Crypto Academy Season 3: Week 4 Homework Post For @awesononso
Introduction
In this homework task we are looking at the blockchain folks and this is a very interesting topic for me as a new crypto enthusiast. Let's get down to it then
What is a Fork?
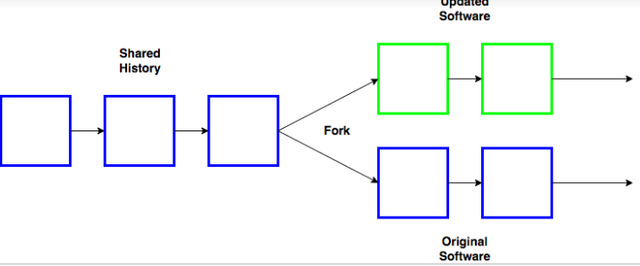
A folk is an occurrence of separation on the Blockchain network. Simply put, it is a change in the blockchains protocol in software use. It can either be an update to the software governing the distributed Network that makes the existing existing rules valid or invalid, or creation of a prototype from the same Blockchain, both having the same Genesis Block.
Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum run on the decentralized blockchain software that relies on communities to maintain and develop their underlying code. If therefore a community makes a change to the blockchain's protocol due to some disagreements or a need to upgrade, it will ultimately result into a split in the Blockchain producing a second blockchain that shares all of its history with the original Blockchain.
The split can be two-way causing two types of forks;
Soft Fork
This is basically a software upgrade on the blockchain.Hard Fork
This fork happens when the code on the blockchain changes so that the new version is no longer backward compatible with the earlier blocks.
Why do Forks occur?
The main reasons why these folks occur on the blockchain might include the following;
- To address security risks.
- To handle a disagreement within the community about the cryptocurrency.
- To add functionality and flexibility with improvement in features and efficiencies other versions might have lacked.
- To fix bugs on a network and upgrade security systems against hackers.
- To deal with theft for instance the Ethereum DAO attack, that saw creation of the Ethereum Classic.
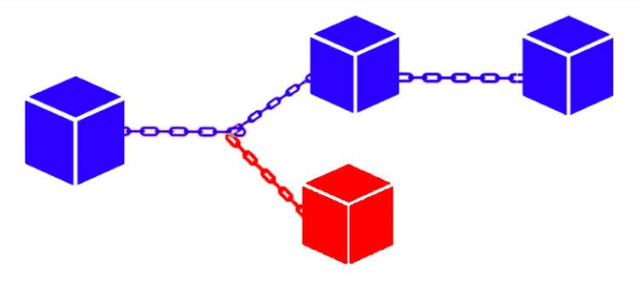
Explain in details what a Hard Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain).
A Hard Fork
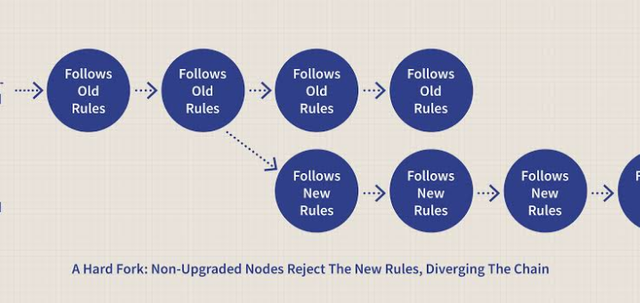
Source
It is the separation of the blockchain into two completely separate blockchains; the original and the new version. I had fork splits a cryptocurrency into two when different parties disagree and alternatively revert protocol the blockchain.
The change in protocol causes that the new blockchain and the old become incompatible as tho old nodes do not accept the new blocks. New blocks are viewed as valid and old blocks, invalid. This means that all the nodes that want to walk in corporation with the new rules have to upgrade their software in tune to the new blockchain. One group of users use the old software while the other group of users use the new software.
KEY TAKE AWAYS;
- A hard fork is backwards-incompatible.
- Holders of tokens in the original blockchain are granted tokens in the new Fork and they must choose which blockchain to continue verifying.
The original version is the continues with the original protocol or code while the new version follows a new set of rules. This separation creates an entirely new cryptocurrency apart from the old one and is the root of many popular cryptocurrencies.
Examples of Hard Forks are the Bitcoin Hard Forks that have seen new cryptocurrency such as Bitcoin Cash and Bitcoin Gold split from the Bitcoin blockchain, the Steem Hard fork that saw creation of Hive, and the Ethereum Hard Fork that brought Ethereum Classic
Bitcoin Cash
This hard fork happened in 2017 as a result of Bitcoin being split into two Cryptocurrencies and was the first of Bitcoin Hard forks. The main aim of this fork was to have lower transaction costs as the size limit of blocks added to the Blockchain was changed. Bitcoin Cash is a faster and cheaper option than Bitcoin and therefore has the advantage of speedier crypto transactions.
