[The Governance of the TRON Ecosystem]- Crypto Academy / S4W7- Homework Post for professor @yohan2on

Question 1
Who are Super Representatives, SR partners and SR candidates? (The Governance of the TRON Ecosystem)
Tron Ecosystem
The Tron ecosystem is a decentralized blockchain built for entertainment content creators. The blockchain allows the creators to market and sell their creative content to consumers directly which eliminates the need for a middleman. Tron blockchain also allows developers to create DApps, Smart Contracts, and DApp tokens that can run on the blockchain. The Tron blockchain has a native token called Tronix (TRX) which is used within the network and as the governance token of the network.
The Tron Blockchain uses the Delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) as the blockchain's consensus algorithm, where a number of selected delegates are chosen to create blocks. The selected delegates are called Super Representatives (SR).
A) Super Representative (SR)
The Super Representatives of the Tron Blockchain are selected nodes that are voted and chosen from the super representative candidates. The super representatives of the Tron blockchain are 27 in number, and they are charged with the responsibility of creating blocks, validating transactions, and obtaining the corresponding voting rewards.
The super representatives voting is done every Six (6) hours, where the candidates with the highest number of votes in accordance with the number from 1 - 27, is selected as the super representatives while the candidate with voting in accordance with number 28 - 127, are referred to as the super partners.
The election of the Super Representatives is voted by Tron Blockchain Token Holders. Token Holders are individual nodes that stake the TRX tokens in their account, every staking node is eligible to vote during the election process.
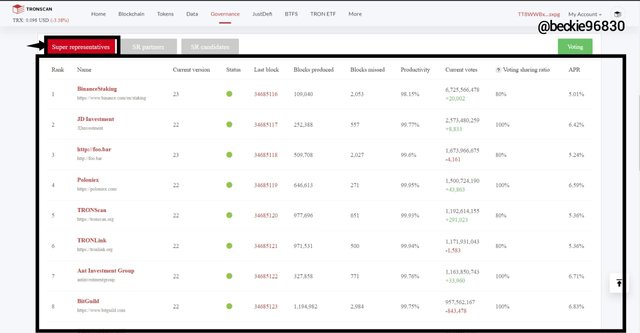
The super representative is rewarded with 32 TRX for validating a block of transaction. The Tron Blockchain generates a new block every 3 seconds, which implies that the supers representatives earn about 336,384,000 TRX annually.
B) Super Representative Partners
The super representative partners (SR partner) are part of the super representative candidates ranked from 28 - 127. They are chosen automatically after the voting has been completed, and the super representative has been selected from the corresponding voting results. Ideally, the SR partners are nodes that failed to reach the spots of 1 - 27 during the voting process
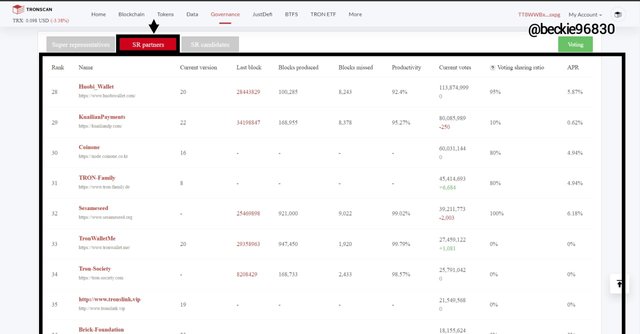
The election of the Super Representatives partners is voted by Tron Blockchain Token Holders. Token Holders are individual nodes that stake the TRX tokens in their account, every staking node is eligible to vote during the election process.
C) Super Representatives Candidates
The super representative candidates refers to the 147 nodes voted by the entire Tron blockchain's token holders. The voting is updated every 6 hours, where the super representatives are selected as nodes with the highest votes in accordance to numbers 1 -27, and the super representative partners are selected as nodes with the corresponding votes in accordance to numbers 28 - 127.
