Different types of Consensus Mechanisms - Steemit Crypto Academy Season 5 - Homework Post for Task 6
(1) What is the difference between PoW & PoS? Advantages & Disadvantages? Which one is better in scaling Capacity? Examples?


What is the difference between PoW & PoS? Advantages & Disadvantages?

Consensus Mechanism
A consensus mechanism is an accepted protocol or mode of ensuring liability, security, transparency, and trust, particularly in a decentralized network. A consensus mechanism can also be applied in a centralized chain but it is not as effective as when applied in a decentralized network because it is prone to interference from a central authority or may only only be applicable to a sub-division of a centralized network.
It is most practical in the area of computer networking and blockchain development. Cryptocurrency, which has come to be one of the major drivers of blockchain technology is run by different consensus mechanisms. Some examples of such consensus mechanisms are Proof of Burn (Pob), Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), Proof of Capacity (Poc), Delegated Proof of Stake (Dpos), Direct Acylic Graph (DAG), Tetris, Proof of History (POH), Proof of Authority (POA), and the two most notable ones which are Proof of Stake (Pos), and Proof of Work (Pow).
Note: Two compatible consensus mechanisms can be combined in a blockchain. For example, Solana combines both Proof of History (POH) and Proof of Stake (Pos) consensus mechanisms.
For this task, I will discuss Pow and Pos consensus mechanisms.
Proof of Work (Pow)
Pow is the first consensus mechanism to be adopted in cryptocurrency blockchain. It was introduced by Satoshi Nakomoto in the BItcoin project to ensure the security, validation, and continuity of bitcoin. It primarily serves as a deterrence to the eventuality of double-spending in bitcoin and by extension, subsequent cryptocurrency blockchains that would adopt this consensus mechanism.
In cryptocurrency blockchain, Pow is an agreed-upon software and mining protocol by the users of a network as stipulated in its publication, whereby miners validate the transactions of a block by solving complex mathematical puzzles after which solutions are broadcasted in the network to be verified and confirmed by the network to avoid double-spending.
Here, miners are rewarded for their effort and input expended in solving complex mathematical problems. For instance, the bitcoin blockchain rewards miners with some BTC for solving the provided problems. It is this rewarded BTC that is sent to exchanges in transactions, hence ensuring the circulation of bitcoin in the market. Without the rewarded BTC, there would neither be circulation nor continuity of Bitcoin.
Note: The amount of BTC rewarded to miners halves after every 210 blocks are formed.
Brief Breakdown on Proof of work
The first thing needed here is specialized computational devices that utilize high energy to solve these complex mathematical puzzles.
Miners utilize available specialized computers to determine the hash (Cryptographic Identification no) of a block. Put simply, miners do this by decrypting the hash of the previous block and providing a more secured hash for the next block that fits into the previous hashes. Once a hash is discovered, it is broadcasted to the network, after which it is easily verified and confirmed by the network. At this point, a new block is added to the blockchain. The average block time for bitcoin is ten minutes.
Proof of Stake (Pos)
Pos became a reality in crypto blockchain when it was first implemented by peercoin developers - Scot, Nadal, and Sunny king in 2012. It was however somewhat combined with Pow. Pos has since risen to prominence in the world of cryptocurrency.
The first blockchain to purely implement Pos is the Nxt in November 2013. Others include Lisk, Dinar coin, Blackcoin, PIVX, and Polkadot e.t.c.
Pos can be defined as a consensus mechanism where the verification and addition of block are determined by the stake of a participant in the network. This entails that only nodes or participants in the blockchain that hold a relatively large amount of coins (stake) are eligible to select or be selected as the validator of a block.
As opposed to the Pow, Participants of Pos-driven blockchains utilize Initial Coin Offerings(ICO), that is they purchase these coins at their early stage of development, which in turn gives them an influential position in the platform. This position gives them the same power miners have in the Pow blockchain. The more coins you hold, the more "forging" power you have.
To eliminate the possibility of monopoly by the wealthiest nodes on the blockchain, some additional factors are taken into consideration apart from one's stake. They are:
- Random Block Selection
- Coin Age Selection
Random Block Selection
This factor entails that a node is selected randomly based on high coin stake and lowest hash value.
Coin Age Selection
This means that a node is selected based on the age of the stake (that is how long the token has been held without being spent) and high stake.