Explain in details what a Soft Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain).
Soft Fork
This is basically a software upgrade on the blockchain where only previously valid transaction blocks are made invalid. For example, it can be the implementation of a new rule changing a block size from the initial 10MBs to 1 MB. Old nodes then follow the new set of rules, and continue to see all incoming transactions as valid regardless of the upgrade. Only one blockchain will remain valid as users adopt the upgrade.
KEY TAKEAWAYS;
- A soft Fork is backwards-compatible.
- There is no divergence from the old Blockchain.
- Only one blockchain will remain valid.
Even though the soft folks are considered to be a gentler option, they come with their own risks and top of these is that the soft folk can be used by bad actors to trick miners into validating blocks that violate the rules of the blockchain.
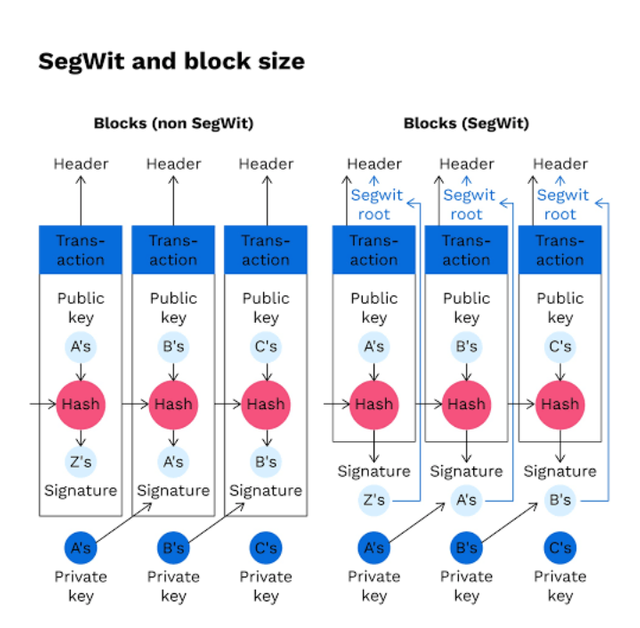
An example is the Segregated Witness ( SegWit) Bitcoin protocol update of 2015.
Segregated Witness (SegWit)
Before the Segregated Witness was implemented to upgrade the Bitcoin cryptocurrency, Bitcoin protocol was more costly by about $30 for transaction and used to consume a lot of mining time. The software developers recognized that there was need to increase the effective block size from 1MB to 4MB.
What are the differences between Hard Forks and Soft Forks?
Each type of folk has its strengths and weaknesses and some of the differences between the two can be the following;
| Soft Forks | Hard Forks |
|---|---|
| there is no division on the blockchain | that is a hard division in the communities |
| There's no creation of a new cryptocurrency | A new currency is created |
| It is basically an upgrade | It is a split |
| The hashing power is not tampered with | Hashing power is split between the networks |
| Computational resources are less used | Uses a lot of computational resources |
| Is backwards-compatible | Is backwards incompatible |
| No repetition of Block heights | Repition of block heights. |
| Only one blockchain remains valid | Both the Old and the new blockchains exist side by side |
Explain the following Bitcoin Forks and explore the blockchain where necessary.
(Indicate if they are hard forks or soft forks);
Bitcoin Cash
This altcoin came into existence after the Bitcoin Hard Fork happened in 2017. Bitcoin was split into two Cryptocurrencies and was the first of Bitcoin Hard forks. The main aim of this fork was to have lower transaction costs as the size limit of blocks added to the Blockchain was changed. Bitcoin Cash is a faster and cheaper option than Bitcoin and therefore has the advantage of speedier crypto transactions. Bitcoin Cash is a Hard Fork.
Both Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash use proof of work algorithm and the difficulty adjustment algorithm to time stamp every new block and adjust mining difficulty respectively.
Bitcoin cash sparked a new trend of creating new cryptocurrencies by forking the Bitcoin Blockchain. In November 2018, Bitcoin cash further split into two Cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin Cash and Bitcoin SV. This hard fork too originated from the difference in block size from 32MB for Bitcoin cash using the Bitcoin ABC (Adjustable Block size Cap) to 128MB for Bitcoin SV (Bitcoin Satoshi Vision).
