The Steemit Crypto Academy Week 6: All About Blockchain Security 2


Course Outline
Introduction
Digital Signature
- What is Digital Signature
- Hash Function/Algorithm
- Public Key
- Private Key
- Public-Key Cryptography (PKC)
Hashing
Secure Hashing Algorithm (SHA)
SHA-1 and SHA-2
SHA-256 and the Blockchain
Conclusion

Introduction
Welcome to another Steemit cryptocurrency academy, and It is good to have you in my class this week. In this class, I will be continuing with the topic "All about Blockchain Security" but unlike in our previous class, we will be expatiating into the topic. The Blockchain has so many characteristics and one of them is being secured which means it is immutable to attacks. There are several mechanisms that make the Blockchain secured and in this post, I hope to discuss them.

Digital Signature
Have you been to the bank to withdraw funds from your account, and after appending your signature, you are told it doesn't match with what is on the system? This happens a lot and the reason why the bank will demand a signature similar to what is on the system is so as to validate the transaction.
Signature
Writing used to authenticate/verify the authenticity of the signer in a document, contract, or agreement. 1
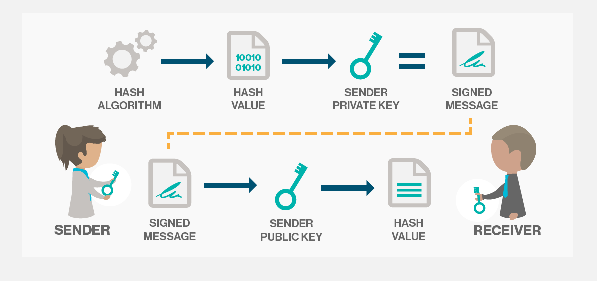
On the blockchain, Digital Signature is needed for ensuring security, integrity, and verifying the authenticity of data recorded. To understand Digital Signature and how it works, knowing the basics of a few mechanisms like Hash Function/Algorithm, Publick Key, Private Key, and Public-Key Cryptography (PKC) will be important.
Hash Function/Algorithm
Since data are sent in a raw form, they can be very large and in the process take a lot of space but with Hash Function/Algorithm, a mathematical function is used to convert the data into a fixed-length of numbers and letters known as Hash Value. The process is called Hashing.
With Hashing, there is an Input (raw data), the Hash/function (the mathematical algorithm/function used to convert the strings of data), and the Hash Value (The Hash you often see in a block). Two different input data cannot produce the same Hash value, and this is why different blocks have different hash values.
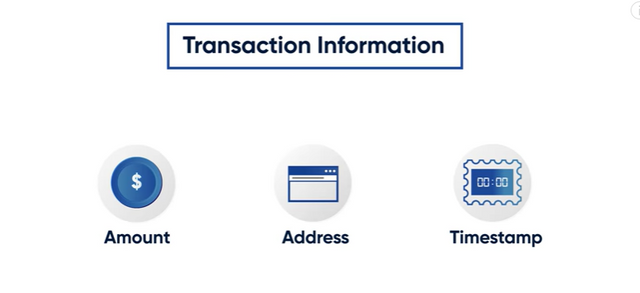
On the blockchain, certain inputs determine the Hash Value of a block, they are; Amount sent, Sender and Reciever Address, and Time Stamp. With these three inputs, it is very impossible to get the same hash twice on the blockchain even if the same amount is sent to the same receiver, the time stamp will differ. The hash value produced is what is referred to as the Transaction ID 2.
Public Key
Public keys are encrypted keys used in a transaction. With cryptocurrency, the public key is used to encrypt information. It can also serve as the wallet address which will be stored on the blockchain.
Private Key
A private key is an encrypted set of alphanumeric codes, that can be used to access a wallet. It is used to grant permission to a transaction from a wallet.
Public-Key Cryptography (PKC)
This is referred to as Asymmetric encryption, where both the private key and the public key are needed to send encrypted data as well as decrypt the data on the blockchain. The public key is used to encrypt the data while a private key is used to decrypt it.
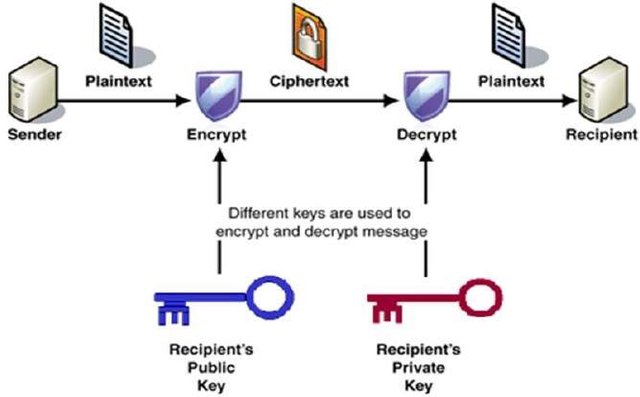
With PKC, a sender sends a message which should only be read by the receiver, and in other to do this, the sender encrypts the message with a public key which is owned by the receiver. The message gets to the receiver and the message is decrypted with a corresponding private key. 4
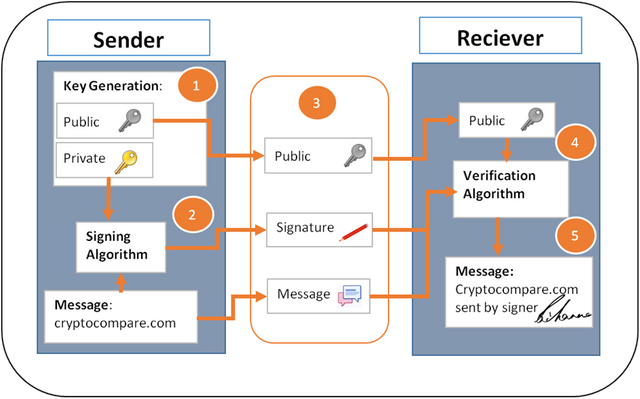
With Digital Signature, three processes are required; hashing, signing and verifying. Where all data inputted into a block is hashed, after which it is signed by the sender using public-key cryptography, where the private key is used to sign the message and the receiver verifies the authenticity with the help of a corresponding public key (the sender's public key) 5. With Digital Signature, both sender and receiver can trust that the message wasn't tampered with during the process of sending and a change in the message after sending will change the signature completely.

