Crypto Academy / Season 3 / Week 6 - Homework submitted to @stream4u | Let's Open the Blockchain
- What is blockchain and what are the types of blockchains/ explain in detail the types of blockchain
Blockchain is a distributed, irreversible ledger that makes recording transactions and managing assets in a corporate network much easier. Assets can be tangible and intangible. Tangible assets include house, car, cash, or land while intangible assets are copyrights, intellectual property, or patents. Any valuable property can be tracked and recorded on a blockchain network which reduces risk and cuts cost. Each block on the chain comprises a range of transactions, and whenever a new transaction occurs on the blockchain, a record of that transaction is added to the ledger of each participant.
Blockchains are actually ideal for delivering information. This is due to the fact that it delivers immediate and transparent information kept on an irreversible ledger that can only be viewed by network members who have been granted permission. A blockchain network can track payments, orders, accounts, orders, etc. and the details of every transaction can be seen by the users.
What are the types of blockchains?
There are about four types of blockchains and they include:
- Public blockchain
- Private blockchain
- Hybrid blockchain
- Consortium blockchain
Public blockchain
Public blockchains are open-sourced just anyone (users, miners, developers, or community members) can participate. Transactions that take place here are transparent which simply means that anyone can see the transaction details. Public blockchains are actually decentralized with no one person controlling the transactions that are recorded in the blockchain. They are also highly resistant to censorship since it is very accessible for anyone to join the network. As a result, it makes it difficult to be shut down by authorities. In addition, there are tokens associated with them as the goal is to reward participants of the network.
Advantages
Complete Independence
Public blockchains are completely independent of any institution so the blockchain will continue running even if the organization that started it ceases to exist.Transparency
All transactions and orders made on the public blockchain can be seen by the users as long as they obey the security protocols and methods. It is also worthy to note that public blockchains are highly secure.
Disadvantage
Slow network: the network can be quite slow as companies and organizations cannot restrict access to it. Consequently, the network slows down as more users join the network.
Uses
Public blockchains are commonly used for mining and exchanging cryptocurrencies. It can also be used to create a record with a chain of custody which can be property ownership or electronic notarization of affidavits. More so, it is also ideal for companies that are built on trust and transparency such as NGOs and social support groups.
Private blockchain
Private blockchains are also called permissioned blockchains because participants must get consent to join the networks. Transactions are not transparent and are only visible to users of the network. In addition, private blockchains are more centralized as compared to public blockchains and may not have a token. This blockchain is on a much smaller scale and profitable for organizations that want to join and share data but won’t want their business data to be out to the public.
Advantages
Effective control
The organization in charge sets the security, authorization, accessibility, and levels of permission. It can determine which node can change data and view.Speed
private blockchains are limited in size hence they are very fast and transactions are processed even more quickly.
Disadvantages
It is difficult to achieve full trust and confidence since it is centralized and can easily be compromised. It is argued that it isn’t a blockchain because it faults the idea of blockchain which is decentralization. More so, there is no anonymity for its users.
Uses
They are mainly used in cases where the blockchain needs to be secure cryptographically but the organization in control doesn’t want the public to access the information.
Hybrid blockchain.
A hybrid blockchain simply combines the qualities of both private and public blockchains. It uses the permissioned and private benefits of the former and the security and transparency of the latter. This makes it very unique and avails businesses the flexibility to choose what data they want to make private and which they want public.
Users can simultaneously post to numerous public blockchains, increasing transaction security and benefiting from combined hashpower. Dragon blockchain is an example of a hybrid blockchain. Hybrid blockchain records and transactions are not accessible to the public, but they can be verified if necessary by granting access via a smart contract. When a user joins the blockchain, he has full access to the network although his identity is left discreet unless they engage in a transaction.
Advantages
- Hybrid blockchain works in a closed ecosystem and hackers outside the system can’t mount a 51% attack on the network.
- It protects the privacy of users while allowing communication with third parties.
- Transactions are relatively cheap and fast and it has better scalability as compared to the public blockchain network.
Disadvantages
It is not entirely transparent as information can be shielded. More so, it can be challenging to upgrade and there is no incentive for users to contribute to the network.