Segregated Witnesses(SegWit)
Before the Segregated Witness was implemented to upgrade the Bitcoin cryptocurrency, Bitcoin protocol was more costly by about $30 for transaction and used to consume a lot of mining time. The software developers recognized that there was need to increase the effective block size from 1MB to 4MB. Segwit is a Soft Fork.
To 'segregate' means to 'remove from' so in this case of the SegWit, data was removed from the transactional data on every block on the blockchain, to free up space for more transactional data per block. With this soft folk, the Bitcoin blockchain was able to accept the new 4MB blocks and 1MB blocks at the same time in a great engineering process that created new rules without breaking the old ones.
Segregated Witness Soft folk allowed old notes to also validate the new blocks.
6.Write on the Steem and Hive Hard fork and show similarities in their Genesis Blocks(Provide screenshots).
Hive is a Blockchain that runs the Hive blog, a social media blogging platform. The currencies on this blockchain are HIVE and Hive Backed Dollars(HBD). The influence token is Hive Power (HP) just as Steem has Steem Power (SP).
Hive was created by implementing a hard Fork of the existing Steem code and it runs independently from the existing original blockchain.
How did Hive happen?
The hard fork in Steem blockchain came when community members opposed TRON's acquisition of the Steem Blockchain DaPP, Steemit. Steem implemented the hard Fork code-named 'New Steem' while dropping some of the former Steem witnesses, Block validators and stakeholders who had created a splinter group called Hive.
The hard folks GitHub page went ahead to list all users (64 in total) whose tokens had been seized, with their accounts amounting to $6.3 Million. The hard Fork was a struggle for the control of the steam blockchain soon after Justin Sun's TRON Foundation acquired Steemit.
Check out the Hive Blog on https://hive.blog
Screenshots of their Platform Home pages.
STEEM
HIVE BLOG
![Screenshot 2021-07-22 at 17-28-15 Steemit Crypto Academy [Beginners’ Level] Season 3 Week 4 Blockchain Forks — Steemit.png](https://steemitimages.com/640x0/https://cdn.steemitimages.com/DQmS1RhiSPyTGegZWkrBQeJbXzt5EvRz2XkyUD6shnv2pAk/Screenshot%202021-07-22%20at%2017-28-15%20Steemit%20Crypto%20Academy%20[Beginners%E2%80%99%20Level]%20Season%203%20Week%204%20Blockchain%20Forks%20%E2%80%94%20Steemit.png)
Similarities in their Genesis blocks.
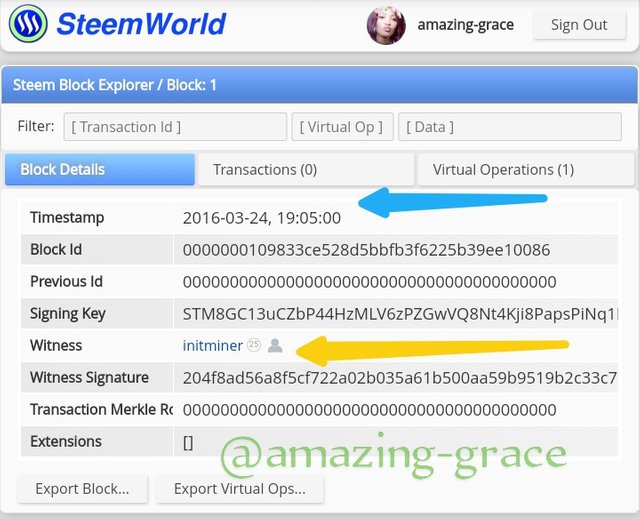
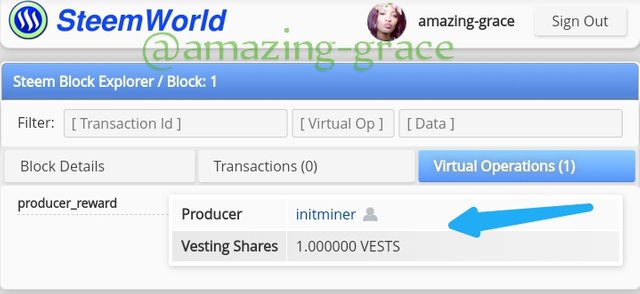
STEEM GENESIS BLOCK
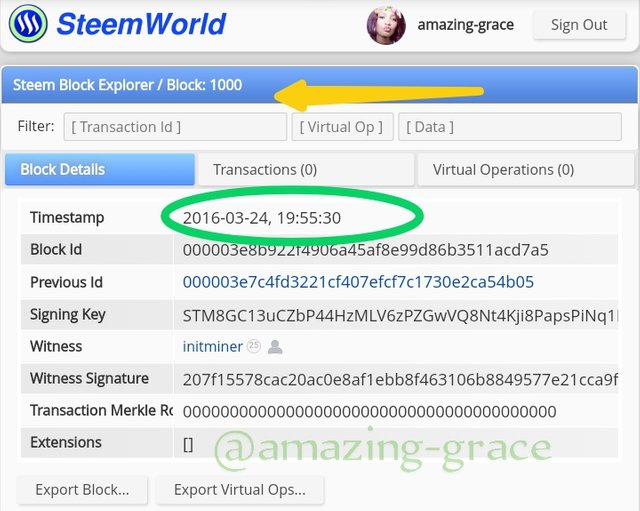
To locate the steam Genesis block we can head to the site; https://steemworld.org.