Hashing
Do not forget that we are looking at the mechanisms that make the blockchain secured and we have previously explained the Hash Function above. Hashes are pseudo-random sets of characters that are designed to make data secured.
Secure Hashing Algorithm (SHA)
Secure Hash Algorithms is a cryptographic signature that is used to encrypt data and on the blockchain, it is used to encrypt passwords and messages. No matter how long or short a data is hashed, it doesn't go above a certain string of characters. Hashing allows for easy verification of data should in case it has been tampered with (a hash will not occur for two inputs).
SHA-1 and SHA-2
SHA-1 was the first version of the Secured Hashing algorithm which was developed in 1993 and published in 1995by the United States National Security Agency (NSA) 6. It is a 160-bit hash with a combination of 40 digits.
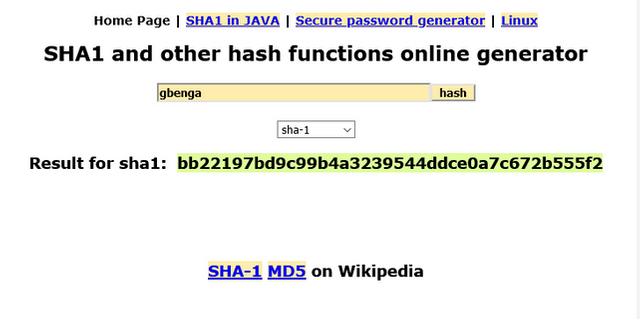
SHA-256 and the Blockchain
The Secure Hash Algorithm 256 was first developed in 2001 by the NSA. It converts strings of different words and characters into 256-bits, with 64 alphanumeric characters. It became a part of the blockchain with Satoshi Nakamoto introducing it into Bitcoin. It has since been used in several blockchain projects especially forks of Bitcoin such as Bitcoin Cash (BCH).
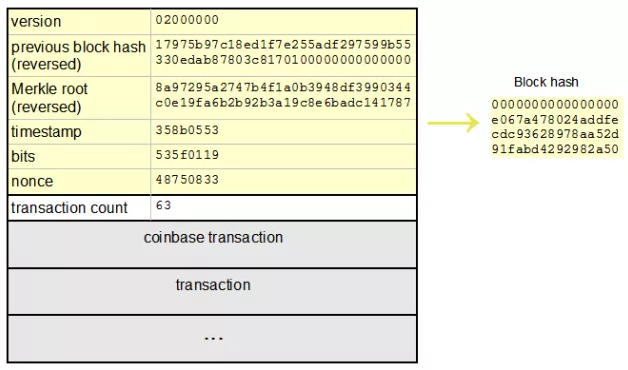
It is no doubt that SHA-256 is an integral part of the blockchain and it was the first algorithm for the mining of Bitcoin via Proof of Work making it part of the blockchain security mechanisms.

