Avalanche Blockchain - Crypto Academy / S5W8 - Homework post for pelon53.

INTRODUCTION
Technical explanation of blockchain may sound difficult or complex to understand but in simple terms, it is the distribution and storage of data in groups or blocks that have been connected together in a series or sequence. This makes sure that the data that has been secured cannot be manipulated. It is utilized in cryptocurrency networks for transparent, secured, and quicker transactions of cryptocurrencies on their platforms.
Bitcoin was the first blockchain to be launched, after it was introduced, it was realized that it could be made better. So other blockchains were launched to find solutions to the defects in areas such as speed, scalability, high transaction fees, and latency of the Bitcoin blockchain. Examples of these blockchains are;
- Ethereum
- Solana blockchain
- Avalanche blockchain
- Etc
Question 1
Explain X-Chain, C-Chain and P- chain in detail
Answer
The Avalanche blockchain is one of the various blockchains to help with the defective features of the previous blockchains. This blockchain focuses on low transaction fees, eco-friendliness, and high transaction speed. It was developed by Marfan “Ted”, Emin Gun Sirer, and Kevin Sekniqi and launched in September 2020.
This blockchain has a very unique feature as it has three different chains each with their own function that work towards the success of the Avalanche blockchain. In other blockchains, their features are mostly managed by a single chain.
To transfer the Avax coin from some exchanges, users have to make a choice between the various chains to transfer the asset to. The Avalanche network has different chains, each with its own features and abilities that users must be aware of before participating in any activity on it. The various chains are the C-Chain, X-Chain, and P-Chain.
The ability to send or transact with funds across the various chains on the Avax wallet is one of the good features of the Avalanche network.
I am going to explain in detail the various chains mentioned above.
X-Chain
The X-Chain is also known as the Exchange Chain is the chain in the Avalanche network that takes care of exchange. Its function is to facilitate the exchange of some tokens and all transactions on the Avalanche network.
Using the API (Application Programming Interface) users can create digital assets which are obliged to abide by some rules or principles of the consensus protocol that governs the chain.
It uses two mechanisms to mint new assets, they are JSON 2.0 RPC and AVM.MINT. JSON-RPC is a form of RPC (Remote Procedure Call) protocol that utilizes JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) to encrypt requests and responses between client and server. These new tokens are often a representation of real-life resources or assets or currencies, they are also some rules that the tokens have to abide by. Also, there is a transaction fee charged in AVAX tokens for the creation of those coins. The API of the X-Chain also allows users to create and exchange assets.
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) does not support X-Chain which means it cannot be linked to Ethereum DeFi apps or wallets like MetaMask. The X-Chain wallet can however be obtained via the Avalanche wallet.
C-Chain
The C-Chain is the second chain on the Avalanche network. Its function is to enable developers to develop DApps (Decentralised Applications) on the network. It also facilitates the creation and operation of smart contracts.
Unlike the X-Chain, the C-chain is supported by the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) which means it can be linked to Ethereum based DApps, and also the DeFis that are based on Ethereum can also distribute different versions of their products onto the Avalanche network and operate successfully.
The C-Chain uses the snowman consensus algorithm in its operations which is a different version of the Avalanche Consensus.
The P-Chain
Is the last chain to talk about on the Avalanche network. The P-Chain is an abbreviated form of the platform chain. Its function is to create a new Avalanche Subnet and also track the Subnets that are active. Just like the C-chain, the P-chain also uses the snowman consensus protocol.
This chain manages some operations on the blockchain such as validating, transfers through cross-chains, and staking.
To clear the doubts, a subnet is a collection of validators that function together to reach a consensus on the details of a block in a blockchain network. Every network is validated by a subnet. Before it can do so, it must abide by some requirements.
The subnets have their own rules which a node has to follow in order to join or become a member of the subnet. The subnets are not restricted to a single blockchain, they can cross to other blockchains and validate transactions.
To be a validator on the network, the user is required to transfer their assets to the P-chain and claim the rewards on the P-Chain. The rewards can then be transferred to the X-Chain or the C-Chain where we can transfer it to other exchanges.
Question
Explore the Avax Network platform . Screenshots required
Answer
To explore the platform, we will visit https://avax.network. When the page is done loading, we can see the main menu with a list of options. The option are, Developers, Individuals, Avalanche X, Press, Community, Contact
Now let us look at these options one by one
Developers
This menu contains two submenus which are Validators and Start Building
 source
source
Validators
This option allows users to partake in the validating process of the network. AVAX holders who stake their tokens are rewarded with some tokens at a certain proportion to their staked token in return.
This section also shows some useful metrics and reasons to validate ln the network
Clicking on become a validator today shows some steps to stake on the platform, I will be demonstrating those steps later after I have created my wallet.
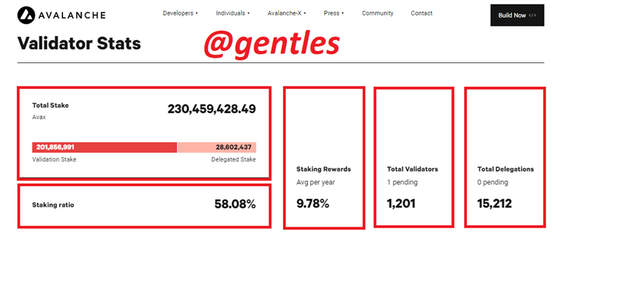
Scrolling down on the page will show some validation statistics on the platform. currently, the total stake on the platform is 230,459,428.49 AVAX which can be further categorized into two, Validation stake and delegated stake which is currently 201,856,991 and 28,602,437 respectively. The staking Ratio is currently at 58.08%. the average staking rewards per year is 9.78%.
The platform has 1,201 validators with one currently pending and 15,212 delegators with zero pending.
Why validate Avalanche
Here are some reasons why you should validate on the avalanche network
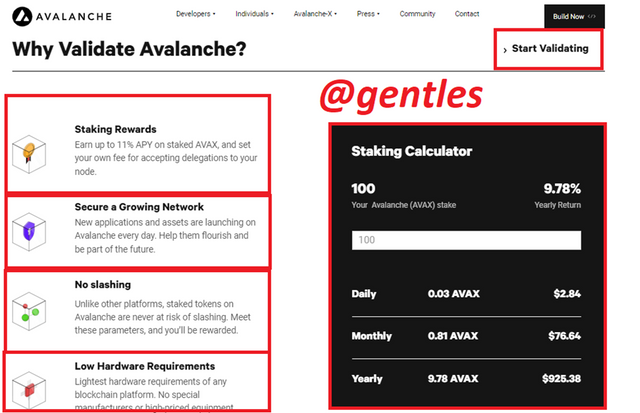
The platform offers an APY on staked AVAX tokens that are up to 11%. It also allows users to set a fee to other users in case they want to delegate to your node
Applications and assets are created every time on the network, validating on the network will help them grow for the development of the network as a whole
Unlike other platforms, avalanche does not slash their validators. Slashing is when a percentage of the staked token is taken by the platform as a form of punishment to validators when they display harmful behaviors.
