Dynamic Risk Management In Crypto Trading.
.png)
Assalamu Alaikum friends, I have come to participate in the week three of the Learning Challenge Scripto Academy. The topic of this swearing-in learning is Risk Management. I am sharing the link of the contest here for your convenience. Let's talk about the content, I am trying to present it in detail below.
As applied to cryptocurrencies, dynamic risk management refers to a process of evaluating potential risks, and corresponding business approaches, on an ongoing basis with the intention to maximize profits and minimize potential losses. This approach relies on working with actual data to analyze the happenings in the markets to enable traders to act quickly to the changes. These are placing of stop loss orders, asset and risk diversification and use of risk to return ratios for trade opportunities analysis. Traders use enhanced applications and interfaces to interpret risk statistics and be notified of large fluctuations in the marketplace. Through the use of such practices, the traders will be in a position to manage themselves in the unstable crypto market hence improving their overall performance in trading.
Explain the principles of risk management in cryptocurrency trading. Discuss key practices such as position sizing, stop-loss placement, and diversification, with examples relevant to the Steem/USDT market.
Position Sizing
Position sizing on the other hand can be defined as the process through which an individual comes up with the quantity of trading capital to apply in a particular trade. Another wise word of advice in cryptocurrency trading, especially being in the Steem/USDT highly volatile market at the moment is to avoid much exposure to the market by not investing more than you would afford to lose on a particular trade. There is a typical convention of not putting more than 1-2% of the capital in a single trade. For instance, if you are trading with $10000, and you choose to risk 1% per trade, then your Steem/USDT pair will amount to only $100.
Stop-Loss Placement
A stop-loss order is also a really important tool when it come to minimizing possible losses. It gets rid of your asset for you after it has been priced at a certain amount. In case of Steem/USDT trading where you purchase Steem at $0.50 with a stop loss placed at $0.45, if the rate falls to that level, you will be liquidated so that your loss is limited at 10%. It also means that such traders are able to avert emotional decisions that could occur during volatile market periods.
Diversification
This means investing in different securities to lower the risk of holding a particular security in an investor’s portfolio. This could mean not only trading in the Steem but trading in other cryptocurrencies or even stable coins such as the USDT. For example, instead of investing in all amounts in the Steem/USDT pairs, a trader might as well consider BTC or ETH to reduce risk that is related to volatility of any particular asset.
Using historical Steem/USDT data, demonstrate how to calculate the risk-reward ratio for a trade. Provide a practical example, including entry and exit points, to highlight how this metric guides decision-making.
Now, to decide on risk-reward ration for a trade using historical Steem/USDT data one has to determine the entry price, exit price as well as the stop loss level. Having been used in the previous sections, the risk-reward ratio is a ratio that allows traders find how much profit the trade can bring to him should it turn profitable as compared to the potential loss.
- Step 1: Define Entry and Exit Points
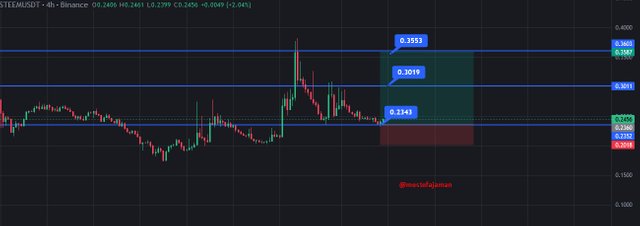
For the purpose of illustration; you may follow the press and determine that you’re going to trade at 0.2343 USDT for Steem. You expect the price to increase to as high as 0.3019 USDT, and given that is my stop loss 0.20 , it’s the exiting point.
- Step 2: Set Stop-Loss Level
To mitigate the risk you place the stop-loss at a price of 0.20 USDT. This means if the price falls to this level, profit taking measure will kick in and all your positions will be closed.
- Step 3: Calculate Risk and Reward
Risk per Share: This is determined as the difference between the entry level up to the defined stop loss point. Risk=Entry Point −Stop-Loss = 0.50 − 0.45 = 0.05 USDT supose to be .
