Different Types Of Consensus Mechanisms-Steemit CryptoAcademy Season 4: Homework Post for Task 6
Hello there again👋👋👋👋👋
It's @cosai99 again with the next homework post for Task 6 for Steemit CryptoAcademy Season 4 Introductory Course. Today, in this task, we will discuss the various consensus mechanisms used by various blockchain networks we have, especially the most common ones, PoW and PoS. We will talk about these two extensively while making mention of the others. This lecture was facilitated by Prof. @sapwood and reviewed by @nane15 and @dilchamo.
Let's take a look at today's task, shall we?🚗🌫🌫
Overview of Different Types of Consensus Mechanisms ❄🤝🔐💬
As we have discussed previously, we mostly now notice most of the Cryptocurrency networks adopting the decentralized system. This disintegrates the delegations of powers into the hands of stakeholders and hence creates an opportunity to develop a lot of servers being the nodes of the blockchain. Hence, there is a need for verification and security of these blocks being created every second. We would then need a form of mechanism for all block verification to agree to for security to be maintained. This also has to have a root to the Genesis Block of the blockchain to have a certain level of consistency. Therefore, we then tend to establish a Consensus Mechanism for all blocks, previous and incoming, to agree to and as a result, provide a sense of security to the information contained in these blocks.
Image Source
There are various consensus mechanisms adopted by various blockchain networks depending on the kind the network has agreed to work on. These include:
- Proof-of-Work

Proof-of-Work
- Proof-of-Stake
.jpg)
Proof-of-Stake
- Proof-of-Burn

Proof-of-Burn
- Proof-of-Capacity

Proof-of-Capacity
- Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance
But in this homework post, we will concentrate on PoW and PoS more.

QUESTION 1
What is the difference between PoW & PoS?
Before we begin, let's start with what exactly is PoW and PoS.
Proof-of-Work(PoW)
This consensus mechanism is based on the number of transactions Miners are able to confirm. As we already discussed, the blocks are in the form of hexadecimal codes(cryptographic puzzle), which is machine language and cannot be read by humans. Hence, puzzles concerning transaction blocks are taken from the unconfirmed pool to miners to solve. The computer runs these codes based on the codes and gives feedback to the Validator to verify if the block is the same and hence if found so, would be confirmed verified. Upon solving the puzzle, the miners are rewarded with cryptocurrencies as thanks for their effort. The level of mining depends on the level of specs of the computer components like processors number and strength therefore the higher these factors are, the more block you can solve within a given time limit and hence the more the rewards. It must be noted that this consumes a lot of electricity and hence is very costly to run.
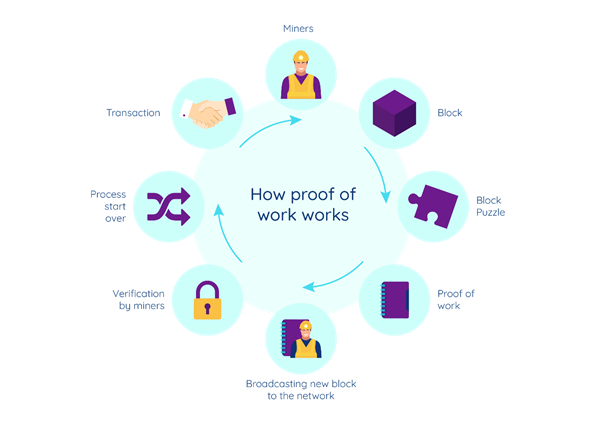
Process of PoW
It must be also noted that the miners are chosen at random. The speed of producing the blocks varies from network to network. The mining rig s where miners take their puzzles and get to solve them and they only get 1 attempt to solve each puzzle.
Proof-of-Stake(PoS)
With this consensus mechanism, a stakeholder is selected based on the number of tokens he possesses. He/she also becomes a validator to verify the blocks that are created in the network. Unlike PoW, it doesn't require any decryption or solving of puzzles but just to verify the blocks coming. Therefore, the mining power of stakeholders depends on the number of tokens you hold, hence the more you possess, the better the chances of being a Validator in the blockchain.
The validators do not receive any block rewards like in PoW but rather network fees.