Being a validator on the network does not require sophisticated or expensive equipment to operate
There is a Staking calculator here that shows the user how their rewards will be like if they stake a certain number of tokens. For instance, with an APY of 9.78%, when 100AVAX are staked, the user will receive 0.03AVAX daily which is equivalent to $2.84. In terms of months, they will receive 0.81AVAX which is $76.64. And in a year, they will receive 9.78 AVAX equivalent to $925.38
Start Building
Start building allows the user to view written tutorials on a variety of activities like launching an Ethereum app, running a validator, minting a token, integrating an exchange, or viewing some developer’s documentation. Clicking on any of the options here will show a detailed description of how that particular activity is done on the platform.
 source
source
For instance, clicking on Mint a Token will open a page that gives a tutorial on how to mint the token on the platform
Individuals
This section offers services for individual users. It has some sub-options like Roadmap, Solutions, Ecosystem, Avalanche Wallet, Avalanche Explorer, and Avalanche Bridge
Roadmap
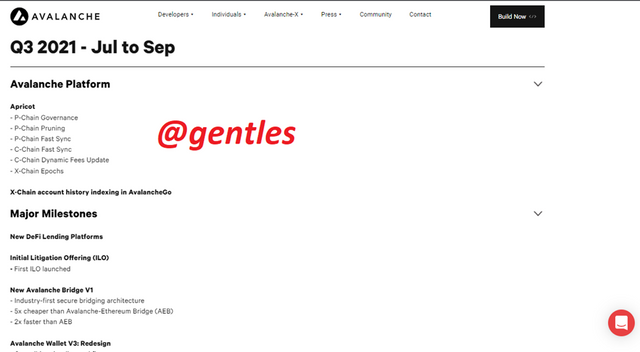
Selecting this option shows a detailed description of some plans, achievements, and aims of the platform in 2021. The roadmap considers sectors such as developments on the Avalanche network, some Major Milestones, and Ecosystem projects.
For instance, in the third quarter of 2021, July to September, the Avalanche platform reached some major milestones like launching new Defi lending platforms, initial litigation offering which gather funds to take care of legal issues. A new avalanche bridge was also launched
Solutions
This section shows some industry use cases that operate within the platform to provide solutions. It has been categorized into various sections, they are Decentralised Finance (DeFi), Institutions Enterprises and Governments then Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
Decentralized Finance. The platform has some DeFis such as Pangolin, SushiSwap, Snowball, TrueUSD, etc. These DeFis has features and services such as Automated Market Makers (AMMs), Asset Issuance, some offer Borrowing, and lending services, peer-to-peer payments, insurance, etc.
Institutions Enterprises and Governments
The Avalanche network has partnered with some government platforms, Congress of Quintana Roo, and some litigation market financing platforms, Ryval to offer services such as Asset Issuance & Trading, Debt Financing, Digital Identity, Document Tracking, Fund Management, Insurance, Intellectual Property, Lending, Real Estate, Supply Chain and Trade Finance
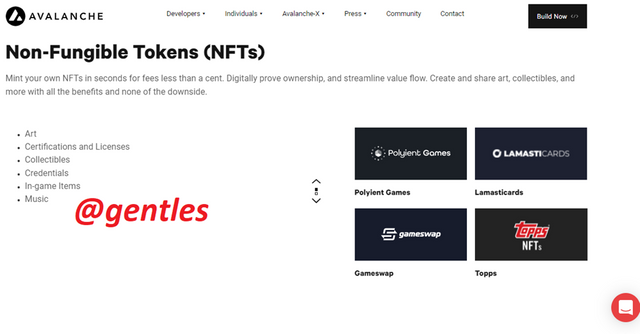
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFT)
There are platforms here such as Polyient games, Lamasticards, Gameswap, Topps, etc that help the user to Mint their own NFTs in a very short time at very affordable fees. They also offer services such as sharing arts, collectibles, and more.
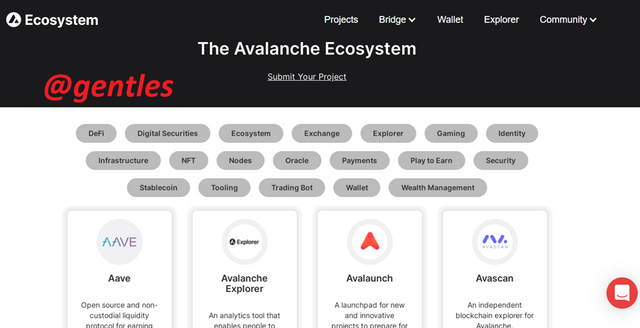
Ecosystem
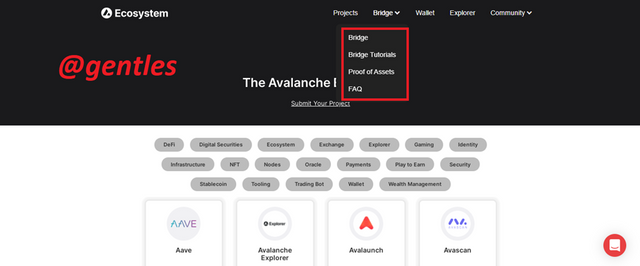
This section contains a lot of other subsections. We have Projects, Bridge, Wallet, explorer and community.
The Project section is where we can find the DApps on the network. Every Project that has been deployed to the Avalanche platform can also be found here. They have been filtered based on their features and functions such as DeFi, digital securities, exchange, play and earn, etc. This is to make it easier to navigate the DApps.
The Submit Your Project option on this page allows users who want to add their projects to the avalanche network to fill a certain form to add their project. Users must make sure the project is live on the mainnet of Avalanche before they fill the form. Users must also ensure that they fill the form with complete and accurate information.
To add a project, click on submit your project.
In the next page click on Start or press enter on your keyboard.
Start filling the form by entering your email and click on OK
Enter the name of the project and press enter or click on OK
The next question will be to enter the URL of the project then click on OK
Give a vivid description of the project, preferably in one sentence and not more than 100 characters
If there is a logomark for the project, upload it and click on submit.