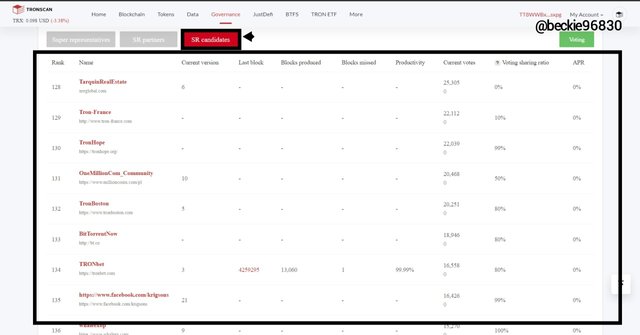
The candidate from 128 - 147 will remain on standby till the next voting window. After each voting exercise, the selected SR candidates are rewarded with 115,200 TRX, which is shared amongst the candidate in the proportion of the votes obtained by each candidate. This implies that the super representative candidates earn 168,192,000 TRX annually.

Question 2
What’s the difference between DPOS and POS consensus mechanisms?
Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
The Proof-of-Stake (PoS) is a type of consensus algorithm that shares the blockchain's responsibilities based on the number of crypto assets held by the nodes, allowing more rights and contributions to the selected nodes. This consensus algorithm was created in response to the problems associated with the proof-of-work consensus algorithm which are high cost of operation and high consumption of energy.

In the proof-of-stake consensus algorithm, network nodes (users) allocate (stake) a percentage of their assets to a selected node. The nodes utilize the staked assets to take on assigned on-chain responsibilities that generally sort for better development and functionality of the blockchain like, validation of transactions, new protocol implementation, governance, creating guild lines, etc.
Blockchains that use the proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus algorithm are Cardano, EOSIO, Polkadot, etc.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
The Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) is an internal arrangement by nodes within a blockchain to vote and choose from the selected eligible nodes to make take on certain blockchain responsibilities like validation of transactions and generation blocks. Although the DPoS consensus algorithm is built upon the principles of proof-of-stake (PoS), the voting of selected nodes (delegates) offers a more decentralization, where a wider range of Blockchain nodes choose the delegate of their choice.
The delegate voting is done by nodes through staking their assets in a stake pool affiliated with the selected node (delegate), such that the delegated node acquires a more allocated stake of the blockchain's token. The selected delegates receive rewards from transactions fees which are shared according to the percentage of token staked by the voter in the subaccounts.
Proof of Stake(PoS) Vs Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
Although DPoS and DoS share similar protocol buildup principles of staking assets, there are some notable differences, and they include the following:
1- Scalability
The proof-of-stake (PoS) is adaptable in a growth and expansion of a decentralized network, where nodes are selected by the number of assets staked. While the DPoS is not will scale poorly as voting is required to select nodes.
2- Security
The Delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) is considered to be more secured than the Proof-of-stake (PoS) because of the randomized probability of selecting a new delegate node. This prevents Blockchain attacks like 51% attacks.
3- Delegates
The delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) relies on the selected delegates for the Performance of the blockchain, which can result in a positive outcome like: preventing on-chain congestion and increasing the network throughput. Or in a negative outcome like possible attack plots through falsified voting nodes. The DoS rely on staked tokens to elect eligible nodes.

Question 3
Write a Step by Step tutorial showcasing how to stake/freeze TRX and vote for SRs
SR Voting
As previously explained, voting super representative candidates requires the use of Tron power which is in form of staked TRX, where 1 Tron power is equivalent to 1 TRX.