Information of PoS
This characteristic gives some sense of centralization and hence the system was further modified to solve that problem. As a result, the Delegated Proof-of-Stake system was introduced.
Delegated Proof-of-Stake(DPoS)
This is slightly different from the PoS system in the sense that here, the power is delegated to a group of stakeholders to become validators. They are chosen based on the votes they receive from stakeholders in the network. Hence the highest number of votes attained by a stakeholder grants the highest influence amongst the validators. They are usually referred to as Witnesses. The task of validating blocks falls on them all and it becomes a shared responsibility. The number of witnesses needed differs from network to network.

DPoS system
For example, STEEM has a 20+1 number of witnesses whiles Tron Network has 27 witnesses.
Difference Between PoW and PoS.
| Proof-of-Work(PoW) | Proof-of-Stake(PoS) |
|---|---|
| PoW consumes a lot of resources like electricity since processors need to solve the cryptographic puzzle within a given time frame to iterate the code to achieve the required result. | PoS doesn't require that much electricity as PoW since delegates just need to confirm the transactions on the blockchain without solving any puzzle. |
| In PoW, the selection of miners isn't centralized but rather chosen at random. | In PoS, since the delegates are selected by the number of tokens they hold it is a bit more centralized than PoW. |
| In PoW system, the rewards given are the block rewards(obtained from deciphering the codes to confirm the transition). | In PoS, the rewards gotten are not block rewards but then network fees that are aportioned to witnesses. |
| The PoW system is based on the number of blocks one can mine corresponding to the processor speed. | The PoS system is based on the number of tokens held by stakeholders and hence determines the mining power of stakeholders, |

Advantages & Disadvantages?
Proof-of-Work(PoW)
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| It is very secure as when edits a particular block incorrectly it affects the entire blockchain and hence rejects the altered block. | This consumes tons of electricity and amounts to a lot of bills to pay, making the system very cost and energy ineffective. |
| it has very limited scaling capacity meaning that compared to its alternates, PoW can handle lesser transaction blocks due to the fact that a limited number of blocks can be confirmed per second. This also depends on the speed of processing the required minimum number of zeros for the hash of a block. |
Proof-of-Stake(PoS)
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| This system is energy and cost efficient since it doesn't require so much resources to execute. | Due to the mechanism of the system, stakeholders are required to hold a lot of native coins of the blockchain thereby limiting the chances of becomes a Validator. Also, this results to the phenomenon where the rich get richer since the stakeholder has too stake a lot of coins to better the chances of mining success. |
| Here, proper validation is incentivized hence producing a higher level of transparency. Since it is known that miners are given transaction or network fee, they lose the stakes if they approve a fraudulent transaction. This encourages a decent level of accountability in the blockchain | This system has high susceptibility to 51% attack. An attack is the situation where a stakeholder takes advantage of the blockchain mechanism after owning more than 50% authentication capabilities. This means that as the highest stakeholder takes more transaction fees, they can stake higher tokens to secure them the highest position to continue to Validate the transactions. This will in effect devalue the cryptocurrency and affect the real-time value of the coin. |

Which one is better in scaling Capacity?
From what we discussed we have established that the PoS system has more scaling capacity than PoW. This is because the PoS system doesn't require expensive hardware and high energy cost to run but rather the number of naitve token staked. This encourages more people to try their chances of becoming a validator.

Examples?
Examples of PoW system includes Bitcoin, Dogdecoin , Litecoin, .etc.
Examples of PoS system includes Cardano, Polkadot, Solana, Avalanche, Tron, EOS, Algorand, and Tezos, With STEEM and Tron having DPoS systems.

Conclusion
We have spoken extensively about the consensus mechanisms and also touched on the two most popular which are PoW and PoS. To conclude, we have discussed how the decentralized come to a form of agreement in how to validate blocks in the blockchain to provide better security to users.