Conclusion
Blockchain security is very important to its existence. The combination of digital signature, hashing, and cryptography is no doubt a strong mechanism ensuring the security of data on the Blockchain.

Task

The Rules
- Everyone is eligible to participate in this task.
- The Post should be a minimum of 300 words and should be submitted in the crypto-academy community for visibility.
- You should include the exclusive tag #gbenga-week6, #cryptoacademy, and a tag of your country (for example #nigeria).
- Post should be your original content. Show references for images used when writing your post.
- Task runs until Sunday, March 21st, 2021

Image Credit
Wikimedia Commons
Lisk
Tutorials Point
Cryptocompare
mycryptopedia
Hi again @gbenga, this is my week 6 task:
https://steemit.com/hive-108451/@allbert/crypto-academy-week-6-all-about-blockchain-security-2-post-for-gbenga
Hi teacher @gbenga this is my homework for week #6, Crypto Academy Week #6 Homework Post for Professor @gbenga . I hope you like it. Greetings and good wishes.
Compartido en twitter: tweet-link
Hello dear sir @gbenga my home work task for week 6 is here. Hopefully you will soon visit my post and review it.
https://steemit.com/hive-108451/@steemlover63/steemit-cryptoacademy-home-work-task-week-06-for-gbenga-or-or-all-about-blockchain-security
Thank you a lot.
Hello @gbenga this is my homework task submission.
https://steemit.com/hive-108451/@okoyeclinton400/crypto-academy-week-6-homework-post-for-gbenga
For sure, no security, no savings. Blockchain wallet is a heavy tool for savings with no task. Only if the private keys created are in save hand or box.
Thanks @gbenga my boss in our dear country Nigeria. Respect my able Crypto proffesor of our time
Please here is my homework task submission.
https://steemit.com/hive-108451/@okoyeamaka11/crypto-academy-week-6-homework-post-for-gbenga
Hello dear sir @gbenga . My home work week 5 has not been reviewed.
Please checkout my post and review the post as soon as possible.
https://steemit.com/hive-108451/@steemlover63/home-task-week-5-for-prof-gbenga-or-or-security-problems-with-cryptocurriencies
Thank you a lot. !
Alright Sir, I'll do that..
thank you dear sir for visiting my post.
teacher my homework 5 has not been corrected yet, it has 4 days waiting, check please
https://steemit.com/hive-108451/@endersontowers/the-steemit-crypto-academy-week-5-all-about-blockchain-security-for-gbenga-by-endersontowers
You haven't checked my homework 5 yet, please check it
https://steemit.com/hive-108451/@eulalia1202/the-steemit-crypto-academy-week-5-all-about-blockchain-security-gbenga-eulalia1202
Thanks Prof. for this exciting lesson. Please my question is this...
What are the limitations of this Hashing?
Meanwhile, I humbly appeal that you please check out my previous Homework for your professional rating.