When this is done, you will be notified of a period when submissions that are complete and accurate will be live
 source
source
Bridge
Under the bridge option, there are other options too. They are Bridge, Bridge tutorials, Proof of Assets, and FAQ (frequently asked questions)
Bridge
A Bridge in the blockchain is the connection that enables the import and export of tokens across all chains. Those different chains have different rules and protocols; however, the bridge is able to give away that allows the chains to be interoperable that allows the tokens to be supported by the chains at both ends of the transfer securely
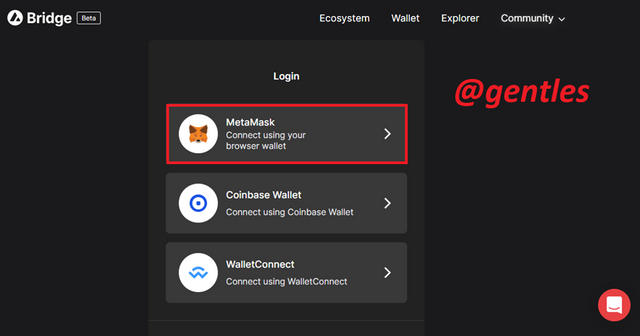
Before we are allowed to use the bridge, we have to connect a wallet. The page gives a list of wallets to choose from. Select your preferred one to connect. I will select the MetaMask wallet.
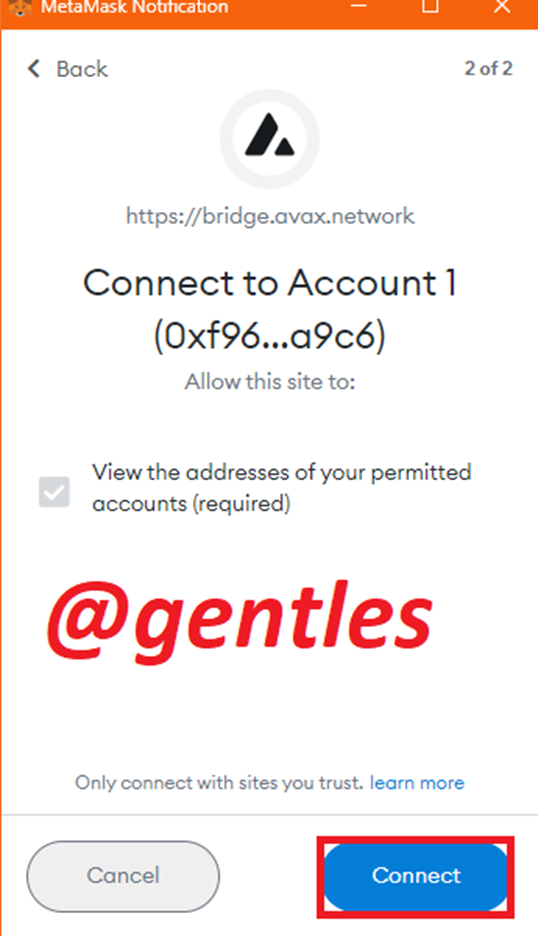
You will be notified by the wallet to allow the connection. Click on Next
Click on connect to connect the wallet successfully
It can be seen that the wallet has been connected successfully. We can now transfer funds from the Ethereum blockchain to the Avalanche blockchain and vice versa.
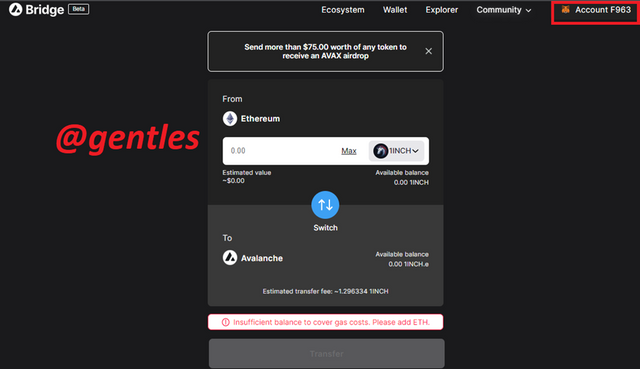
Bridge Tutorials
This option redirects the user to a youtube channel with a lot of videos that describe how to perform some activities like how to transfer from Ethereum to Avalanche, how to add new tokes, converting ETH to WETH, upgrading tokens, and transferring from Avalanche to Ethereum on the Bridge.
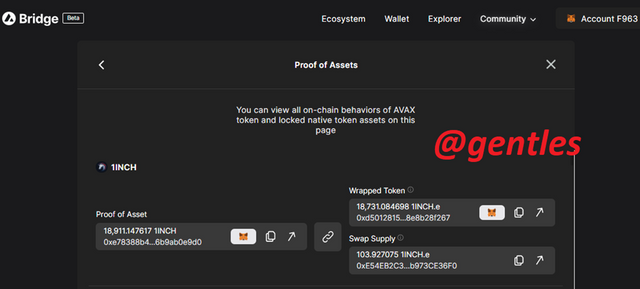
Proof of Assets
Here is where we get to see all on-chain conducts of the AVAX tokens and staked native tokens.
Avalanche wallet
The Avalanche wallet is described as a secure, simple, decentralized wallet that is used to store assets on the Avalanche network.
This wallet has some outstanding features such as using one private key for about 3 different wallet addresses, the X-Chain, P-Chain, and C-Chain. Users must also swap tokens from one chain to another depending on how the token will be used.
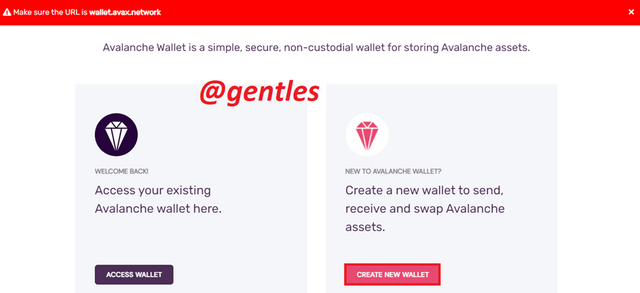
Now let’s look at how to create a new wallet on the avalanche blockchain. To access this site, go to individuals on the avalanche homepage and click on avalanche wallet under it or you can visit https://wallet.avax.network.
This page has two options, Access Wallet and Create New Wallet.
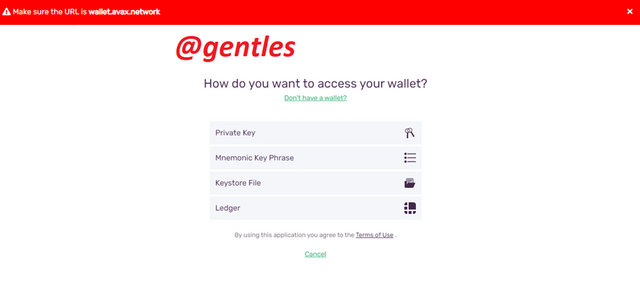
If you have an existing wallet and want to open it click on access wallet, then choose the method in which you want to open the account. Enter the key based on the method selected.