Uses
There are strong uses for hybrid blockchain such as real estate, highly regulated markets, and storing of medical records. The Government can also use it to store the data of its citizens which cannot be viewed by third parties but can be shared securely between institutions.
Consortium blockchain
The consortium blockchains are also known as the federated blockchains are considered a different designation from private blockchains and this is because they are governed by a group rather than a single body. It has the same benefits as private blockchains and is often considered as its sub-category. The collaborative model brings together a group of businesses that work together but compete against each other. This makes them more efficient both collectively and individually, by collaborating in some aspects of their respective businesses. Anyone can participate including central banks, supply chains, and the government. The consortium blockchain has a validator node that initiates, receives, and validates transactions and the consensus procedures are controlled by preset nodes.
Advantages
It is more secure, scalable, and efficient than the public blockchain and offers access controls just like hybrid and private blockchains.
Disadvantages
It is less transparent and can be compromised if a member node is breached. The regulations of the blockchain can impair the functionality of the network.
Uses
It is mainly used for banking and payment. It can also be used by research organizations. Furthermore, it is ideal for supply chains especially food and medicine apps.
- What are the benefits of blockchain?
- Increased security
- Greater transparency
- Improved traceability
- Increased efficiency and speed
- Automation
Increased security
Blockchains are highly secure by creating a record that is immutable and encrypted end-to-end. It also helps prevent fraudulent and unauthorized activities. It handles privacy issues by creating anonymity to personal data and using permissions to prevent access. Furthermore, information is stored across a network of computers and not a single server and this makes it difficult for hackers to access data.
Greater transparency
Participants of the network are allowed to have permissioned access to the same information at the same time which increases transparency. This is because blockchain uses a distributed ledger, data and transactions are recorded exactly in different locations. The transactions are immutably recorded with date and time-stamped. This helps users to see the entire history of transactions and curbs the ability to fraud.
Improved traceability
There is an audit trail that records the provenance of an asset at every point of the transaction. It can be used to provide proof for any company troubled by fraud and counterfeiting. It can also be used to share data about provenance to customers directly although it can also expose the weakness in any supply chain.
Increased efficiency and speed
Blockchain reduces conventional paper-heavy processes which are time-consuming, prone to human error, and requires an intermediary. Transactions on the blockchain are completed faster and more efficiently. The documents can be stored on the blockchain together with the transaction details which eliminates the need for paper. Settlement and clearing are faster because there is no need to reconcile multiple ledgers.
Automation
There is an automation of transactions using smart contracts which makes it faster and more efficient. Smart contracts minimize human interactions, as well as intermediaries, and the next step in the process is automatically triggered once the pre-specified conditions are met.
- Explain blockchain distributed ledger
A distributed ledger is a database of any transactions that are maintained in a decentralized form and accessible across different sites, locations, and people. This eliminates the need for a centralized system to keep check against alterations. This simply means that a central authority is not required to validate transactions. The information on the distributed ledger is secure and stored accurately using cryptography and they are immutable. The said information can be accessed using keys and cryptographic signatures.
The use of distributed ledgers has reduced cybercrimes and financial fraud. It has also sped up the time taken for transactions to go through as well as reduce operational inefficiencies. They can either be permissioned or permissionless. This determines the mode of operation if anyone or only approved people can validate transactions by running a node. They also vary between consensus algorithms and may be mineable.
Properties of distributed ledger technologies
Immutable: It is immutable and valid transactions are irreversible
Transparency: It is transparent and all network users have a copy of the ledger
Unanimous: There is a unanimous agreement between users
Anonymous: There is the anonymity of participants
Secure: Transactions are secure and records encrypted.
Distributed ledger can be used in the following industries
- Artwork
- Finance
- Entertainment
- Precious assets
- Supply chains
Benefits of distributed ledger technologies
- DLTs removes intermediaries to engage with direct and trusted transactions which increases efficiency and reduces the cost
- They are highly accessible and people can carry out their transactions freely without restrictions on participation or transaction.
- They are resistant to tampering which makes them secure and trustworthy
- They are immutable which adds to their credibility.