Pos rewards its validators with transaction fees of several transactions that make up a block as opposed to new coins that are rewarded to miners in Pow blockchains.
Tabular differences between Pow and Pos
| Pow | Pos |
|---|---|
| Pow reguires specialized equipments and high power for mining of coins | It requires high stake to forge coins |
| Pow rewards miners with new coins | Pos rewards validators with block transaction fees |
| There is high competition among miners to mine a block | There is little or no competition as validators are elected based on amount staked |
| A node must possess 51% of "computational power" to override the system and add a malicious block | To override the network, a node must possess 51% of all the "cryptocurrency" on the network |
| Pow is a more decentralized network | Pos is a less decentralized network |
| A node that validates a block is a miner | A node that validates a block is called a validator |
| coins are mined | coins are forged |
| Pow is less scalable | Pos is more scalable |
| Historically, bitcoin is the forerunner of Pow in cryptocurrency | Historically, peercoin is the fore runner of Pos in cryptocurrency |
| Miners may not be "hodlers" of the coin | Validators must be "hodlers" of the coin |
| Mining can be done collectively | Forging is more singular |
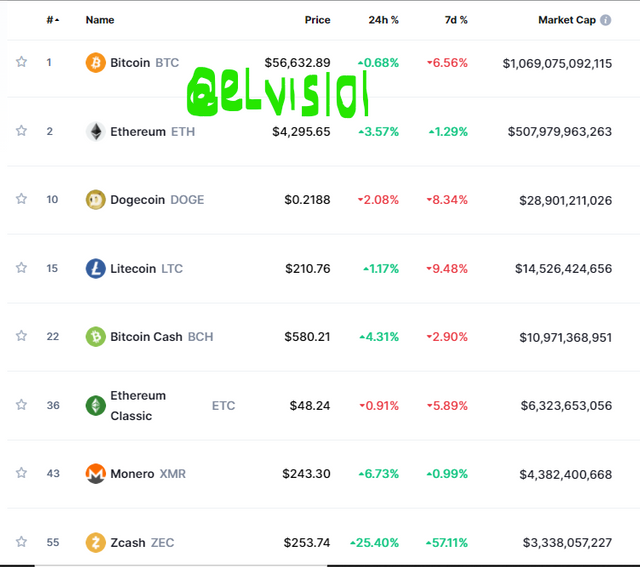
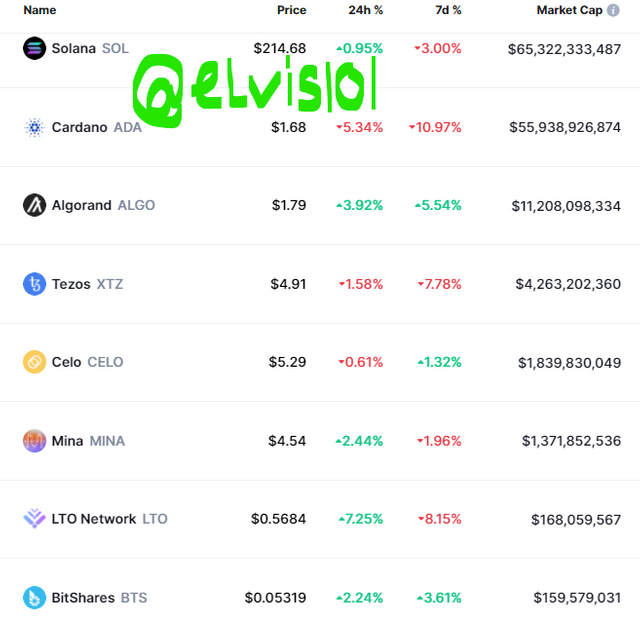
| Example of Pow-driven cryptocurrencies are Bitcoin, Litecoin, Ethereum, Monero, Zcash, and Dogecoin e.t.c | Example of Pos-driven cryptocurrencies are Tezos, Dash, Algorand, Bitshares, Lisk, and Cardano e.t.c |
Advantages of Pow
- Equal mining probabiity
Pow is open to capable miners. They all have an equal chance of coming up with a solution to the presented mathematical problems. There is no need to conduct any governance voting which may be prone to bias. The challenge and openness posed by Pow make it an ingenious and sustainable consensus mechanism. It is a more independent consensus mechanism than the Pos.
- Security
Pow ensures that hacking the blockchain is pretty difficult as a hacker must have to override about 51% of the mining power to be able to disrupt the network. Since this is almost impossible or at least would be a pyrrhic victory if done, the tendency of such eventuality occurring is very low.