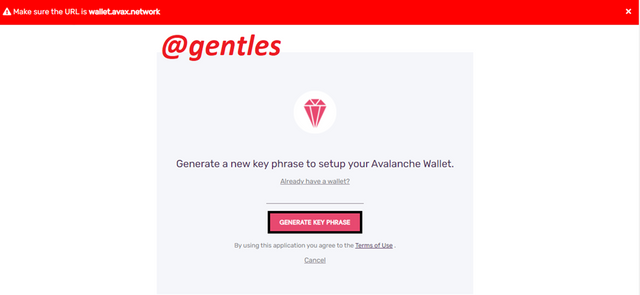
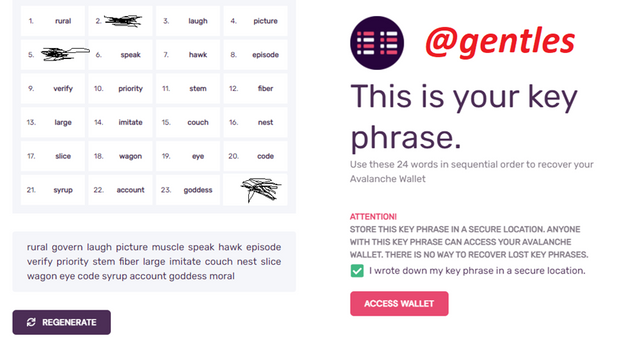
To create a New Wallet if you don’t have one already, click on Create New Wallet. On the next page shown below, navigate and click on Generate Key Phrase
Twenty-three random words will be provided as a key phrase, write down these words and keep them in a secure place. Tick the “I wrote down my key phrase in a secure location” box and click on Access Wallet
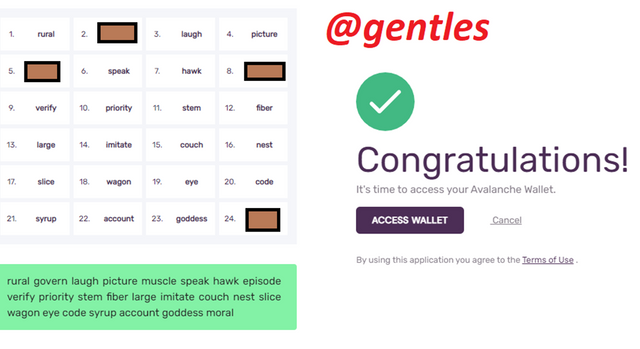
Verify the mnemonic key by filling in the empty spaces provided with the missing words and click on Verify.
Now click on Access Wallet to open your newly created Avalanche wallet.
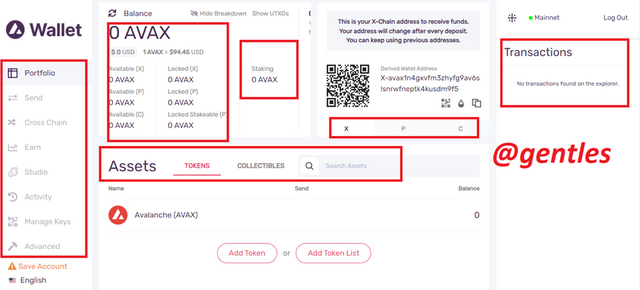
The wallet has been created successfully.
The portfolio section of the wallet as we can see is the section that displays everything about all the assets, tokens, and collectibles of the user. The page also shows the amount of AVAX tokens that is available in the various chains (X-chain, P-chain, and C-chain) and how much of the tokens have been locked in those chains. If the user has staked any of his AVAX tokens, it is shown in the Staking area.
Also, clicking on any of the chains will show an address and a QR code to receive funds into that chain.
Transactions show every transaction made by the user
Let us talk about the other options in the wallet menu. Those options are; Send, Cross Chain, Earn, Studio, Activity, Manage keys and Advance.
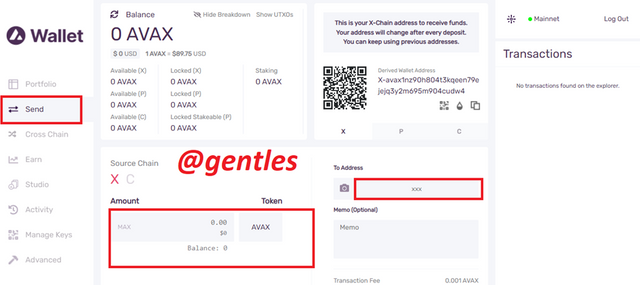
Send
This is where the user can come to and transfer assets to a given address. First, choose the chain you want to send from as the source chain, the X-chain, and the C-chain either of them can be used to transfer the funds. However, using the X-chain is much cheaper. Enter the amount in the amount box, select the token and enter the receiving address in the To address box.
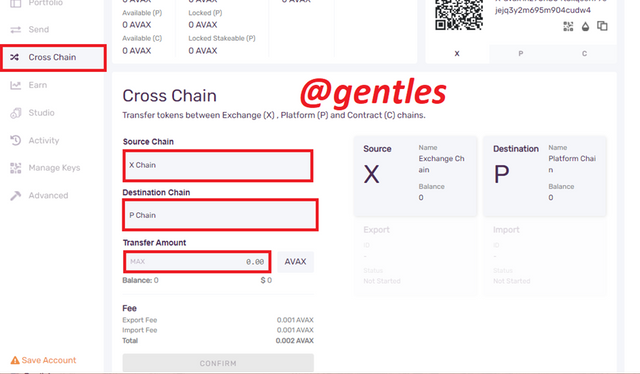
Cross-Chain
This works just like the bridge, it allows users to transfer funds across the chains on the platform. choose the source chain as the chain you are sending from and the destination chain as the receiving chain then enter the total amount. However, there is a fee charged at 0.001 AVAX each on the exports and imports.
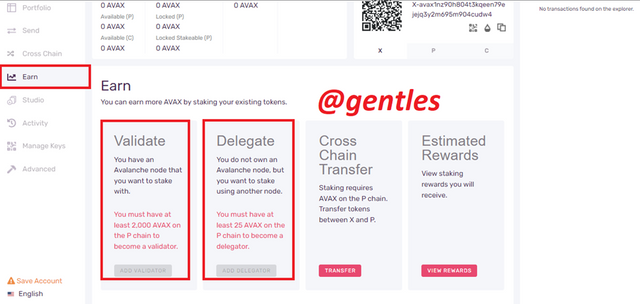
Earn
This is where users can come and validate and delegate on the platform. Users must have a minimum amount of 2 AVAX on the P-Chain to validate and a minimum of 25 AVAX on the P-chain to delegate. Estimated staking rewards can also be viewed here.