- What is blockchain double-spending and how bitcoin handles this problem
Double spending in the blockchain is a situation where a digital currency is spent twice. This occurs when the network is disrupted and the cryptocurrency is stolen. This tends to be an issue for digital currencies because digital information can be easily reproduced by people who understand the system and computing power required to manipulate it. This is particular with Bitcoin which requires a 10minutes block validation time.
A hacker can send a worth of an asset to a particular address and within the time he is waiting for the confirmation of his transaction, he may manipulate the system, reverse the worth and create another transaction. He does it in such a way that the first asset looks unspent or as though initial transactions have never occurred. More risk of double-spending comes in the form of a 51% attack.
How bitcoin handles this problem
Bitcoin handles the problem of double-spending by implementing a confirmation mechanism, deactivating partial spending of UTXO, and maintaining a universal ledger called a blockchain.
All transactions sent to the network are made to go through confirmation. The first to pull through is sent to the stated destination while the failed ones pull out of the network. In addition, bitcoin also uses complete sending where a user can’t spend the unspent transaction output. What is does is to create two outputs after confirmation automatically. The main withdrawal is sent to the destination wallet while the balance is sent back to the user’s wallet through a change address.
- Practical + theory, visit Blockchain Demo and check section Blockchain and then explain in detail how blocks hashes work in blockchain, what will happen when any middle of the blocks gets changed, try to give screenshot for each possible detail.
To begin, let us explore the blockchain demo website and I will first be using the Hash section.
I will input data to see the result
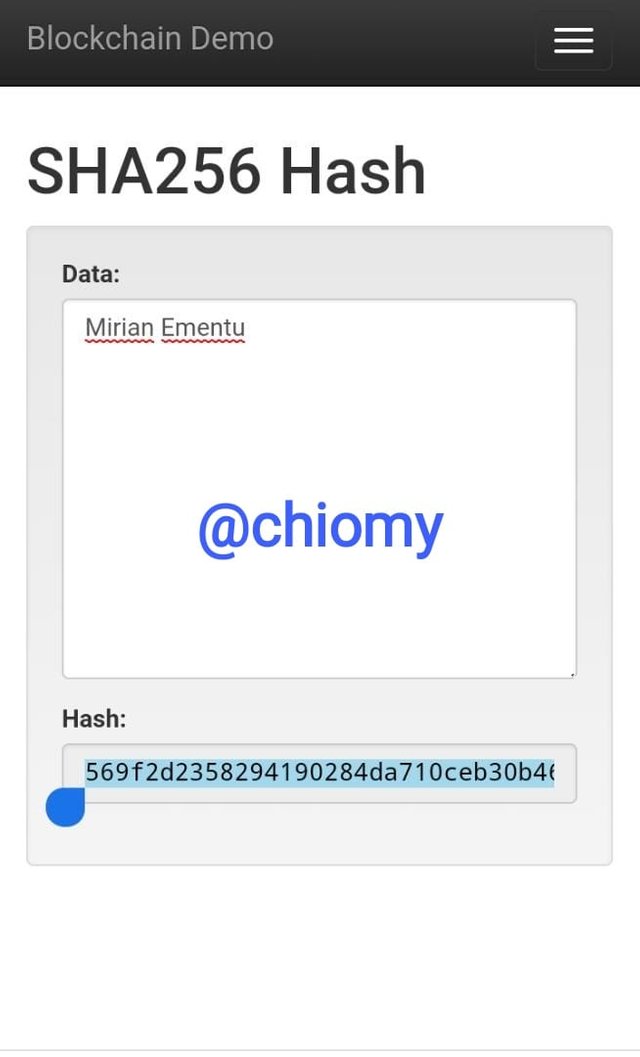
The resulting hash for “Mirian Ementu” is 569f2d2358294190284da710ceb30b463d0786315107431a39ae405755293526.
I will add more input and see what the outcome will be.
