Understanding How Bitcoin Works

Bitcoin is a digital currency that became popular in 2013. This currency is not controlled by banks or other institutions. This decentralized currency is designed to protect our money from those who want to take advantage. But how does a digital currency work? How can this currency be valid if no one can say they keep it.
Bitcoin consists of three parts: block chain , mining network , and wallet . In order to understand how Bitcoin works, we must understand how each part of it works. Make a cup of coffee/tea and enjoy this article.
- Block Chain
The block chain is a list of every Bitcoin transaction that has ever occurred. Before the transaction enters the block chain , the transaction has not been completed. As the name implies, a block chain is a series of blocks. The block contains a new set of transactions and is linked to the previous block. Anyone can validate the block chain by following all the records that record every transaction up to the first transaction when Satoshi Nakamoto created Bitcoin.
At this point, you may be thinking hard, who is in charge of managing this block chain . The answer is: none. No single organization or individual holds its own copy of the block chain . Bitcoins are built to be well distributed, so there is no point of error that could damage the block chain either intentionally or unintentionally. The block chain is held by every computer that mines Bitcoin.
- Mining Bitcoin
The people who mine Bitcoin ( miner ), are the people who keep old transactions and make sure new transactions are recorded. Their job is to create (or mine) new blocks. These blocks store new transactions that occur. As compensation for mining these new blocks, they are given some Bitcoins. Incentives like this ensure there are enough people to do the mining so the Bitcoin network system keeps going.
- Wallet
Wallet is the part of Bitcoin that users often see. The term wallet itself is not quite right because the wallet does not actually store Bitcoin. The wallet only stores a private key that allows the owner to add transactions to the block chain at an address in the form of a public key . The Bitcoin is stored as a transaction record in the block chain .
The previous paragraphs gave an outline of how Bitcoin works and we can start mining or using Bitcoin. However, there is a chance that you may not trust this currency because of how it works, which is a bit odd.
The great thing about this currency is its cryptographic techniques that protect users. Let's take a more in-depth look at how this technique works.
Bitcoin security comes largely from hashing , and it is these hashes that are used to link blocks to other blocks in the block chain . Each block stores a hash of the previous block, and that hash value cannot be changed without changing the hash value of the current block (which also needs to be changed in the next block, etc.). Everyone can check that no transaction has ever changed the hash value because, if it did then the next hash value would be affected and no longer linked.
- Trade with Bitcoin
When we make a transaction with Bitcoin, we send the transaction to a network of miners. To ensure that no one can make transactions using our wallet without being noticed, there are several security measures in place.
Bitcoin transactions occur between two or more wallets. As explained earlier, these two wallets are just a public/private key pair that is used to encrypt data. The way these two key pairs work ensures that all data encrypted with the public key can be read with the private key, and vice versa.
In Bitcoin, we don't have piles of money that can go up and down like in Banks. Instead, we have a pool of Bitcoins that can be traced back to the first miner. When making a transaction, we must reference the transaction when we get the Bitcoin (can refer more than one). Next, we have to digitally tag each referenced transaction. That is, we hash the details of the transaction and encrypt it with the private key. Since the public key will always be associated with our address (as well as the referenced transaction), it will ensure that only we have the authorization to perform the transaction.
Note that no physical data leaves the wallet other than messages to the block chain . The amount of Bitcoin in a wallet is calculated by looking at the transactions in the block chain . This means that anyone can check the amount of Bitcoin in any wallet . However, that does not mean that anyone can find out who owns a particular wallet because it is not easy to determine the owner of each wallet .
When this transaction reaches the miners, it is added to the next block . As we have seen, each block chain can be further subdivided (and a miner with large computing power can share it continuously). There is no guarantee that transactions will enter the block chain directly , but judging from the number of blocks available. If there is only one block, then a lucky attacker can mess up the entire mining network . With more blocks that enter the block chain , the attacker's work will be more and more difficult.
Six blocks are usually considered sufficient to ensure a transaction is correctly added to the block chain . At a rate of one block every ten minutes, the process of adding transactions can occur within an hour. To deal with large nominal, you might wait a little longer before the transaction is completed in- transfer .
Block chain is a publicly verifiable record of each transaction. Every transaction detail will be disseminated to all miners on the bitcoin network with a request to be added to the next block.
In order for a miner to be paid for his work adding a block, two things have to happen: they have to make sure the hash is valid and the block is recorded in the block chain . The first requirement is purely a technical challenge, while the second condition will force them to examine all possibilities. If the block chain contains invalid transactions (e.g. someone makes a transaction with a coin they don't own), then the next miner who gets a shipment from that miner will refuse so he doesn't get paid. Therefore the miner will check each transaction to ensure its validity before being added to a block.
