Steemit Crypto Academy | Season 3 |Week 4 Homework Post for Professor @awesononso - Topic: Blockchain Forks by @kelechisamuel
The lesson today places understanding on the concept of Forks, their roles in blockchain including their kinds, merits and demerits.
What is a Fork? (In your own Words)
My understanding of Forks :
Forks can be understood to be a situation where the software in charge of a distributed network is upgraded and based on the agreement of nodes or their disagreements, existing rules are made valid or invalid. An example of a Fork could be seen as Bitcoin Cash which is of Bitcoin. I'll explain this more as we go into further details in the definition of Forks.
We also understand that the basis of a Fork is based on agreements between the Miners of the blockchain and a complete node users agreement would be the only certificate for the implementation of the new rules and changes made.
More so, this Fork, has an open source nature and so seems to be able to happen anytime and brings a volatile period to the market due to the unsure decisions of the investors for example Bitcash was out as a Fork in 2017 when Bitcoin, experienced a volatile market trend.
Finally,the need for Forks are the ultimate demand by humans for blockchains to have better features day after day or this could be a move for crowd funding of other projects , hereby making this want for change unending
Explain in details what a Hard Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain).
Hard Forks could be seen as a resultant effect of the absolute division of a block chain into two chains making one a new protocol and the other a continuation of the former protocol.
These kind of Forks arise from incomplete agreements on the new protocol movements on the blockchain.
More so, the two separate chains, now regard themselves invalid and become impossible to work with each other and making any chain willing to work with the new network opt for an upgrade first and also the use of a new crypto currency irrespective of the fact that the new protocol users could have funds on the new blockchain network since they did too on the old one. We also see that in a hard fork, holders of tokens in the former blockchain would be granted in the new one as well.
The reason for the creation of a hard could be, to remedy security risks, make platforms better etc.
Advantages of a Hard Fork include :
A Hard fork provide absolute solutions to problems that make its blockchain slow, untrusted or less efficient
It leads to diversification of the crypto market, ie creating other blockchain /digital assets and release of free tokens to blockchain users and promotes efficiency on every blockchain since there is competition
It's disadvantages too include :
- Volatility :During a hard fork, there is relative volatility which makes the crypto asset a bad store of value and could even lead to blockchains being less trust worthy
*It brings a wave off in the interest of investors or potential users who perceive the instability of a blockchain from its split during a hard fork.
EXAMPLES
An example of a Hard Fork is the Ethereum and the Ethereum Classic in 2010 as the Ethereum Classic came up as a divided version of the Ethereum blockchain.
This division occurred so as to return maliciously taken funds to their actual owners in accordance to records before the hack which resulted to the two protocols existing differently.
Another one is the Bitcoin Cash that moved out from bitcoin to offer cheaper and faster transactionhich moved the platform from software rules to the hands of the Miners and nodes
Explain in details what a Soft Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain).
A soft fork could be seen as a situation where the software protocol is changed and only former confirmed transactions blocks are made invalid since old nodes will regard the new blocks as valid ie old and upgraded nodes still work together on the network
And unlike the Hard fork this one makes the original blockchain better without actually splitting the actual chain leaving it with a same history and post qualities.
This also, works by majority of the nodes consenting to the upgrade of the system. We also see that soft Forks could occur when there is a non-permanent obstruction in the blockchain ie when Miners using, non updates nodes misappropriate rules their nodes aren't aware of
There are also advantages and disadvantages of this Soft Fork including :
Advantages :
The Soft fork makes the cryptoassets stronger :
When a crypto blockchain gets divided, it reduces the resources and input that could have been focused on making one better therefore the soft fork makes the blockchain able to work on one blockchain and make it utmostly strongIt encourages more investors :The Soft fork nature makes it less problematic and encourages rational investors who would always prefer straight forward projects.
Disadvantages :
The Soft fork with its majority node nature doesn't bring about a complete change /upgrade in all blockchain issues and may sometimes create inefficiency
Left out to the Soft Fork operation system, the blockchain would be left with same blockchains, hereby creating no need for diversity on the blockchain
EXAMPLE
An example of the Soft fork could be seen as :could be seen as the new statement saying that blockchain size would be enhanced, from the present 1mb size to 800kb
What are the differences between Hard Forks and Soft Forks?
Differences between the Soft Fork and Hard Fork include :
Firstly, in a Soft fork, no new cryptocurrency as just one blockchain remains valid instead,in the Hard Fork, two new crypto currencies are formed after the division and the two blockchains remain valid
The Soft Fork, has a backward compatible system while the Hard fork, is a backward incompatible system
In the Hard fork, the network regulations are updated, and the chains do not co-exist instead, they split and can't take part in verifying transactions making users basically in knowledge of the updates and now use the two simultaneous blockchains formed where as in the Soft work, the chains co-exist, don't split and can take part in verifying transactions even with the updated blockchain that is not split
The Hard fork creates a difficult time mostly for cryptocurrencies bringing about volatillity most times while the Soft Fork brings about the opposite mostly
Explain the following Bitcoin Forks and explore the blockchain where necessary. Indicate if they are hard forks or soft forks;
- Bitcoin Cash
- Segregated Witnesses
Bitcoin Cash
The Bitcoin Cash could be seen as a hard fork resultant blockchain of Bitcoin that was founded in 2017. In July that year, the Bitcoin Miners, brought up a proposition for the improvement of the blockchain based on the fact that the Ssgregated Witness which we would see in the second part of this question would activate at Block 477,120
At the time of this Hard Fork, anyone owning Bitcoin had its equivalent in the Bitcoin Cash when they decides to switch to the other blockchain.