At the site click on block explorer
Click to find block 1, the Steem Genesis Block.
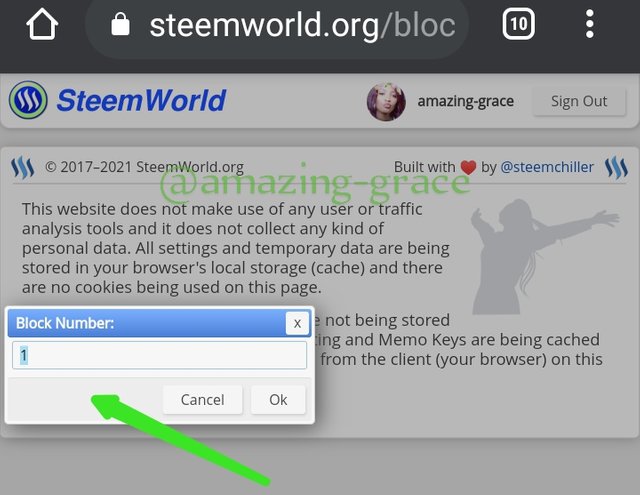
Find block 1, sign into Steem World in the top right corner
HIVE GENESIS BLOCK
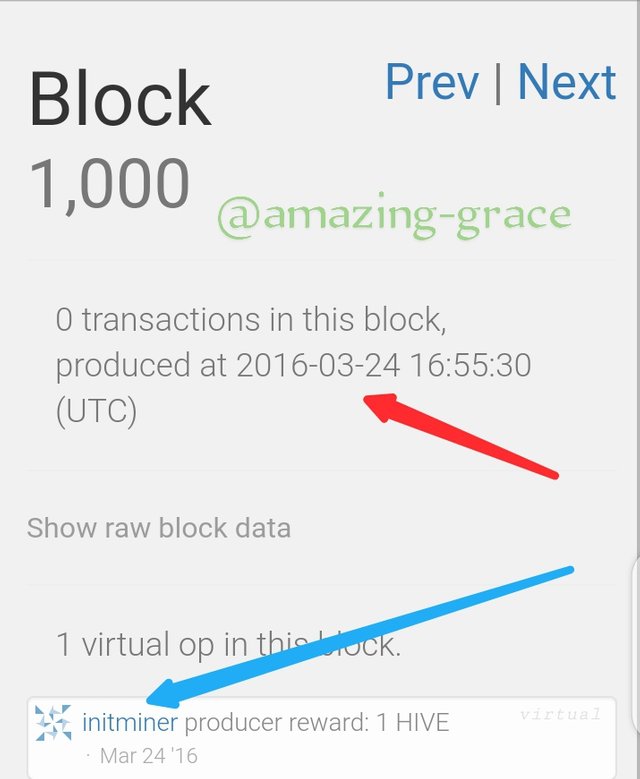
To see this, we go to https://hiveblocks.com/ and search for the Genesis block by typing '1'.