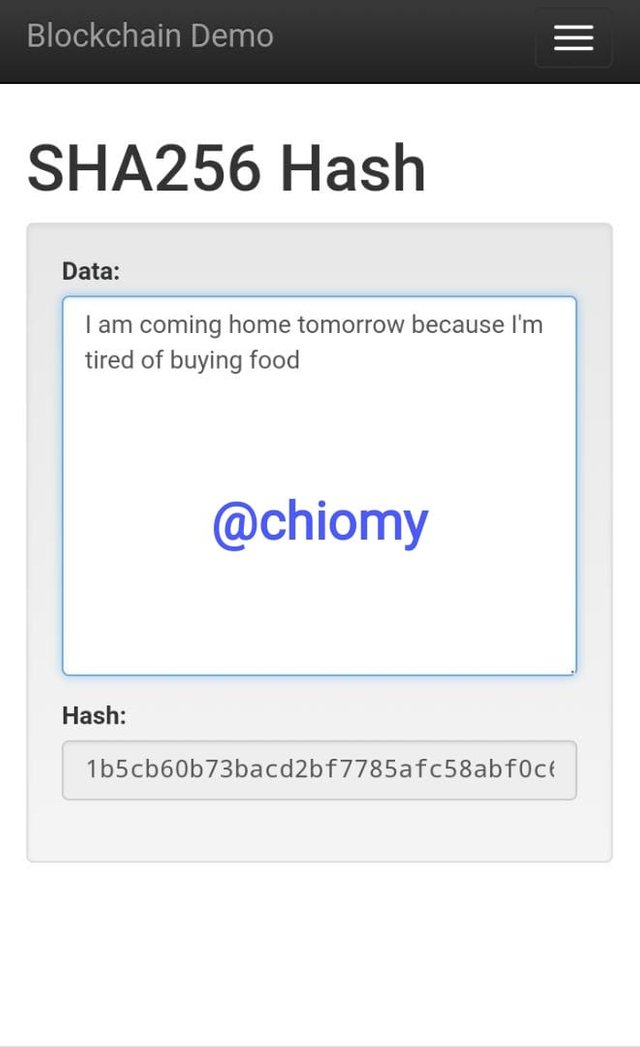
I inputed “I am coming home tomorrow because I’m tired of buying food” and the resultant hash has remained fixed length and is 1b5cb60b73bacd2bf7785afc58abf0c6c0026776fb7ea1adaad145544bd97958
Let’s go through the blockchain section of the website to see blocks hashing process.
From the picture above, I clicked on blockchain and I am fully in the section. The landing page is shown below
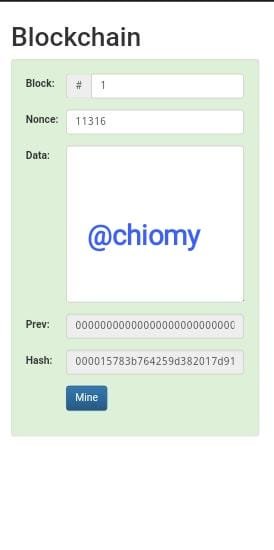
A hash must begin with a few zeros for it to be considered a valid block ready to be added to the chain and the output above is valid. The hashing output is 000015783b764259d382017d91a36d206d0600e2cbb3567748f46a33fe9297cf
Now, I will add my input to see what the hashing result would be.
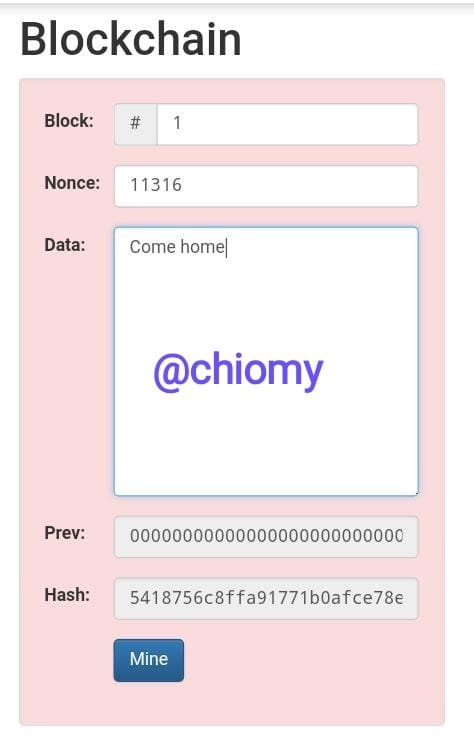
From the picture above, I used “come home” as my input and the resulting hash is 5418756c8ffa91771b0afce78e889f492b15662a6064d71ea9c323f5caca60b1. It is an invalid block because the hash didn’t start with zeros and I have to tweak my nonce.