Reward per Share: This is arrived at as the quantitative difference between the target exit point and entry point.
Reward=Target Exit−Entry Point=70 , 50 =20 USDT
- Step 4: Calculate Risk-Reward Ratio
The risk-reward ratio is then calculated by dividing the risk by the reward:
In the following table, the risk-reward ratio has been calculated 2. Risk-reward ratio=Risk/Reward= 0.05/0.20= 0.25 .This means that for every dollar you risk, you stand to gain four dollars (since a ratio of 1:4 is implied).
The lower the risk-reward ratio the greater the potential for greater rewards than risks undertaken in a particular trade thus helping traders make decisions of whether to take a trade or not.
Analyze how volatility indicators like Bollinger Bands or Average True Range (ATR) can be used to manage risks in volatile markets. Use a chart to illustrate how these tools inform stop-loss adjustments and position sizing.
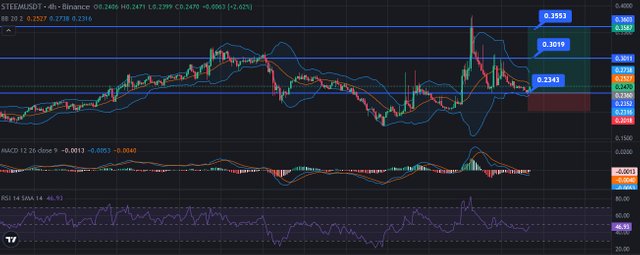
Explaining the Volatility Indicators
The indicators that define the volatility as a key in trading include Bollinger Bands and the Average True of Range (ATR). These indicators give an avenue of viewing the price movement and also assist in decision making where stop loss will be adjusted and the sizes of the trades.
Bollinger Bands
Being an indicator that plots two standard deviations away from a centered moving average, Bollinger Bands have a middle band – the simple moving average. In volatile markets the band width increases thus showing that the price has been fluctuating vigorously. Based on these findings, traders are in a position to employ wider stop loss during volatile times to cover for bigger range of price movement with out getting stopped out. On the other hand, ever if the bands narrow, it gives out indicators of lower volatility, indicating that the stop loss placements should be tightened.
For instance, while using the Bollinger Bands when the trend is up, a trader can decide to place their stop loss below the middle line but close to the upper Bollinger Band of the stock price.
Average True Range (ATR)
The ATR quantifies market oscillation by finding out the average distance between the high and low prices of a security in a given period. Higher ATR mean more volatility in the shares because it measures changes in the stock prices per period. Congurations also indicate that traders use ATR to conduct position sizing; for example, if the ATR is high, small position sizes may be taken in order to limit the risk exposure because of wide price volatility.
However, when using the ATR as stop-loss levels traders usually include a multiple of the ATR value in order to form a stop loss level according to the present market conditions, a multiple of ATR is inserted which could be 1.5 or 2. The method enables the placing of stop-loss orders in areas which are vulnerable to volatility.
Concisely, when Bollinger Bands and ATR are used as a tool, it is easy, based on fluctuating price positions, to define stop-loss levels and control position’s size in an effectively risky stock market. These tools can be fine tuned to suit the traders depending on the market after which risk management is improved.
Design a trading strategy for Steem/USDT that incorporates risk-adjusted principles. Explain how your approach adapts to different market conditions, such as sharp price swings or periods of consolidation.
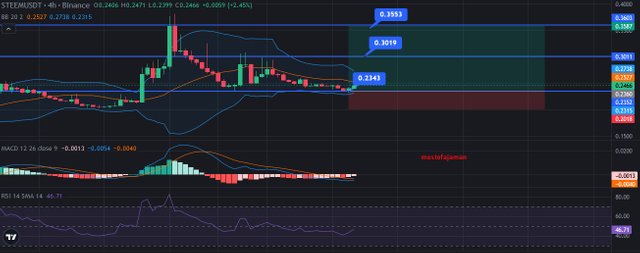
- Overview of the Strategy
I believe in developing a trading strategy for Steem/USDT is necessary and it adapted on risk diversification through the analysis of the identified factors as technical indicators, proper position sizing and adjustments to the market conditions. Actually the major objective of value added capital is to achieve the highest turnover on the invested amount while bearing the least risk of loss.