To illustrate the voting step in the Tron Blockchain, first visit Tronscan's official website and log in. Then, click on connect wallet
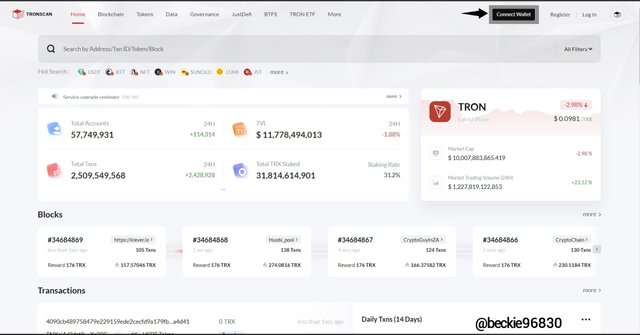
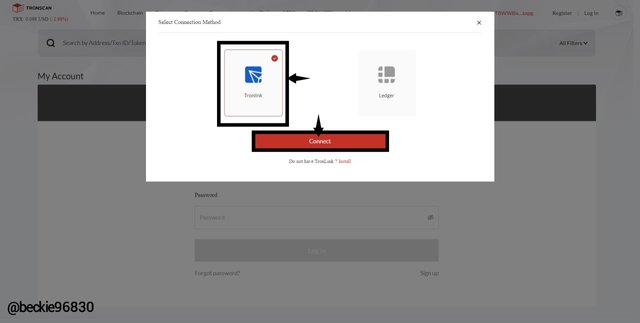
Next, select the wallet option. For this, I chose the TronLink wallet
Then click on Connect wallet
As mentioned above, staking requires Tron power, which implies that a portion of the TRX token in the wallet will be staked for at least 72 hours. To stake a portion of the TRX follow the steps below:
First, click on governance from the top menu, and choose voting.
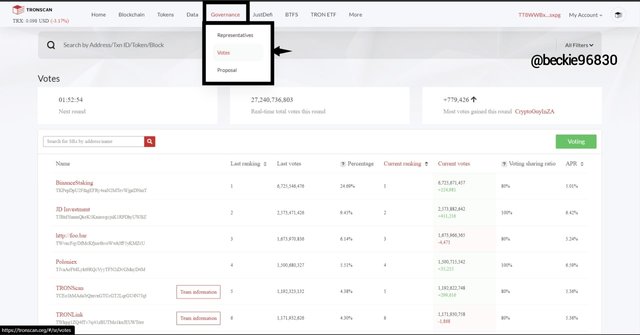
Next, on the voting page, click on Voting and choose Obtain to allocate a portion of the TRX to the stake pool.
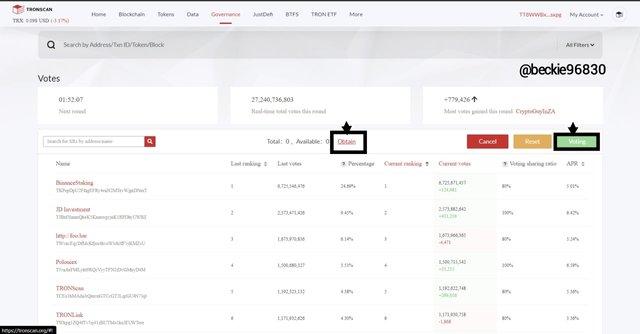
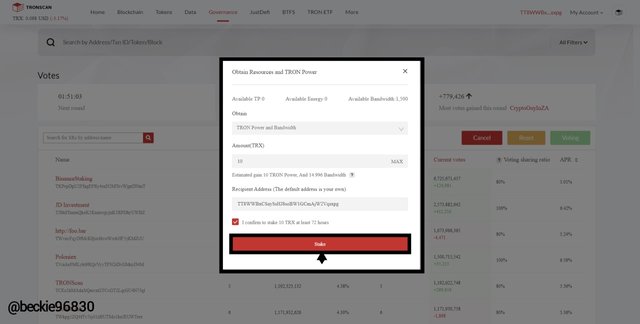
Next, enter the amount of TRX to be staked, and confirm staking for at least 72 hours, then click on Stake
For this illustration, I chose 10 TRX to be staked.
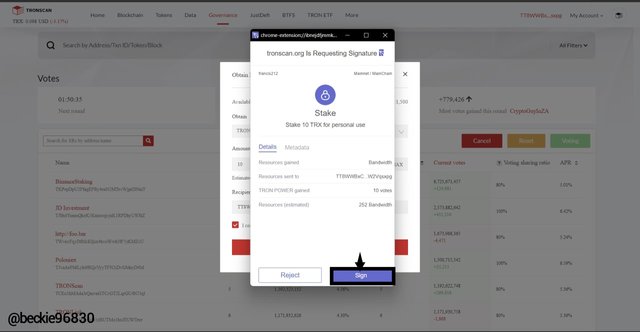
Next, the TronLink wallet will require to sign the swap transaction. Click on sign from the TronLink wallet popup.
