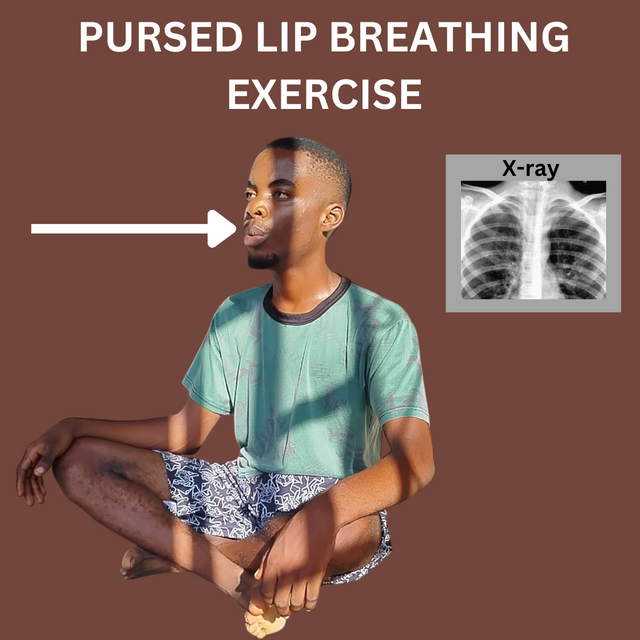
The locomotive exercises demonstrated in the lessons are practical ways to improve breathing rate and functionality of the chest and lungs. During my workout sessions, I usually carry out breathing exercises by breathing out and in for longer hours, thereby improving our breathing rate. The first exercise I carried out is pursed lip breathing exercise.
- Pursed Lip Exercise: This is an exercise that involves positioning your mouth and lips in a narrow way and then breathing in and breathing out through that narrow path of your lips. It helps exhale residual air from the lungs and improve the functionality of the lungs. It also helps in chest rise and fall and to improve shortness of breath, which is a symptom of asthma. I did this exercise by positioning in such a way so as to allow the outflow of air through the pursed lip. This is a video representation of me doing the exercise for a minute.
https://youtube.com/shorts/f1ukIVOCV8c?si=8Iu3uHMp3roqPPri
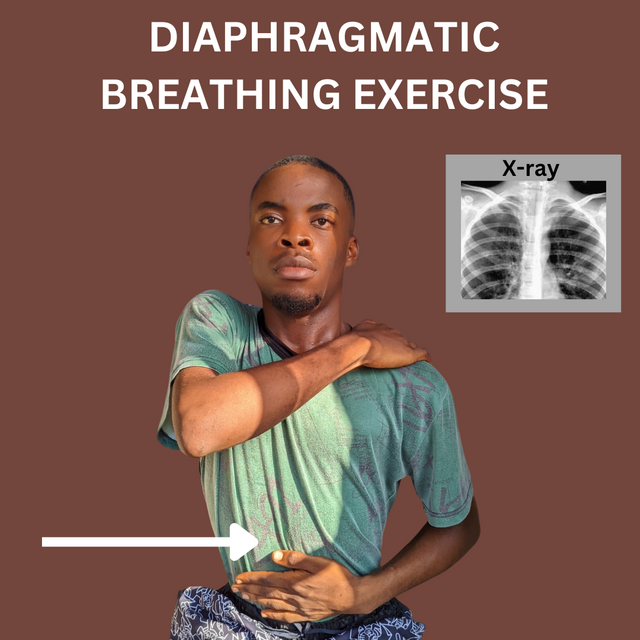
- Diaphragmatic Breathing Exercise: This is carried out by sitting upright on a chair and then positioning yourself in a way that your tummy is tucked and your chest is out. Your right hand crosses to touch your left shoulder. Your inhaling and exhaling makes your tummy go in and out while you control it with your hands. This enhances posture and improves expansion of the lungs. It also improves reduced breathing effort or difficulty encountered doing so. I did this for a minute. I felt the expansion on my chest.
https://youtube.com/shorts/LSnDssuihYg?si=tfzfdMfbJ-3O2ZW5
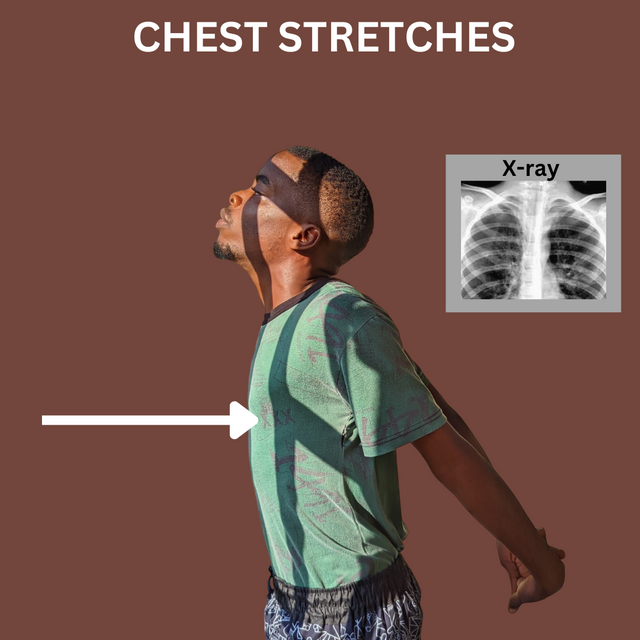
- Chest Stretches: As the name implies, this helps improve the chest and stretches it out to improve tightness. This is done by placing your hands behind your back and trying to lift it up jointly. I felt pain, but I saw the effect of this stretch. This helps improve the muscles in the chest and prevent constriction.
https://youtube.com/shorts/DyiGC0xQies?si=q8aB1Iw0GcswxF2h
Share your review after performing these exercises either on yourself, healthy individual or patient. |
|---|
I'm a healthy individual who's not suffering from asthma. My breathing rate is perfectly okay. My experience performing these exercises can't just be expressed in words. The first exercise I did helped me passively produce Sir narrowing through my lips. I felt some signs of relief during the exhalation process.
The second tackled my chest as I breathed in and out. I felt good, though the chest stretch was painful. I felt that inner expansion. It was as if my chest wanted to tear apart. Overall, the exercises were good. I appreciate my mentor @ashkhan for this lesson.
| Reference Materials | Source |
|---|---|
| Photos | Edited using Canva app |
I invite @whizzbro4eva, @saintkelvin17 and @sahmie