- Technical Analysis Indicators
Such things as Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) averages will help the manager in the identification of signal points for entry and exits. An RSI above 70 may be considered overbought and the RSI below 30 may be considered oversold. Cross overs on the MACD can differ in relation to a possible reversal of trend.
When used, Position Sizing and Risk Management must do the following:
Explain that in the fixed fractional position sizing, no more than two percent of the entire account balance should be leveraged on a given trade. This reduces exposure to the fluctuations especially during moments of volatilities. Further, a trader is allowed to place stop-loss at appropriate points like below the recent ‘support’ levels.Adapting to Market Conditions
Sharp Price Swings: When trading in very sloppy conditions, traders are likely to be stopped out of the market before the start of the normal trading range. Employ trailing stops in order to protect profits once the prices start going in your direction.
Periods of Consolidation: When sideways markets persist, one should use the range trading strategies which include buying or selling at support or resistance respectively. This approach takes advantage of fluctuating stock prices without having to place a portfolio at the mercy of large movement conditions.
- Uninterrupted Supervision and Re‐evaluation
Evaluate often the market situation and change something if it is appropriate. For example, if the position of a market becomes slightly more risky, then either decrease stop losses or else decrease the trading scale even more until the position becomes safer again.
I hope the integration of these elements ensures Steem/USDT pair grows steadily and, in the same process, ensure that risks within different trading situations are well mitigated.
Discuss a real-life or hypothetical scenario where poor risk management led to significant losses. Reflect on what could have been done differently and propose key takeaways for improving future strategies.
The 2008 financial crises, therefore, act as a good example where risk management was poorly done, and the consequences were severe. Mortgage backed securities especially of subprime grade were created in abundance in institutions such as Lehman brothers thus assuming undue risks. These securities were hardly fathomed and a priori evaluated for risk thus worth and these led to over-valuation of assets and exaggerated security for investors.
The mistakes also arise from aspects that could otherwise have been handled or conducted otherwise as follows:
Enhanced Risk Assessment: Financial institutions could have also adopted proper risk assessment measures than those that was witnessed in this study. This includes the use of simulations in which the portfolios of various economic situations are run in order to give an insight of their weaknesses.
Regulatory Oversight: Tighter policies could have been designed to oversee the operations of financial firms much better. This would entail maintaining adequate capital level and sound lending practices of banks in the country .
Transparency in Financial Products: Higher levels of information disclosure relating to the sophistication and the functionality of these products would have enabled investors to avoid the calamity. More informative disclosures concerning the assets that supported those mortgage-backed securities would help reduce some of the risks.
Excerpts for Enhancing Future Strategies
Develop Comprehensive Risk Management Frameworks: To be effective organisations should establish broad risk management frameworks that cover all identified risks namely market risk, credit risk, operational risk and liquidity risks.
Foster a Risk-Aware Culture: Subsequently, practitioners can advance risk management across the organization by promoting the risk awareness of employees at all organisational levels.
Utilize Technology for Risk Monitoring: The use of analytic processing and technological enablers can make the management of risk real-time; thereby providing organizations strategic guidance in the management of the risks that emerge.
In conclusion, the crisis reveals that to curb such big losses, risk management concepts studied in the course are vital.
In the current world of cryptographic currency trading, risk management must hence be fluid in response to fluctuating situations. Through periodic evaluation of market situations, it becomes possible for traders to reduce risks on their capital and reap the highest on their investment. Risk metrics like VaR help to take well-reasoned risks and yet keep the system frequently adjustable so that potent risks might be managed briskly. In conclusion, when it comes to risk management it is recognised that having a proactive approach creates additional benefits of minimizing potential losses whilst also increasing gains in this high risk context.

Thanks to everyone here is an invitation @stream4u @simonnwigwe & @josepha
X promotion link
https://x.com/mostofajaman55/status/1875211502707429826