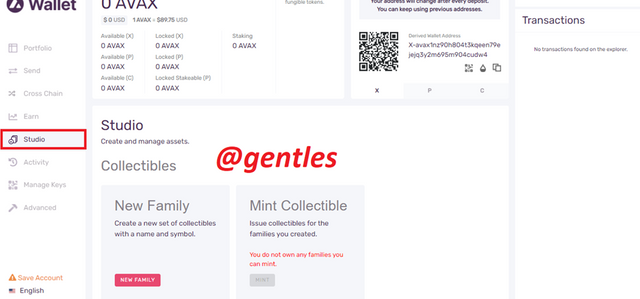
Studio
Here users can create new collectibles and add a name and a symbol to them, they can also mint collectibles here.
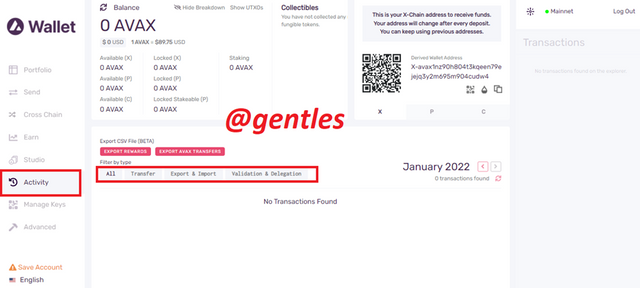
Activity
Every activity of the user on the platform is displayed here. It contains all exports and imports, all validations and delegation, and all transfers.
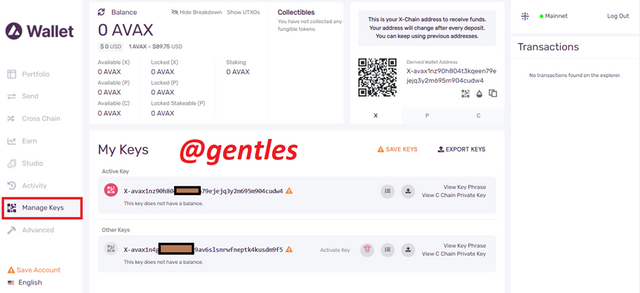
Manage Keys
As the name suggests, this is where users can manage their keys, they can view their key phrases and private keys
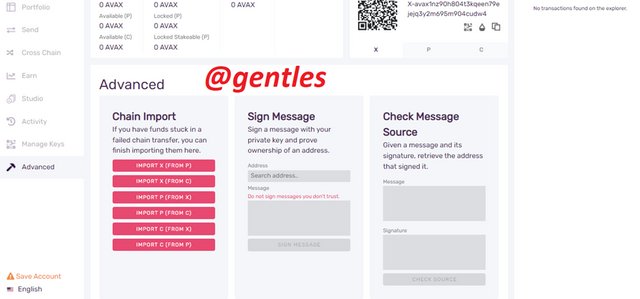
Advanced
In case of a failed transfer between the chains and the funds get stuck, the user should come here and complete the transfer.
Users can also provide proof of owning an address by signing the address with their private key and also retrieve that address that has been signed in the check message source area
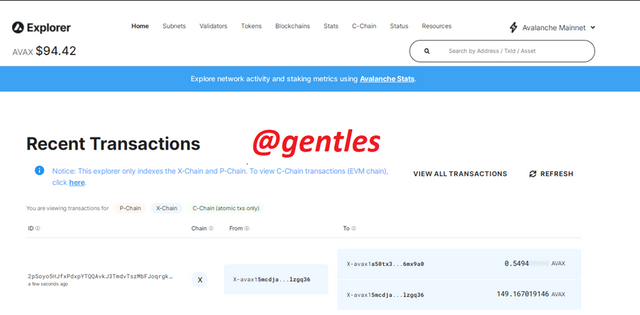
Avalanche Explorer
This is the explorer of the X-Chain and the P-chain, it provides on-chain data about the chains. Here we get to view some essential details like transactions that has been executed on the networks and block details.
I have already talked about the bridge in the previous paragraphs.
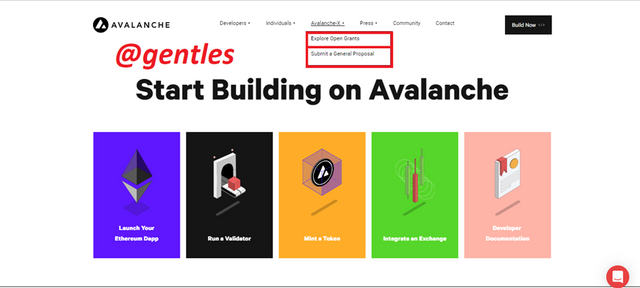
Avalanche-X
This option contains sub-menus which are Explore Open Grants and Submit a Proposal
This section allows users to explore some open grants on the platform. it also allows users to submit their proposals to the platform for consideration by the Avax team.
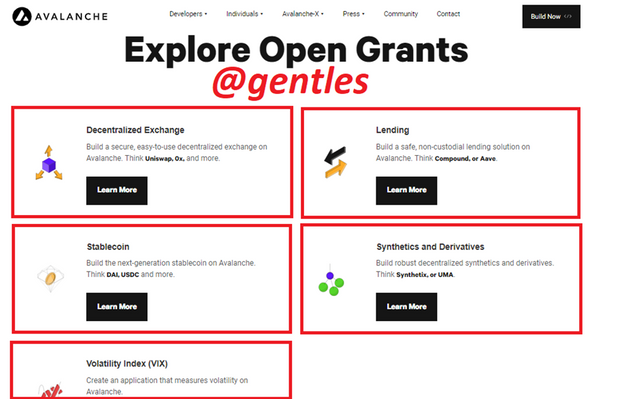
Explore Open Grants
Currently, there are five grants on the platform. It seeks to find more solutions to build secure and convenient decentralized exchanges, develop a secure and decentralized lending platform, build stable coins on the platform, build synthetics and derivatives and also develop applications that can determine volatility on the platform.
Clicking on any of them will allow the user to begin building a project towards that grant. The user will completely and accurately fill a form for the creation of that project.
Submit a General Proposal
This option allows users to offer a general proposal on the platform. This implies the user can build their project on the platform completing the application process.