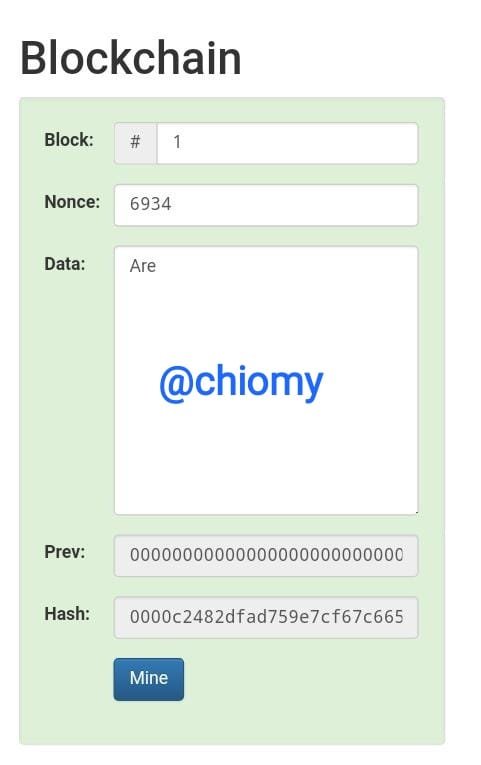
Here I changed the nonce to 6934 and it gave me a valid block starting with zeros. I have been able to get a valid block with nonce “6934” and input “are” to give me a hash output 0000c2482dfad759e7cf67c66551e061aaa38e852e0ef30dce9dc6fa60c671de.
In reality, I will be added to the chain once I am able to get a valid block.
- What is race attack in blockchain
Race attack is closely related to double-spending. This requires the receiver to accept transactions that are unconfirmed as payments. TWhile broadcasting a conflicting transaction to the network, the race attacker gives the victim an unconfirmed transaction. This is actually easy to pull off when the attacker has a connection directly to the victim’s node and possibly sends deposits of the conflicting transaction directly to miners.
It is actually imperative for users to be careful of these attacks and wait for confirmation before releasing assets to the other party.
- Limitations/disadvantages of blockchain
Some limitations of blockchain technology are
1. High energy consumption
Blockchain technology uses a proof-of-work consensus algorithm that relies on the miners to do the bulk of the work. Miners are rewarded for solving difficult mathematical problems, but the enormous energy consumption makes it unsuitable.
2. Data is immutable
This is literally one of the top disadvantages of blockchain. Once data is written, it cannot be removed and this is a problem because a user may not be able to remove his trace from the system and remove things, he doesn’t want there.
3. 51% attack
This is a big issue for blockchain. When hackers get over 50% control of the total computing power, it puts them in charge of mining and they can easily manipulate the system and rake assets to their advantage.
4. Crime
The anonymity of blockchain is disadvantageous as users can transact without due verifications like knowing your customer. This makes it an avenue to be used for illegal money transactions.
Conclusion
The invention of blockchain technology has been beneficial to mankind and brought so many innovations such as effective storage of data and the elimination of intermediaries in transactions. Amongst the many good things about blockchain, there are still some issues such as 51% attack, race attack, etc. more so, Blockchain aids crime due to its anonymity and lack of verification and users have to be very cautious when transacting. Building valid blocks on the blockchain are very tasking and require utmost patience.
cc: stream4u
Hi @chiomy
Thank you for joining The Steemit Crypto Academy Courses and participated in the Homework Task.
Total | 0/10
Cc: @sapwood
Your Homework Task verification has been done by @Stream4u, hope you have enjoyed and learned something new.
Thank You.

@stream4u
Crypto Professors : Steemit Crypto Academy
#affable