When a miner receives a block from another miner, they are incentivized to find fault for two reasons. First, if they reject a block, that means they still have a chance to mine it for themselves. Second, if they receive a block that other miners reject as invalid, then their mining will be in vain because this block will not enter the block chain .
At the same time they will get an incentive when they receive a valid block, because if they reject a block accepted by another miner, then the next block they mine will be rejected by other miners.
- Hashtags
Hashing – also known as one-way encryption – is a method of changing data in an irreversible but verifiable way. Let's look at a very simple hashing example with the modulus operator 10. In this example, we divide a number by 10 and the remainder of this quotient is the hash – so the number 45 has a hash of 5.
There are two crucial functions that a hash should have. The first is easy to verify. Each time, the process should be fast and produce the same results. The second function is irreversible. If someone says the value of a hash is 5, we shouldn't know that the original value is 45.
However modulo 10 is a bad hashing algorithm technique because it allows the same hash value from different data sources. A good hash should have these two elements. A slight change in the initial value will make the hash value change drastically.
Hashes are often used in computer security. An example is storing passwords in Linux. Linux systems never store passwords, but the hash value is stored. We can see the password hash values in Linux by typing:
"sudo cat /etc/shadow"
Every time you log in , the computer will formulate the hash value of the entered password and compare it with the stored hash. If both hashes have the same value, the login was successful. Even though you can see all the hashes in the system, it doesn't mean that the security standard is low because it is very difficult to reverse the hash value to the original value.
In the Bitcoin system, hashes are used to verify the integrity of the block chain , and provide evidence that a miner has mined a block. The job of hashes in the block chain is to ensure that no blocks have been changed since they were mined.
There is a problem that may occur is that two miners can create the same block at the same time and send it to another miner. When this happens, there will be a split in the block chain . Some miners can work in one block, and other miners in the other block. Bitcoin rules state that the longer valid block chain will be used. One of the splits of the two splits one of them will go to the next block first, so the miner will skip the shorter chain in order to get paid to mine the longer chain *.
This rule ensures that a network of miners who want to maximize personal profit while maintaining the integrity of this currency. A group of miners who want to outsmart the system will need more computing power than the correct combination of all the miners (so that they can mine blocks at a faster rate and have a longer block chain ). Hashcash further secures the Bitcoin network through raw computing power .
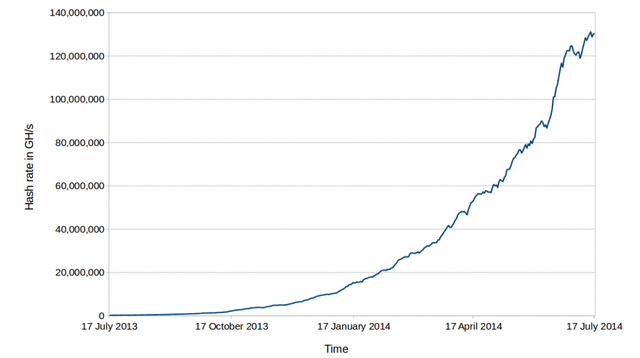
This is the reason why Bitcoin mining must remain profitable. Currently, the Bitcoin network has a performance of 15 hash maps per second and continues to rise. To buy more computing power to beat the figures above will require around 150 million pounds and will continue to grow. This price does not include electricity, storage space, cooling, salaries of the people who run it.
- Hashcash
Hashcash is a system used by miners to verify that they have added a block before it is added to the block chain . Its basic function is to make the block chain impossible to change.
This process relies on hashing processes , particularly the SHA256 hash function. This function accepts an input and outputs a 256-bit number. The numbers entered into the hash function are the block header (in which there is a counter ) and all the hashes of other transactions. The miner's job is to find the value for the counter where the output of the hash function is below a certain value. This value limit will adjust to the current difficulty setting, which normally changes every 2016 block.
The only way to get the required hash value is with a lot of computing power . With more hash values obtained in a faster time, it will increase the possibility of getting a satisfactory value. When the hash value is found, it means that we have added the block and can send it to other miners on the network.
The speed of a network or a Bitcoin mining computer is measured by how many hashes it can try per unit of time (usually calculated in million hashes per second or GHs).
Miners don't have to worry about their work being taken away because it contains hashes of all transactions and one of those transactions is the payment for the miners themselves for mining blocks. This result cannot be retrieved without changing the hash value.
It should be noted that the hashcash algorithm used by Bitcoin is slightly different from the algorithm used to detect spam messages, although the way the two work is almost similar.
- Fraud Prevention
Bitcoin mining profits are controlled by two factors: the difficulty of mining each block, and the number of Bitcoins miners earn in each block. These two things must be balanced by taking into account the computing power and value of Bitcoin which continues to increase in the market.