- It prevents double spending
The primary essence of Pow in cryptocurrency blockchains is to prevent double-spending. By proper cryptographic validation and signing of coins provided by the Pow protocol, coins are made in such a way that they can't be spent twice. This has been tested and proven.
- High Incentive
Pow rewards miners with a good number of coins. This serves as an incentive to the miners especially when the price of the said coin is high. For instance, bitcoin miners receive some amount of bitcoin for right hashing. And with the current price of bitcoin and likely futuristic price increase, miners are incentivized to put in the necessary input to get the reward. Though it is important to note that the increase in the price of a coin leads to a correlational increase (due to an increase in competition) in the need for more specialized computational devices.
Disadvantages of Pow
- It is expensive
The cost of acquiring mining equipment and high power is pretty high. This means that only miners with tons of money or larger mining pools can mine especially when it comes to cryptocurrencies with high prices. Bitcoin and ethereum mining are two notable examples of such high-cost mining.
- Possibility of mining centralization
Due to the cost of mining cryptocurrencies like bitcoin, it is left in the hands of a few large mining pools that have the resources to do so. The danger of this is that an ambitious mining pool can choose to acquire as much as 51% of all the bitcoin mining pools in existence. This means that the mining pool would be able to manipulate mining to their favor, thus leading to a centralized mining system.
- Pow is environmentally unfriendly
One of the negative issues that come with Pow is its negative impact on the environment. The overwhelming energy burned up in the process of mining releases by-products (gaseous substances) that are not so healthy to the environment. The issue of climate has the attention of the world at the time and therefore the negative results of Pow mining on the environment is an issue worth addressing.
- Mining can be frustrating and wasteful
The costly equipment and high energy used in mining are exclusively for discovering the right hash of a block and nothing else. The energy used here is under-utilized as it is too much to just be used for only hashing. Another flip to this is that miners possibly get frustrated over unsuccessful attempts after having put in so much energy to finding the right hash of a block.
- Hoarding is a possibility
With the continuous reduction of mining rewards, miners may resort to hoarding the rewards instead of pushing them out to exchanges in transactions. For instance, in bitcoin mining where rewards are halved after every 210 blocks, continuous halving may see miners hold back BTC in a bid to affect the market price so they can get commensurating rewards for their high input. Theoretically, this may impact negatively on the liquidity of the BTC market.
- Scalability
Scalability is an issue with most decentralized virtual networks as opposed to centralized virtual networks. Centralized networks can process more transactions per second because of their inherent decisive nature in decision making. On the other hand, Pos-driven decentralized cryptocurrency networks are doing quite well in narrowing the scalability gap between centralized and decentralized networks. Pow-driven decentralized networks seem to be the major culprit here. I believe this is so because of the timing nature of mining, validation, verification, and confirmation of a block in a Pow-driven network.
Advantages of Pos
- Forging a block is less expensive and less wasteful
The only resource needed to forge a block here is one's initial stake, unlike Pow where one needs high energy input and costly devices. It is also less wasteful as there is no need to engage in repetitive tasks that are solely meant to solve a singular problem: there is no room for wasted efforts.
- Encourages Long -term investment
Pos encourages users to stake or lock their money in the system over a long period. This drives users towards the healthy habit of long-term savings. Users are also able to benefit from the increase in coin price across time. On the other hand, such positive habit help stabilize the network and increase the tendency for positive price outcomes.
- Faster scalability
By nature, Pos-driven blockchains are more scalable. This is so because most Pos networks take less time to validate, sign and confirm the transactions in a block as opposed to what is obtainable in most Pow networks. As I said earlier, Pos-driven networks are narrowing the scalability difference between decentralized and centralized networks like Vista (processes about 25000 transactions per second).
- Less harmful to the environment
From a climate perspective, Pos is safer to operate than Pow because it is free of high energy consumption that releases gaseous substances into our climate. This is one of the reasons why more Pow networks may eventually change hands to adopt the Pos.
- Stronger immunity to centralization
The possibility of a very ambitious mining pool taking over about 51% of all the mining pools of a crypto network is less likely because block validation is left to the consensual voting of users in the network. This also makes it less prone to attack.
Disadvantages of Pos
- Less incentive
Pos rewards block validators with the transaction fees of a block. When compared to the reward obtainable in Pow, Pos is somewhat less rewarding.