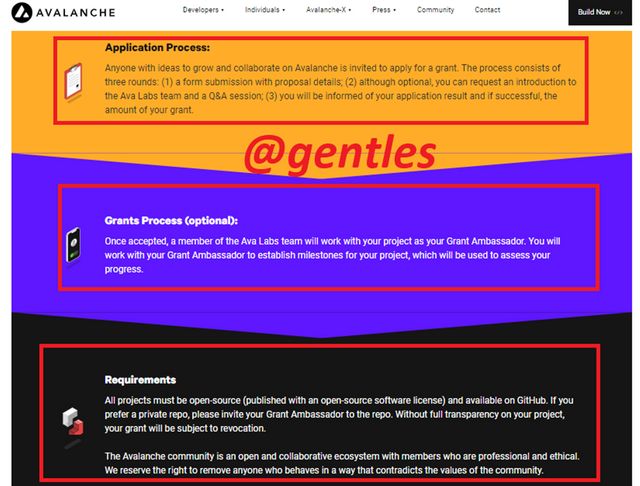
There are some instructions that the user should follow in submitting their proposals. It first shows how the application process is done. After your application has been accepted by the platform, it will be announced to you. An Avalanche team member will collaborate with you to set milestones for the project. It is required that the project be an open-source project and should be available on Github. It should be noted that any project the goes against the norms of the ecosystem can be removed by the platform.
After you have read and understood the conditions click on Submit a General Proposal to submit an application for the project
You will then be redirected to a page where you can start filling a form for the application process
Press
In the Press section, there are interesting articles about news and development of the platform that users can read. This section contains two options Press Enquiries and Press Kits and Media Assets
Press Enquiries
This option gives information to the press such as newspapers, magazines, radio stations, etc. It opens your mail where you can enquire about any information regarding the platform.
Press Kits and Media Assets
This section shows the Press skits and brand assets of the platform.
Community
Here is where the user gets to know about the social media communities and platforms that the Avalanche platform is available to join. It is available on
• Medium Link
• Twitter Link
• Facebook Link
• Telegram Link
• Discord Link
• Forum Link
• Reddit Link
• LinkedIn Link
• YouTube Link
• Meetup Link
• Clubhouse Link
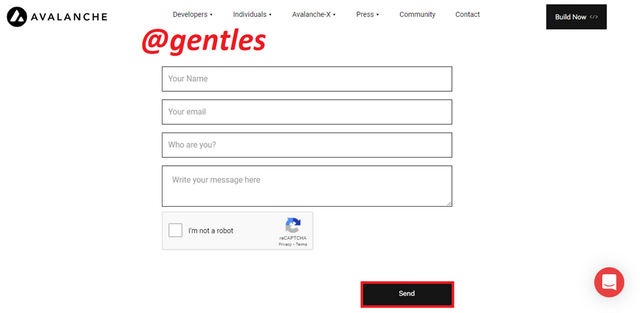
Contact
Users can get access to the Avalanche team and interact with them through the contact section. Fill in the form with your name, email, who you are, then your message, and click on Send.
It was not asked but it would not be right to talk about the Avalanche network and not talk about the AVAX token.
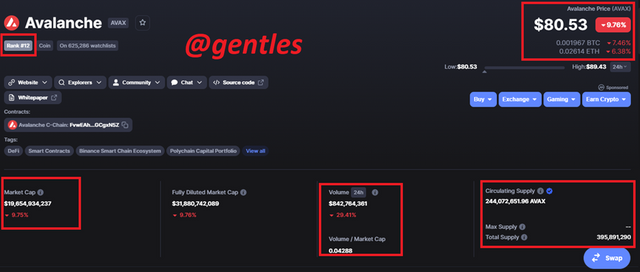
This token is the native token of the Avalanche platform. It is currently priced at $80.53 and ranked 12th on coinmarket cap. This token has a market cap of $19,654,934,237. In the last 24hours, there has been a transaction volume of $842,764,361 and a Volume to market cap ratio of 0.04288.
The total supply of this coin is 395,891,290 of which a supply of 244,072,651.96 AVAX is circulating.
Most transactions and activities on the Avalanche platform are charged in this token. Staking on the platform is also done using this token which allows users to take part in the governance process of the platform.
Question 3
Show The Last Verified Contract In The C-Chain Network And Show The Smart Contract That Was Generated At That Address.
Answer
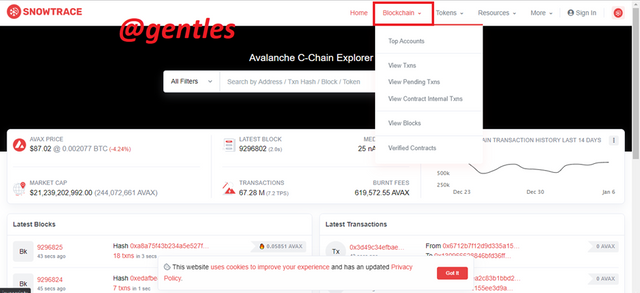