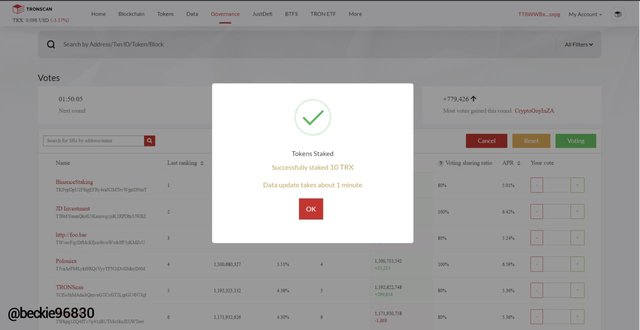
The TRX has been staked, the node can now proceed with voting for the node choice
On the voting page, choose a delegate and enter the amount of Tron power to be staked.
I chose BinanceStaking whose APR is 5.01%. I staked 10 TRX, then click on Voting to vote for the delegate
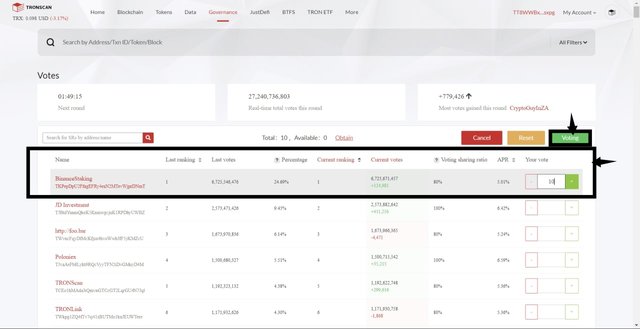
Next, the TronLink wallet will require to sign the swap transaction. Click on sign from the TronLink wallet popup.
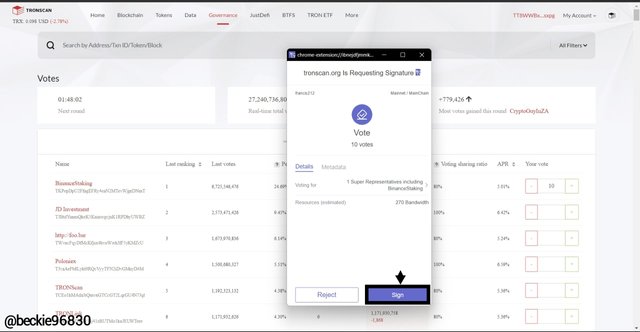
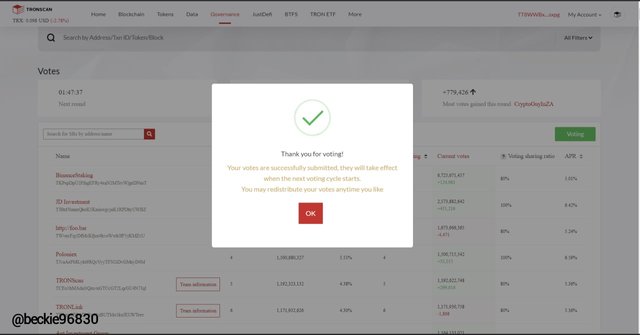
The voting has been completed, and the 10 TRX has been voted to the BinanceStaking.

Conclusion
The Tron blockchain uses the Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DpoS), where delegated nodes are referred to as super representative. The super representative is charged with the responsibility of validating and creating new blocks within the Blockchain. DPoS and DoS share the same build framework, where staking of assets is used as eligibility criteria, but the DPoS offers more decentralization as nodes are tasked with choosing (voting) for the delegate of choice.
Thank you professor @yohan2on for this educative and insightful lesson.
Hi @beckie96830
Thanks for participating in the Steemit Crypto Academy
Feedback
Total| 9/10
This is good work. All questions have been well explained in a clear and detailed way. Thanks for taking the time to research as you create content on the Governance of the Tron Ecosystem.