- One can only acquire coin by purchasing
There is no way a user can become a block validator or acquire more coins without first purchasing them. This is not so with Pow where a user can exclusively acquire coins from mining while also being able to purchase coins.
- Inability to spend locked coins
Though staking coins can be seen as a good financial habit, it may be disadvantageous to users at some point. For instance, a user may want to withdraw coins to avoid a negative financial forecast or needs the coins for an urgent purpose.
- Voting can prove less decentralized
Though the system may have put measures in place to ensure that the selection of a block validator is left to consensual voting and randomization, it is yet accused of selecting the same set of people as block validators from time to time. Let's say five nodes in a network are the wealthiest and are also qualified judging by their coin-age selection, random selection would most likely revolve around these five nodes, thus making the system less decentralized. Some argue that consensus is more theoretically proven than it is practically.
- Less proven track record
On the scale of time, Pos is relatively new, thus may not have been fully tested and proven like its counterpart- Pow. It may yet need to be exposed to the kind of attacks that would determine if Pos is a more recommendable consensus mechanism.

Which one is better in scaling Capacity? Examples?

Scalability
Scalability can be defined as the highest number of transactions that a network can process in a second. It is abbreviated as TPS (Transaction per second). It is the combination of the latency and bandwidth ratio that a network can handle.
Scalability has been an issue with decentralized networks because of the thousands of transactions that the network is expected to effectively process in a given time without any centralized authority regulating the process.
Scalability is one of the major factors to consider when determining the efficiency of a consensus mechanism. To determine the scalability preference between Pow and Pos, I will point out the scalability of some popular Pow and Pos cryptocurrency blockchains.
- Cardano
Cadano is a Pos driven blockchain.
Cardano is an eco-friendly cryptocurrency blockchain that was developed by Charles Hoskinson (Co-founder of Ethereum). Cardano is currently the third largest coin by market cap. The blockchain processes about 257 transactions per second (TPS).
- Bitcoin
Bitcoin is a Pow-driven blockchain. It is the first-ever cryptocurrency blockchain that was developed by Satoshi Nacomoto. By market cap, bitcoin is currently the largest cryptocurrency. It processes about 4.6 transactions per second (TPS) and takes about ten minutes to form a block.
- Solana
Solana is a Pos-driven blockchain. Solana is a crypto blockchain that was developed by Anatoly Yakonko in 2018. The blockchain is notable for its scalability and is currently ranked the 7th cryptocurrency by market cap. The blockchain is capable of processing 60, 000 transactions per second (TPS).
- Litecoin
Litecoin is a Pow-driven blockchain. It is a cryptocurrency blockchain that was founded by Charlie Lee in 2011. Based on ranking by market cap, Litecoin is currently ranked the 14th cryptocurrency. Litecoin processes about 56 transactions per second (TPS).
- Polkadot
Polkadot is a Pos-driven blockchain. It was developed by Gavin Wood in 2016 as a blockchain protocol that connects other blockchains.
By market cap, Polkadot is ranked the no 8 cryptocurrency. The blockchain can process about 1000 transactions per second (TPS).
- Ethereum
Though ethereum has announced its intention to move over to Pos mechanism, it is currently a Pow-driven blockchain. The blockchain was founded by Vitalik Buterin in 2013 and released in 2015.
By market cap ranking, Ethereum is ranked the no 2 cryptocurrency. The blockchain is capable of processing about 27-30 transactions per second (TPS).
From the above examples and pieces of evidence provided by general research, I can comfortably deduce that Pos is a more scalable consensus mechanism than the Pow consensus mechanism.
This is one of the reasons why more blockchains are likely to abandon Pow for Pos in the future. Ethereum seems to be paving the way in this direction.
Every cryptocurrency blockchain has an adopted consensus mechanism that it relies upon to ensure security and transaction validation.
Pow and Pos, the leading cryptocurrency consensus mechanisms,
are being debated to decide which is better. Though most of the highest-ranking cryptocurrency blockchains by market cap are Pow-driven blockchains, they have been criticized for being less effective in terms of scalability - bitcoin being the leading example.
Pos has been gaining recognition in recent years because of its flexible design and scalability and may likely outmatch Pow with time.
However, I believe that the overall preference of both consensus mechanisms continues to be tied to their security.
Thank you for reading.
Courtesy: Prof @sapwood