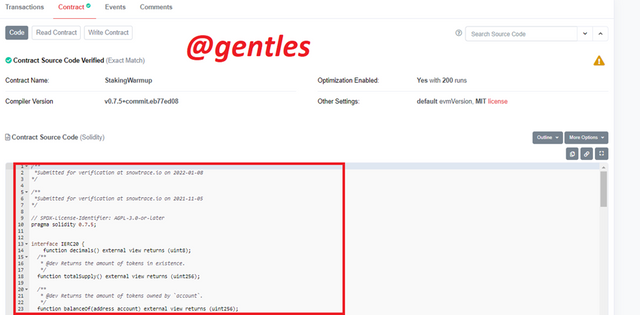
Smarts contracts are generated and explored in the C-Chain of the platform. I will be demonstrating how to access the last verified contract. To find the last verified contract, you have to visit https://snowtrace.io/alli this site is the official explorer for the C-Chain network
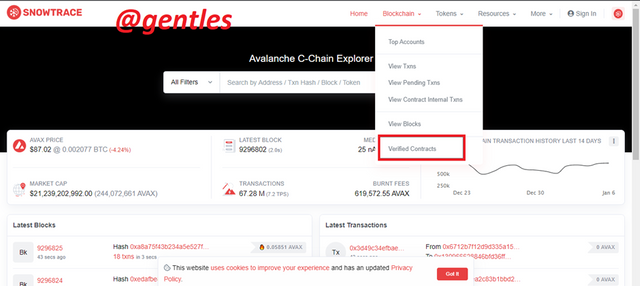
When you visit the site click on Blockchain on the page
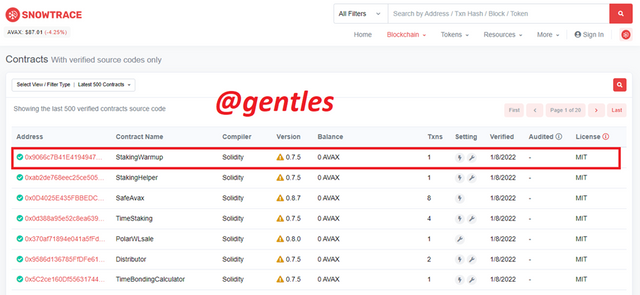
Since we are looking for the last verified contract, we will click on verified Contracts
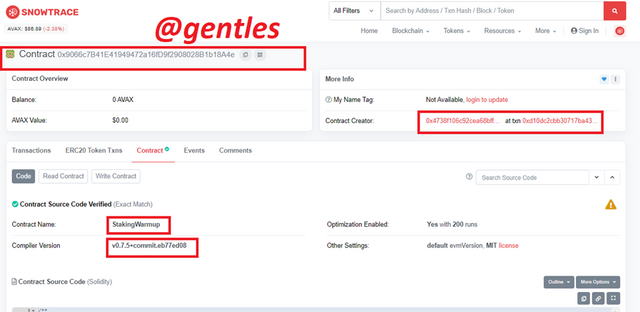
There will be a list of some verified contracts. The last one is always the first. Currently the last contract is named StakingWarmup with the contract address 0x9066c7B41E41949472a16fD9f2908028B1b18A4e. Click on the contract address to view its details
We can find some details about the contract on this page
The details are tabulated below
| Contract Address | 0x9066c7B41E41949472a16fD9f2908028B1b18A4e |
|---|---|
| Transaction Hash | 0x4738f106c92cEa68BFF4b212669F2E5676A25A0C |
| Contract Creator | 0xd10dc2cbb30717ba430eb5b773927a9027fcc711032cc27231e17d0805c8f69a |
| Name of Contract | StakingWarmup |
| Compiler version | v0.7.5+commit.eb77ed08 |
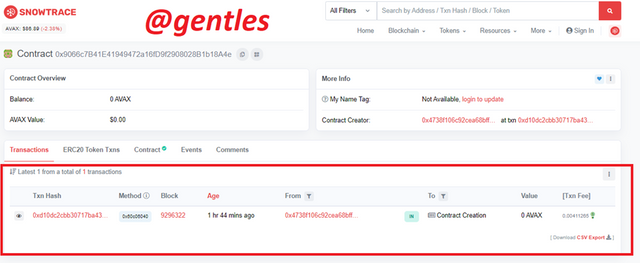
There is only one transaction on this contract, it was for contract creation.
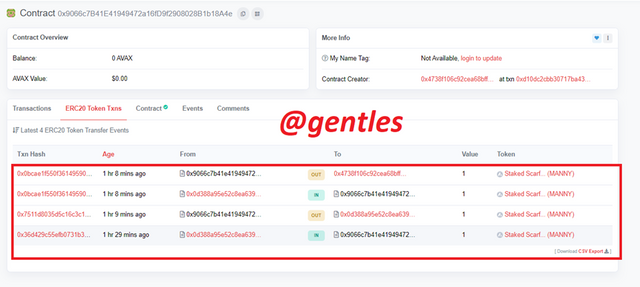
The other transactions on this contract are ERC Token Transactions. There were four of them.
Here are the hashes of the transactions
• 0x36d429c55efb0731b3cf817b6b756697aa06eb7e07cb06379b280462177f25f6
• 0x7511d8035d5c16c3c104af678bb604dd3af1eb2257f1e6441e88a035adb0357f
• 0x0bcae1f550f36149590b1ea95716363cf0d89c4a372062805a6c26d2695ba890
• 0x0bcae1f550f36149590b1ea95716363cf0d89c4a372062805a6c26d2695ba890
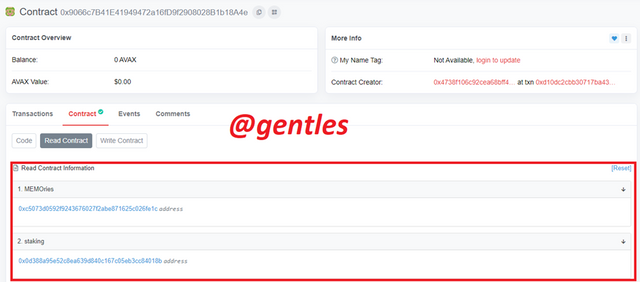
We can also see the information in the contracts below. From the information shown below, I think the contract was for staking on the platform
Here is the MEMOries address and the Staking address
| MEMOries address | 0xc5073d0592f9243676027f2abe871625c026fe1c |
|---|---|
| Staking address | 0x0d388a95e52c8ea639d840c167c05eb3cc84018b |
Here we can also find the written source code for the contract
The Contract’s ABI and Creation Code are shown below.
ABI means the Contract Application Binary Interface (ABI) is the required way to communicate with contracts in the Ethereum network, either from the external blockchain or for the interaction of two contracts.
Questrion 4
Explore the last block generated in the C-Chain network. Screenshots required
Answer
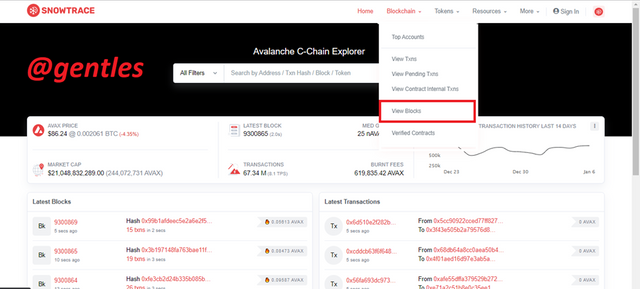
To demonstrate this, we will visit https://snowtrace.io Click on Blockchain from the top menu, and click on View Blocks from the sub-menu.