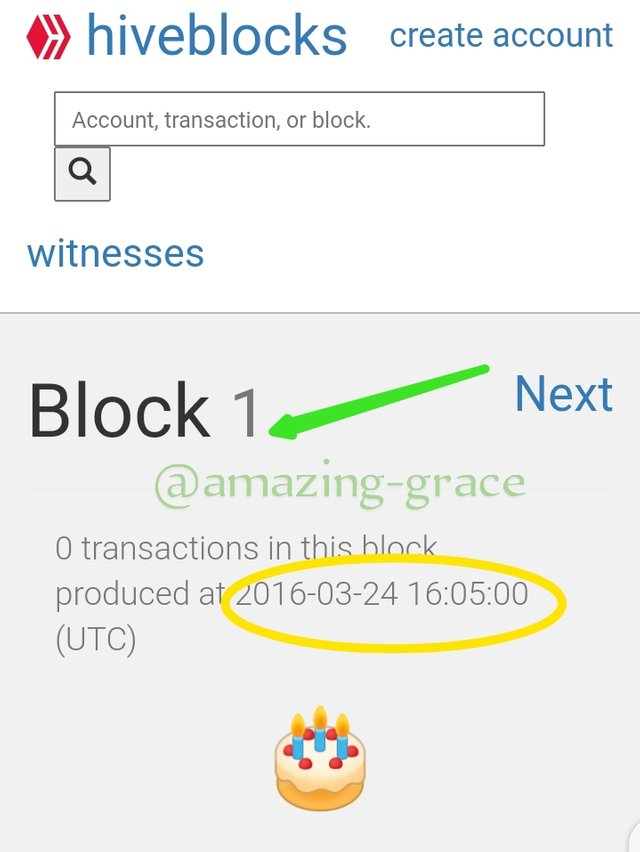
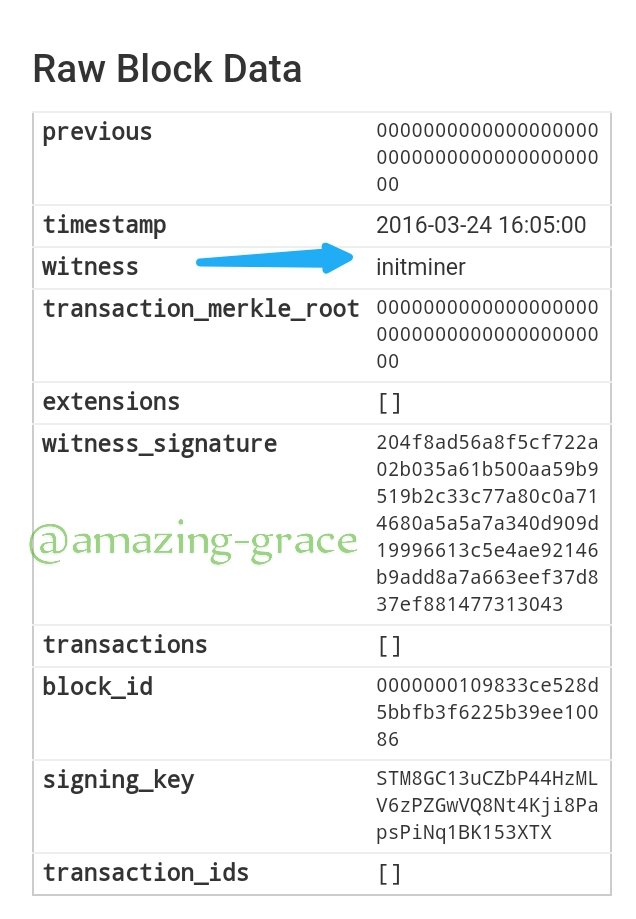
We see that both the mining date and time are similar to those of Steem Blockchain. Same date, same time.
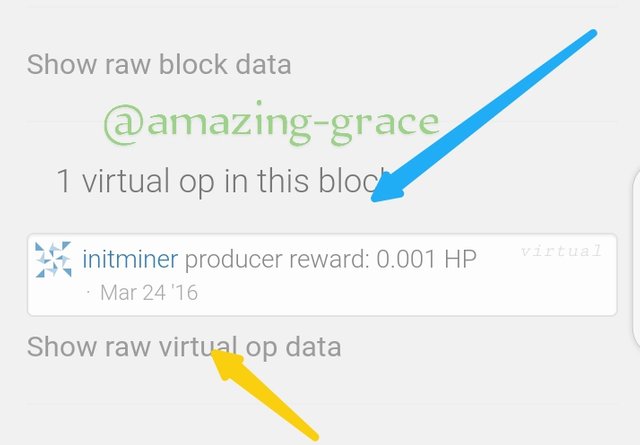
Then click on 'Virtual Operations'
The miner @initminer is the same as the one on Steem.
When we see block 1000, we see that the miner is for both blockchains.
Conclusion
To conclude the above homework task I would love to see that mistakes happen everywhere around us and decisions have to be made. It is the nature of man to disagree. Major changes will always happen anywhere in the world. Forking is one of these changes and it comes with its fair share of advantages and disadvantages. Thank you for this lesson professor @awesononso.
cc lenonmc21