The Bitcoin Cash trades on normal digital exchanges with its name as the Bitcoin Cash
and the currency code by the abbreviation - BCH. We see the Blockchain interface in the picture below and details too about the Butcash including its Block time, Block reward, Time stamping scheme, split ratio,, and supply limit
The Segregated Witnesses
The Ssgregated Witnesses or the SegWit could be seen as a Soft fork result of Bitcoin transactions format. More so, the widely known reason for this soft fork was for prevention of non-intentional transaction allowances and to pass some protocol blockages.
The major issue it meant to solve, was the issues of transaction speed and sizes and achieved this by separating every transact
into two parts removing the witness data from actual part and adding it as a separate structure at its end while the initial part kept on to hold and disseminate receiver data with the new witness form containing parts and contents.
The Signature data in other words would be removed from the Merkle tree history of the sender and receiver of the coins leaving transact IDs strong
Write on the Steem and Hive Hard fork and show similarities in their Genesis Blocks(Provide screenshots).
The Steem and Hive Hard Fork could be relationally explained as a hard fork effect on Steem leading to the generation of the Hive blockchain. We see here of how the Tron blockchain's harsh take over of the Steem block chain had to bring the concept of the Hive with the blockchain's platform with a native currency and their differences being that one was centralized and the other decentralized.
The Steem block chain being created in 2016 kept thriving until in 2020 when the Tron blockchain acquired the Steem blockchain leaving out the Hive forked out blockchain to continue
The Hive Blockchain is explored in the pictures seen below
GENESIS BLOCK OF HIVE AND STEEMIT
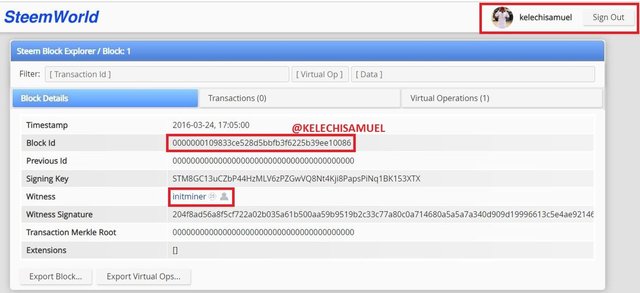
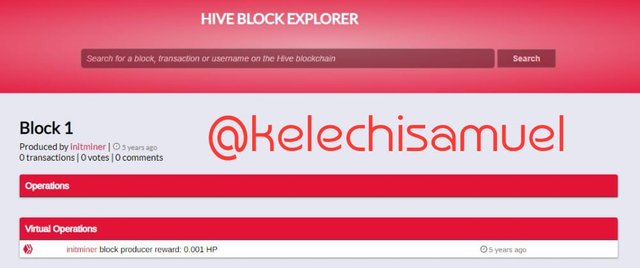
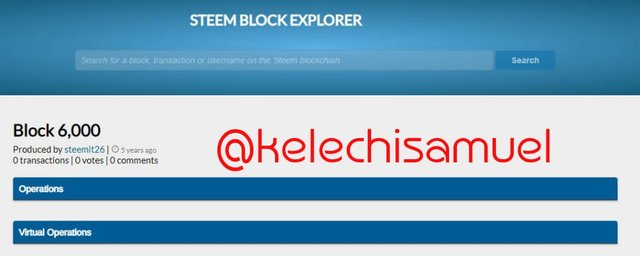
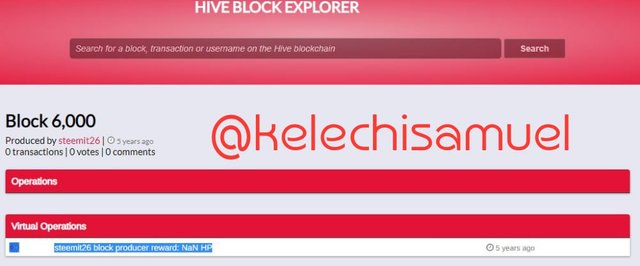
Also tried searching the block 6000 on both steem explorer and hive explorer
And it's shows that the producer of the block 6000 is @steemit26
CONCLUSION
The understanding of the fork , it's advantages and disadvantages their roles and, knowledge of hard fork and soft fork is greatly beneficial and should be greatly understudied by every block chain
Cc
@awesononso