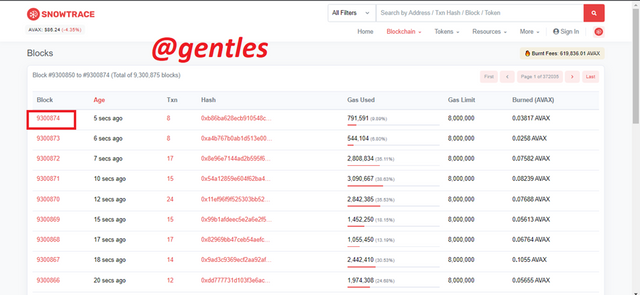
A list of newly generated blocks will be displayed. Click on the first block which is in my case 9300874
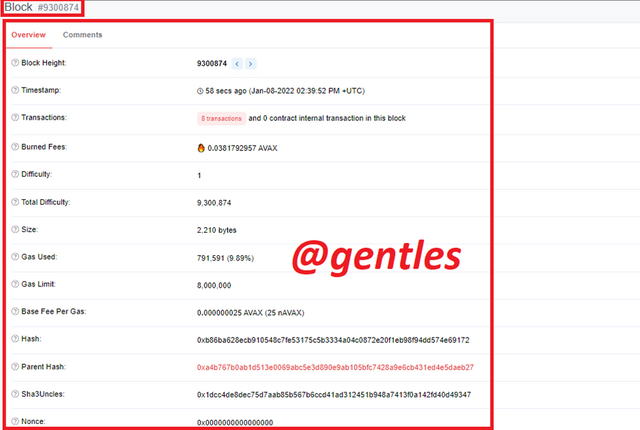
The details of the block will be displayed as shown below
Here are the details
| Block Height | 9300874 |
|---|---|
| Timestamp | 58 secs ago (Jan-08-2022 02:39:52 PM +UTC) |
| Transactions | 8 transactions and 0 contract internal transaction in this block |
| Burned Fees | 🔥 0.0381792957 AVAX |
| Difficulty | 1 |
| Total Difficulty | 9,300,874 |
| Size | 2,210 bytes |
| Gas Used | 791,591 (9.89%) |
| Gas Limit | 8,000,000 |
| Base Fee Per Gas | 0.000000025 AVAX (25 nAVAX) |
| Hash | 0xb86ba628ecb910548c7fe53175c5b3334a04c0872e20f1eb98f94dd574e69172 |
| Parent Hash | 0xa4b767b0ab1d513e0069abc5e3d890e9ab105bfc7428a9e6cb431ed4e5daeb27 |
| Sha3Uncles | 0x1dcc4de8dec75d7aab85b567b6ccd41ad312451b948a7413f0a142fd40d49347 |
| Nonce | 0x0000000000000000 |
Question 5
Explain in detail the Avalanche consensus protocol and the Snowman consensus protocol.
We already know that there are three different chains that come together to make the Avalanche blockchain. Similarly, the Avalanche blockchain has two different consensus protocols that make up the consensus mechanism of the Avalanche blockchain, it is therefore referred to as a multi-protocoled blockchain network. They function together to promote the scalability, transaction speed and security of the network.
Avalanche Consensus Protocol
This Consensus protocol uses probability in its operation to make the risk of error as small as possible. With this protocol, it is almost impossible for errors to happen due to how it is programmed to prevent a collision from the SHA-256 hash or a transaction.
Validators are involved in this protocol, they validate the transactions by a hearing process. When a transaction is to be executed, the validators will be asked in a voiced question to either accept or reject the transaction. The voting is done individually and the responses are sent to the group at large, if the group accepts it, the transaction is verified and if they reject it, the transaction is not verified.
The decision on whether to verify the transaction is made by the group after voting is done to reach a consensus.
In this protocol, the validator can select a certain number of other validators who are weighted by stake in a repeated random subsampling technique to query them of the transactions they prefer and also choose to go with it if there is a consensus reached.
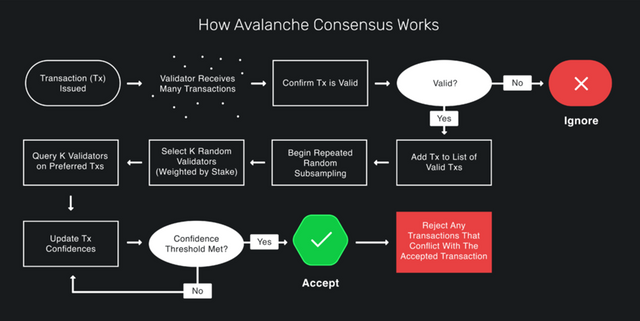
sourceIlustration
Here is a description of the illustration shown
Each individual validator is given some number of transactions that have been initiated and is asked to either choose to accept or reject them. The node clients offer the validators with the transactions who in turn provide their decision on the transaction to the node client.
The transactions are grouped into two, those that are accepted and those that are rejected. The accepted ones do not have any problems and the rejected ones have conflicts. If none of the nodes rejects a transaction, a consensus is reached. However, if there is any form of worry from the nodes, the validators with the worries are given an opportunity to make a choice.
Those validators select a certain number of nodes from the total nodes, say N. The selection process depends on the stake of the node, the higher the stake the higher the chance of being selected. The selected nodes, N, will then be questioned and their choices are added to the system.
If there is still no consensus reached on the decisions of the selected nodes, the process is repeated and nodes that have worries in those selected nodes is asked to select another group of N nodes to make a decision until the selected nodes arrive at one decision which is regarded as the decision of the node that did the selection and a consensus is reached.
If a consensus is reached, the decision of the consensus whether accepted or rejected is sent to the Virtual Machine which takes the decision and regards the transaction as accepted or rejected based on the decision of the nodes.
To add to this, in this protocol, blocks are not created, but instead, they are made parallel on the network. New transactions on the network are tied to the old ones using a mechanism called the Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) to make the validation process easy and quicker for the nodes.
All this process happens in a matter of seconds.
Snowman Consensus Protocol
This consensus protocol is regarded as the extensive form of the Avalanche protocol. It is used in the P-Chain in which there are subnets and also used in the C-Chain where smart contracts are managed. This Protocol helps in the creation and managing of smart contracts to manage the services of the DApps and DeFi on the platform.
Also, transactions in this protocol transactions are linear, not parallel as in the Avalanche Protocol. The nodes exist on this protocol in a variable manner.
Conclusion
The Avalanche blockchain was developed by Ava Labs. This platform makes use of three different chains namely; X-chain which manages token transfers and creation, P-Chain which coordinates validators and the C-chain which manages the creation of smart contracts.
This platform has an aim of making the creation of projects and DApps very affordable for every user irrespective of their financial status by given users the opportunity to apply for grants.
Just like most blockchains, this blockchain also has a native token called the AVAX token. This token can be staked on the platform to yield rewards and also the token is used to pay for some transactions on the network.
The platform is run by two consensus protocols namely; the Avalanche consensus protocol and the snowman protocol. The avalanche protocol uses the Directed Acrylic Graph mechanism to make the transaction parallel for easier validation. This also makes transactions faster and increase scalability.
The snowman is an extension of the Avalanche protocol and the main different difference between the two protocols is that the transactions are parallel in the Avalanche protocol and linear in the snowman protocol.
In this post, I also wrote about the avalanche block explorer. This explorer is the explorer of the C-Chain. I demonstrated how to view the last verified contract and also demonstrated how to view details of the last block on the network.
I explored the Avalanche platform and demonstrated how to open an existing wallet and also create a new wallet. During the exploration of the platform, I showed how to stake on the network.
Much gratitude to Prof. @pelon53 for this task













Good work done bro.
Thanks bro