The number of Bitcoins awarded per block changes at a precise rate: starting at 50.5 every 210,000 blocks (approximately four years) until 21 million Bitcoins have been mined, and no more Bitcoins can be given to mine further blocks.
The difficulty level varies every 2016 blocks. The Bitcoin network is designed to create a new block on average every 10 minutes. This time was chosen for two reasons: a shorter time will make transactions happen faster, but too short a time can also make more than one miner create a new block at the same time so that there will be wasted resources because there are two block chains that compete with each other to be longer.
You may be able to see a slight flaw in the previous explanation. First, the author states that the security of the system depends on the computing power it has which ultimately depends on the profitability of mining. But then the author states that someday in the future when 21 million Bitcoins have already been mined, there will be no more wages for mining.
This is not entirely true. Even though there are no new bitcoins as mining wages, when making transactions we can add transaction fees that will go into the miners' pockets. Transaction fees are rarely carried out nowadays because the mining process is still quite profitable so people don't have extra change, besides that the transaction volume is still small.
Each block has a size limit of 1MB (the decision to change this number is debatable). That is, there is a limit to the number of transactions for each block. If a miner finds a situation where there are more transactions than space in the block, they will decide which transactions to add. Of course, miners will choose transactions that have higher transaction fees. Other transactions will not be lost, they will just be saved for inclusion in the next block. The greater the transaction fee, the faster transactions enter the block chain .
Most Bitcoin transactions today do not have a transaction fee. It has not been determined whether this transaction fee will be the only way or there will be other features.
- Satoshi Nakamoto
Bitcoin is now very well known and is worth billions of pounds, but for all that fame, there is one secret that is tightly tucked away: the identity of its creator. The creator of Bitcoin is known as Satoshi Nakamoto. It is unknown whether this Satoshi is a boy or a girl, whether it is a single person or a group.
Satoshi mined quite a lot of Bitcoins in his early days (possibly up to a million), so at today's exchange rates, he is already rich. Despite having a wealth of considerable value, until now Satoshi had never spent it at all.
- Anonymous Transaction
Bitcoin has become famous as the currency of choice for online transactions, especially for illegal online shops like Silk Road. However, Bitcoin is not designed as an anonymous currency, and in fact it cannot be done because of the way the block chain works which records all Bitcoin transactions and allows anyone to see the flow of any Bitcoin.
The only factor that makes Bitcoin popular as a means of anonymous transactions is that we can create Bitcoin wallets without revealing who we are. In this sense, the wallet will remain private, but the currency will remain public.
This means that if we obtain coins anonymously (for example, we mine them or buy through untraceable avenues), spend them in an untraceable way (for example, pay for something that is not delivered or personally linked in any way), and do not link the wallet with a physical location (for example, only using a wallet via Tor) then this transaction should be anonymous. But this anonymity must be done properly. If one fails, the transaction can be traced to the end.
Although anonymous transactions are possible with Bitcoin, cash is still the safest way. Block chains are a gold mine for big-data analysts and there will likely be laws governing them in the future.
- Using Bitcoin
The benefit of a currency, for most people, is how to use it. Most of the world's currencies are used involving a metal circle or a piece of paper, but there is no such thing for Bitcoin.
To make a transaction, the first thing you need is a Bitcoin wallet . This wallet is just a public/private key pair that is used to mark transactions. However, we need a safe place to store this key because if it is lost all the coins will also disappear from the face of the earth.
The level of security depends on the amount of money you want to save. There are various types of wallets for almost all computer devices including gadgets or smartphones . It's worth remembering that there is no fee to create a wallet, so there's nothing to limit us from creating a few.
All Bitcoin wallets work the same way, and store all the information needed to receive and send Bitcoins and view past transactions.
After creating a wallet , we need to get coins. For most people, that means we need to buy from an exchange like Coinbase . Unfortunately, this option is not as easy as buying most items, and it is rare to use a credit card or Paypal in buying and selling coins.
This happens because many people who have purchased using this method complain to this credit card provider company that they have never received the coins purchased and then ask for a refund for the money that has been received by the seller.
Credit card companies can easily check block chains , but they used to prefer to side with the buyer and as a result now most exchanges don't accept credit cards. Currently the most common way to buy coins is by bank transfer. When buying Bitcoin we will be asked for a wallet address . When the bank transfer has been made, the exchange will send the coins to the wallet .
Spending coins is much easier than buying them. More and more companies are accepting payments via Bitcoin. In the checkout section there will be a wallet address to send coins. Keep in mind that we do not send transactions to the seller, but to the network. The seller will receive the block chain from the network and check the transactions sent to the specified wallet .
Companies that receive money will usually wait until the transaction reaches six blocks or more, which can take up to an hour. When the transaction is complete, we will get the desired product.